Introduction
- Human Settlements: Places where people live, such as villages, towns, or cities, shaped by the environment and human activities.
- Settlements can be rural (villages, agriculture-based) or urban (cities, industry-based).
- This chapter compares settlement patterns and urbanization in India and Brazil, focusing on types, distribution, and influencing factors.
- Key skills: Reading maps, identifying settlement types, and understanding urbanization trends.
Settlement Patterns in India
Overview
- India has a variety of settlement patterns due to its diverse climate, landforms, water availability, and development levels.
- Two main types of settlements: Nucleated and Dispersed.
Types of Settlements
1. Nucleated Settlements (Figure 7.1a):
Definition: Houses are closely packed, forming a compact settlement.
Locations:
- Northern Plains: Fertile lands of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh.
- Narmada Valley: Plateau region with cultivable land.
- Vindhyan Plateau: Fertile agricultural areas.
- Other Cultivated Areas: Paddy fields and flat lands across India.
Reasons:
- Fertile soil supports agriculture.
- Availability of water (rivers, canals).
- Flat terrain makes building easier.
- Presence of facilities like markets and schools.
Example: Villages in the Ganga Plains.
2. Dispersed Settlements (Figure 7.1b):
Definition: Houses are spread out, far from each other.
Locations:
- Himalayan Slopes: Rugged, uneven terrain.
- Eastern and Southern Rajasthan: Dry, desert areas.
- Central India: Tribal areas with forests.
- Dissected Topography: Uneven, hilly regions.
Reasons:
- Difficult terrain (mountains, hills).
- Lack of fertile land or water.
- Inaccessibility and limited facilities.
- Harsh climate (cold or arid).
Example: Scattered homes in the Himalayas.
Factors Affecting Settlement Patterns
Favorable Factors:
- Flat, fertile land (e.g., northern plains).
- Availability of water (rivers, wells).
- Moderate climate.
- Access to transport and facilities.
Unfavorable Factors:
- Rugged terrain (mountains, hills).
- Dry or extreme climate (deserts, high altitudes).
- Dense forests or inaccessibility.
- Lack of resources or infrastructure.
Urban vs. Rural Settlements
Rural Settlements:
- Found in villages, agriculture-based.
- Limited facilities (e.g., small schools, local markets).
- Often nucleated in fertile plains or dispersed in hilly areas.
Urban Settlements:
- Found in cities, industry and trade-based.
- Advanced facilities (e.g., hospitals, universities, malls).
- Mostly nucleated due to high population density.
Examples:
- Rural: Villages in Bihar (nucleated), Himalayan hamlets (dispersed).
- Urban: Mumbai, Delhi (nucleated).
Settlement Patterns in Brazil
Overview
- Brazil’s settlements vary due to its coastal development, natural resources, and interior challenges.
- Early settlements were formed by European settlers along the coast, now densely populated.
Types of Settlements
1. Nucleated Settlements (Figure 7.2b):
Definition: Compact, densely populated settlements.
Locations:
- Southeast Coast: Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro.
- Eastern Coastal Plain: Pernambuco, Bahia.
Reasons:
- Fertile soil (e.g., Sao Paulo’s coffee-growing land).
- Rich natural resources (e.g., iron ore).
- Steady energy supply and good transport systems.
- Proximity to the sea for trade and ports.
- Moderate climate despite being hot and humid.
Example: Sao Paulo (major metropolitan and industrial area).
2. Dispersed Settlements (Figure 7.2a):
Definition: Scattered, sparsely populated settlements.
Locations:
- Amazon River Basin: Northern Brazil.
- Northeast Highlands: Dry, drought-prone areas.
- Central Brazil: Interior highlands.
Reasons:
- Thick equatorial rainforests (Amazon Basin).
- Unhealthy, humid climate unsuitable for living.
- Limited use of natural resources.
- Poor transport links and inaccessibility.
Example: Small settlements in the Amazon Basin.
