Introduction
- Population: The total number of people living in a region, an important resource for a country’s growth.
- A qualitative population (healthy, educated, skilled) is key to economic and social progress.
- This chapter compares the population of India and Brazil, focusing on distribution, density, sex ratio, age structure, growth rate, life expectancy, and literacy rate.
- Key skills: Reading maps, graphs, and understanding population characteristics.
Population of India
Overview
- Population (2011 Census): Around 121 crores (1.21 billion), making India the second most populous country in the world.
- Global Share: India has 17.5% of the world’s population but only 2.41% of the world’s land area.
- Population Density: Average of 382 persons per sq. km (2011 Census).
- Distribution: Very uneven due to physiography (landforms) and climate.
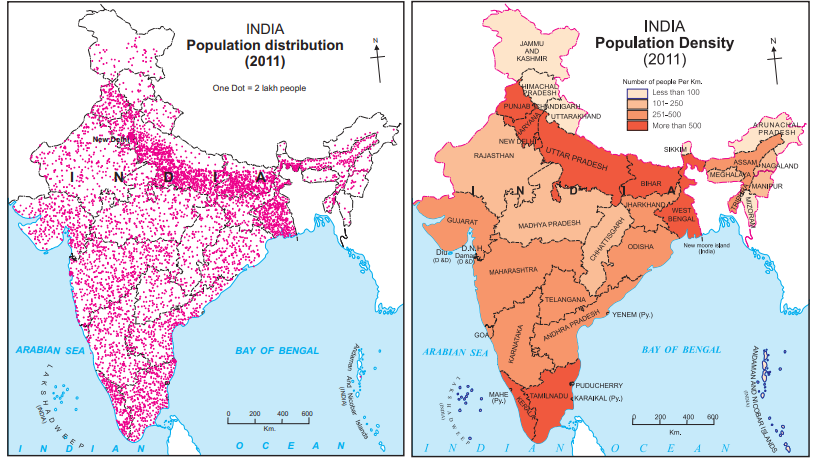
Population Distribution (Figure 6.1a and 6.1b)
High-Density Areas:
- Northern Plains: Fertile land, availability of water, and flat terrain support agriculture (e.g., Uttar Pradesh, Bihar).
- Coastal Regions: Ports and industries attract people (e.g., Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata).
- Urban Centers: Cities like Delhi, Pune, Bengaluru due to jobs and facilities.
Low-Density Areas:
- Himalayas: Mountainous, cold, and inaccessible (e.g., Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh).
- Thar Desert: Dry, lack of water (e.g., Western Rajasthan).
- Dense Forests: Inaccessible, limited facilities (e.g., parts of Northeast India).
Key States:
- Highest Density: Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal.
- Lowest Density: Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh.
Factors Affecting Distribution
Favorable Factors:
- Fertile land (e.g., Ganga Plains).
- Availability of water (rivers, canals).
- Flat plains (easy for settlements).
- Industries and trade (urban centers).
Unfavourable Factors:
- Rugged terrain (mountains, hills).
- Dry climate (deserts).
- Dense forests (inaccessibility).
- Lack of facilities (roads, schools).
Correlation with Climate and Physiography
Climate: Moderate climate in the plains supports agriculture and settlements, while extreme cold (Himalayas) or aridity (Rajasthan) limits population.
Physiography: Flat, fertile plains (e.g., Ganga Plains) attract dense populations, whereas mountains and deserts have sparse populations.
Population of Brazil
Overview
- Population (2010 Census): Around 19 crores (190 million), making Brazil the fifth most populous country in the world.
- Global Share: Brazil occupies 5.6% of the world’s land but has only 2.78% of the world’s population.
- Population Density: Average of 23 persons per sq. km, much lower than India.
- Distribution: Very uneven, concentrated near the coast.
Population Distribution (Figure 6.2a and 6.2b)
High-Density Areas:
- Southeast Coast: Fertile land, industries, and ports (e.g., Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro).
- Eastern Coastal Plain: Agriculture and trade flourish (e.g., Pernambuco, Bahia).
Low-Density Areas:
- Amazon Basin: Unfavorable climate, heavy rainfall, dense forests, and inaccessibility (e.g., Amazonas, Roraima).
- Central and Western Brazil: Highlands with moderate density (e.g., Mato Grosso, Goias).
Key States:
- Highest Density: Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Pernambuco.
- Lowest Density: Amazonas, Roraima, Acre.
Map Type: Dot map (distribution) and choropleth map (density).
Factors Affecting Distribution
Favorable Factors:
- Nearness to the sea (ports, trade).
- Fertile land (agriculture).
- Industries and urban centers.
- Moderate climate.
Unfavorable Factors:
- Dense forests (Amazon Basin).
