Introduction
- Natural Vegetation: Plants and trees that grow naturally in a region, influenced by climate, rainfall, and soil.
- Wildlife: Animals and birds that live naturally in a region, depending on the vegetation and environment.
- This chapter compares the natural vegetation and wildlife of India and Brazil, focusing on their types, distribution, and environmental issues.
- Key skills: Reading maps, correlating vegetation with climate, and understanding conservation needs.
Natural Vegetation of Brazil
Overview
- Brazil has the largest number of vegetation species in the world due to its varied climate and physiography.
- Vegetation types depend on rainfall:
- Equatorial regions: Heavy rainfall (2000 mm) supports dense forests.
- Away from equator: Less rainfall leads to grasses, shrubs, and thorny vegetation.
- Brazil’s Amazon rainforests are called the ‘lungs of the world’ because they release oxygen and absorb carbon dioxide, reducing global warming.
Types of Vegetation
1. Evergreen Forests:
- Location: Equatorial regions (e.g., Amazon valley) with rainfall throughout the year (2000 mm).
- Features: Dense, broad-leafed trees with hardwood (e.g., Pau Brasil, rubber, mahogany, rosewood).
- Special: High biodiversity with various orchids and creepers.
- Importance: Helps maintain global oxygen levels.
2. Deciduous Forests:
- Location: Regions with seasonal rainfall (1200-1500 mm).
- Features: Trees shed leaves in dry seasons to conserve water.
3. Temperate Forests:
- Location: Southern Brazil near the Tropic of Capricorn (e.g., Parana Basin).
- Features: Found in cooler climates with moderate rainfall.
4. Grasslands and Thorny Shrubs:
- Location: Areas with low rainfall (600 mm, e.g., Brazilian Highlands).
- Features: Short grasses, thorny bushes, and sparse vegetation due to dry conditions.
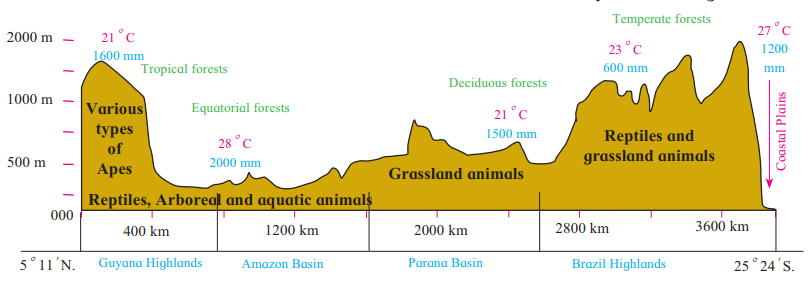
Distribution (Based on Figure 5.2)
- North (Amazon Basin): Equatorial evergreen forests, high rainfall (2000 mm), hot climate (25°C-28°C).
- Central (Brazilian Highlands): Deciduous forests, moderate rainfall (1200 mm), warm climate (23°C).
- South (Parana Basin): Temperate forests, lower rainfall (1500 mm), cooler climate (21°C).
- Coastal Plains: Mixed vegetation, high rainfall (2000 mm), mild climate (27°C).
Wildlife of Brazil
Overview
- Brazil has the greatest diversity of wildlife in the world due to its varied ecosystems (forests, grasslands, wetlands).
- Habitats include the Amazon rainforest, Pantanal wetlands, and coastal regions.
Major Wildlife
Mammals:
- Monkeys, pumas, leopards, guinea pigs in forests.
- Jaguars and capybaras in grasslands.
Reptiles:
- Anacondas in Pantanal swamps.
- Crocodiles and alligators in rivers and wetlands.
Fish:
- Piranhas and pink dolphins in rivers.
- Swordfish in coastal seas.
Birds:
- Condors (large, high-flying), macaws, parrots, flamingoes.
Insects:
- Millions of insect species, adding to biodiversity.
Notable Species
- Golden Lion Tamarin: Small monkey in coastal forests.
- Macaw: Colorful parrot in rainforests.
- Condor: Large bird in highlands.
Habitat Reasons
- Forests: Dense vegetation provides food and shelter for monkeys, macaws, and jaguars.
- Wetlands: Swampy Pantanal supports anacondas and crocodiles.
- Rivers: Aquatic animals like piranhas thrive in nutrient-rich waters.
- Coastal Areas: Support fish and birds due to abundant water and food.
Natural Vegetation of India
Overview
India’s vegetation varies due to rainfall, altitude, and soil:
- High rainfall areas have dense forests.
- Dry areas have thorny shrubs.
- Coastal areas have unique mangroves.
Major forest types cover different regions, with deciduous forests occupying the maximum area.
Types of Vegetation
1. Evergreen Forests:
- Location: Areas with >2000 mm rainfall (e.g., Western Ghats, Eastern Himalayas).
- Features: Broad-leafed, dense, hardwood trees (e.g., mahogany, rosewood, rubber), high biodiversity with creepers.
- Reason: Abundant rainfall and sunlight support year-round growth.
2. Deciduous Forests:
- Location: Areas with 1000-2000 mm rainfall (e.g., Central India, parts of Peninsular India).
- Features: Trees like teak, bamboo, banyan, and peepal shed leaves in dry seasons to save water.
- Reason: Most common because moderate rainfall is widespread in India.
3. Thorny and Shrub Vegetation:
- Location: Arid regions with <500 mm rainfall (e.g., Rajasthan, Gujarat).
- Features: Small-leafed plants like catechu, acacia, khejadi, and cacti (aloe vera, agave).
- Reason: Low rainfall and dry summers limit plant growth.
5. Coastal Forests (Mangroves):
- Location: Eastern coast, swampy areas, estuaries (e.g., Sunderbans in West Bengal).
- Features: Trees with oily, light, durable wood, adapted to saline soils.
- Reason: Moist, saline conditions near coasts support mangrove growth.
6. Himalayan Forests:
- Location: Indian Himalayas, varying by altitude.
Types:
- High Altitude: Seasonally flowering trees.
- Medium Altitude: Coniferous trees (pine, deodar, fir).
- Foothills: Mixed forests with sal trees.
Reason: Altitude and cooler climate influence tree types.
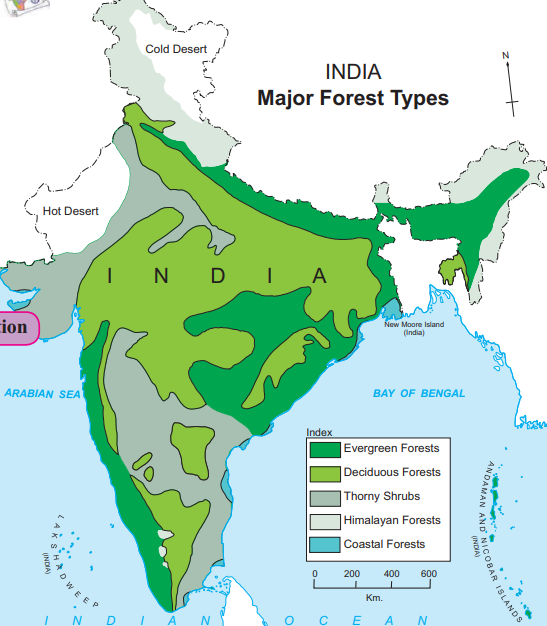
Distribution (Based on Figure 5.3)
Western Ghats and Eastern Himalayas: Evergreen forests, high rainfall (>2000 mm).
Central and Peninsular India: Deciduous forests, moderate rainfall (1000-2000 mm).
Rajasthan and Gujarat: Thorny shrubs, low rainfall (<500 mm).
Sunderbans (Eastern Coast): Mangroves, saline and moist conditions.
Himalayas: Coniferous and mixed forests, varying by altitude.