- Heavy rainfall and inaccessibility.
- Lack of roads and facilities.
- Rugged highlands.
Population Composition
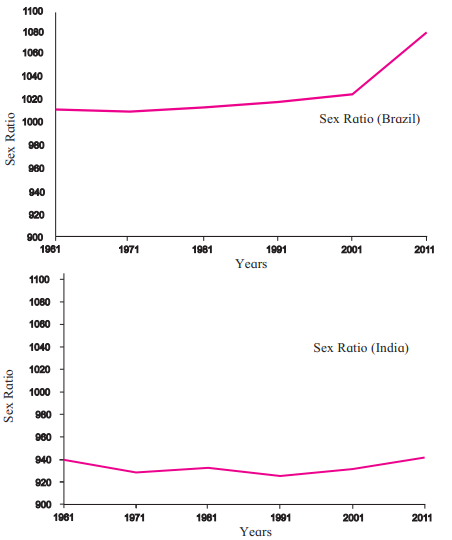
Sex Ratio (Figure 6.3)
Definition: Number of females per 1000 males in a region.
Brazil:
- Sex ratio is above 1000 (more females than males) since decades.
- Number of women has increased significantly since 2001.
India:
- Sex ratio is below 1000 (more males than females).
- Slight increase in sex ratio after 1991, but men still outnumber women.
Reasons for Low Sex Ratio (India):
- Gender discrimination, female infanticide, and neglect of girls.
- Not all Indian states have low sex ratios (e.g., Kerala has a higher sex ratio).
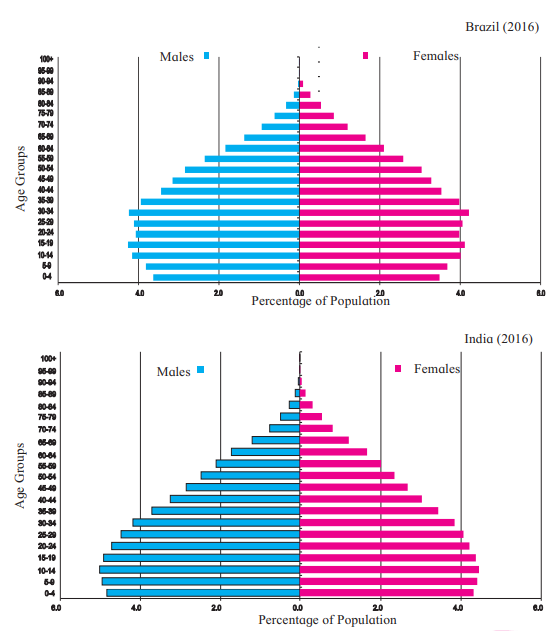
Age and Sex Pyramid (Figure 6.4)
Definition: A graph showing the distribution of males and females across age groups, also called a population pyramid.
Brazil (2016):
- Population is slowly aging.
- Higher proportion of older people (above 80 years).
India (2016):
- Higher proportion of youth, indicating a larger working population.
- More children compared to Brazil.
Use: Helps understand the proportion of children, youth, and elderly, and plan for education, jobs, and healthcare.
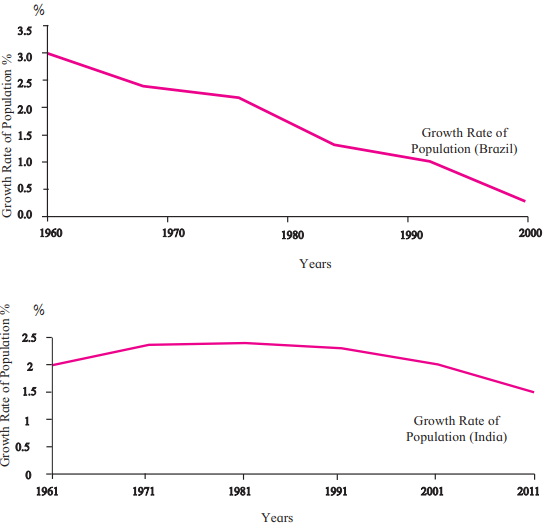
Population Growth Rate (Figure 6.5)
Brazil:
- Growth rate is declining significantly.
- Population may stop growing in the next two decades.
India:
- Growth rate was high until 1971, then stabilized.
- Population grew by 18.2 crores from 2001 to 2011, but growth rate is now declining.
Key Point: A downward trend in growth rate does not mean population is decreasing; it means growth is slower than before.