Wildlife of India
Overview
India is a mega-diverse country with unique wildlife due to varied habitats (forests, deserts, wetlands, mountains).
It is the only country with both tigers and lions.
Major Wildlife
Mammals:
- Elephants: Hot, humid forests (e.g., Western Ghats, Northeast India).
- One-Horned Rhinos: Swampy lands of Assam.
- Snow Leopards and Yaks: Himalayan snow-capped regions.
- Wild Ass and Camels: Arid lands (e.g., Rann of Kutch).
- Tigers and Lions: Forests and grasslands (e.g., Sundarbans, Gir Forest).
- Indian Bisons, Deer, Antelopes, Monkeys: Peninsular region.
Reptiles:
- Crocodiles and Gharials: Rivers and estuaries.
- Olive Ridley Turtles: Coastal areas.
Birds:
- Peacocks, Indian Bustard, Kingfishers, Cranes, Parakeets: Forests and wetlands.
Aquatic:
- Gangetic Dolphin: Rivers like the Ganga.
Notable Species
- Bengal Tiger: Sundarbans, Central India.
- Lion: Gir Forest, Gujarat.
- Nilgiri Tahr Goat: Western Ghats.
- Swamp Deer: Wetlands of North India.
Habitat Reasons
Forests: Provide food and shelter for tigers, elephants, and monkeys.
Wetlands: Support rhinos, dolphins, and crocodiles due to water availability.
Arid Lands: Adapted species like wild ass survive with minimal water.
- Himalayas: Cold climate suits snow leopards and yaks.
- Coasts: Turtles and mangroves thrive in saline conditions.
Environmental Issues
Brazil
Problems:
- Deforestation: Clearing Amazon forests for agriculture and logging (5831 sq. km degraded in 2016).
- Slash-and-Burn Agriculture (Roca): Forests are cut and burned for temporary farming, reducing soil fertility.
- Illegal Smuggling: Wildlife like parrots and anacondas are poached.
- Pollution: Rivers and air are polluted, harming ecosystems.
Impact: Endemic species (unique to Brazil) are at risk of extinction.
India
Problems:
- Poaching: Tigers, elephants, and rhinos are hunted for skins and horns.
- Deforestation: Forests are cleared for agriculture, industry, and urbanization.
- Pollution: Rivers and air pollution harm wildlife habitats.
Impact: Species like cheetahs are extinct; tigers and elephants are endangered.
Conservation Efforts
India:
- National Parks: E.g., Jim Corbett, Kaziranga.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries: Protect specific species.
- Biosphere Reserves: Preserve ecosystems (e.g., Sundarbans).
- Tiger Reserves: To save the national animal.
Brazil:
- Efforts to protect the Amazon rainforest and Pantanal wetlands.
- Laws against illegal wildlife trade.
Need: Both countries need conservation to save biodiversity and prevent extinction.
Comparison of Brazil and India
Vegetation
Similarities:
- Both have evergreen forests in high-rainfall areas.
- Both have deciduous forests in moderate-rainfall areas.
- Both have thorny shrubs in dry regions.
Differences:
- Brazil: Larger area of equatorial forests (Amazon) due to its equatorial location.
- India: Has Himalayan forests (coniferous) and mangroves, not found in Brazil.
- Diversity: Brazil has greater vegetation diversity due to its vast rainforest ecosystems.
Wildlife
Similarities:
- Both have rich biodiversity with mammals, reptiles, birds, and insects.
- Both face threats from deforestation and poaching.
Differences:
- Brazil: More diverse wildlife (e.g., anacondas, piranhas), especially in the Amazon.
- India: Unique species like one-horned rhinos, lions, and Gangetic dolphins.
- Exclusive: India has both tigers and lions; Brazil has no lions.
Environmental Issues
- Brazil: Major issue is Amazon deforestation and roca agriculture.
- India: Focuses on poaching and urban-related deforestation.
- Common Need: Both require strong conservation to protect forests and wildlife

Leave a Reply