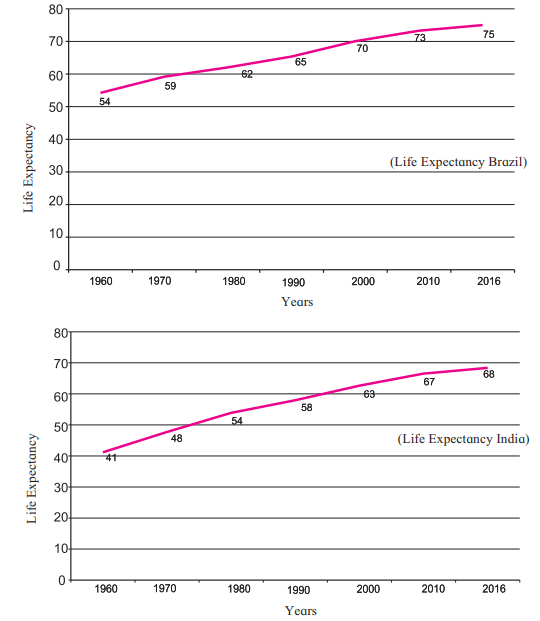
Life Expectancy (Figure 6.6)
Definition: Average number of years a person is expected to live.
Brazil:
- Average life expectancy: 75 years (2016).
- Higher due to better healthcare and living conditions.
India:
- Average life expectancy: 68 years (2016), up from 41 years in 1960.
- Improving due to better health facilities and nutrition.
Significance: Higher life expectancy indicates social and economic development.
Relation to Population Growth: Increased life expectancy can lead to slower population growth as people live longer but have fewer children.
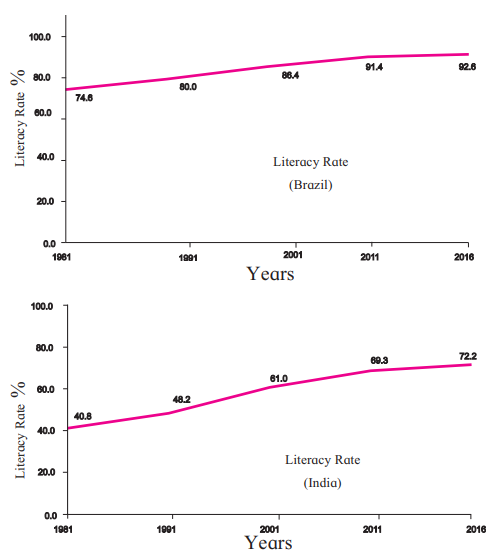
Literacy Rate (Figure 6.7)
Brazil:
- Higher literacy rate compared to India.
- Steady increase over decades due to education policies.
India:
- Literacy rate is improving but lower than Brazil.
- Significant progress since 1960 due to government efforts.
Importance: A literate population contributes to economic growth and social development.
Comparison of India and Brazil
Population Size and Density
India:
- Population: 121 crores (2011), second highest globally.
- Density: 382 persons per sq. km, high due to limited land and large population.
Brazil:
- Population: 19 crores (2010), fifth highest globally.
- Density: 23 persons per sq. km, low due to large land area and sparse interior regions.
Distribution
Similarities:
- Both have uneven population distribution.
- High density in fertile, coastal, and urban areas.
- Low density in inaccessible or harsh regions (forests, deserts, mountains).
Differences:
- India: Dense in northern plains and urban centers; sparse in Himalayas and deserts.
- Brazil: Dense in southeast and eastern coasts; sparse in Amazon Basin and central highlands.
Sex Ratio
- Brazil: More females than males (sex ratio >1000).
- India: More males than females (sex ratio <1000).
Age Structure
- Brazil: Aging population, more elderly.
- India: Younger population, more youth and children.
Growth Rate
- Brazil: Declining rapidly, may stabilize soon.
- India: Declining but still growing significantly.
Life Expectancy
- Brazil: Higher (75 years).
- India: Lower (68 years) but improving.
Literacy Rate
- Brazil: Higher literacy rate.
- India: Lower but improving.
Importance of Population
Why Population is a Resource:
- A large, skilled population drives economic growth (e.g., labor for industries, innovation).
- A youthful population (like India’s) provides a strong workforce.
- Educated and healthy people contribute to social progress.
Challenges:
- High population density (India) strains resources like food, water, and housing.
- Low density (Brazil’s interior) limits development in those areas.
- Gender imbalance (India) affects social equality.
- Aging population (Brazil) increases dependency on the working population.
Solutions for Population Management
Utilizing Manpower:
- Provide education and skill training to youth (e.g., vocational programs).
- Create job opportunities in rural and urban areas.
Improving Sex Ratio:
- Promote gender equality through campaigns like “Save Girl, Teach Girl.”
- Enforce laws against female infanticide and ensure girls’ education.
Controlling Population Growth:
- Spread awareness about family planning and contraception.
- Improve healthcare to reduce infant mortality, encouraging smaller families.

Leave a Reply