Factors Affecting Settlement Patterns
Favorable Factors:
- Fertile land and water supply (coastal plains).
- Natural resources (minerals, energy).
- Good transport and trade facilities.
- Urban development and industries.
Unfavorable Factors:
- Dense forests (Amazon).
- Extreme climate (heavy rain, droughts).
- Rugged terrain (highlands).
- Lack of infrastructure in the interior.
Urbanization in India
Overview
Urbanization: The percentage of people living in urban areas compared to the total population.
Level (2011): 31.16% of India’s population lives in urban areas, low compared to developed countries.
Trend (Figure 7.5, 1961-2011):
- 1961: Around 18% urbanization.
- Highest Growth: 2001-2011 decade (fastest increase).
- Lowest Growth: 1961-1971 decade (slowest increase).
- Inference: Urbanization in India is slow but increasing due to the expansion of cities and new towns.
Regional Variations
High Urbanization:
- Goa: 62% urban population (most urbanized state).
- Delhi: Over 80% urban.
- Southern States: Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Kerala, Gujarat (industrial growth, better infrastructure).
Low Urbanization:
- Northern States: Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Rajasthan (rural, agriculture-based).
Reasons:
- Southern states have more industries, ports, and urban facilities.
- Northern states rely on agriculture with fewer urban centers.
Historical Context
- India has a long history of urbanization since ancient times.
- Ancient urban settlements: Indraprastha (Delhi), Varanasi, Harappa, Mohenjodaro, Ujjain, Pratishthan (Paithan).
- Shows India’s tradition of urban development.
Urbanization in Brazil
Overview
- Level: About 86% of Brazil’s population lives in urban areas, making it highly urbanized among developing countries.
- Definition Issue: The definition of ‘urban’ in Brazil is unclear, complicating data.
- Key Area: Rapid urbanization in the South and Southeast, especially Sao Paulo (major metropolitan and industrial hub).
Trend (1960-2010)
- Data Interval: 10 years (Census data).
- Rapid Urbanization Period: 1960-1980 (fastest growth due to industrial and coastal development).
- Analysis:
- Urban population share increased steadily.
- Growth driven by industries, trade, and infrastructure in coastal states.
- Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro became major urban centers.
- Interior regions (e.g., Amazon Basin) remain less urbanized.
- Government promotes “Go West” policy to develop western interiors and reduce pressure on coastal cities.
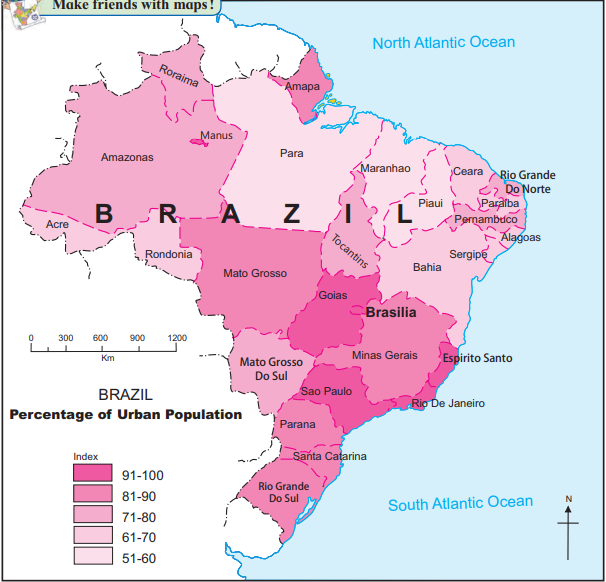
Regional Variations (Figure 7.6)
Most Urbanized States:
- Sao Paulo, Goias, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro (coastal, industrial).
Least Urbanized States:
- Amapa, Roraima, Amazonas (interior, forested, or remote).
Example:
- Manaus: A port city in the Amazon Basin, urbanized due to its location at the confluence of the Negro and Amazon rivers.
Factors Affecting Urbanization
Coastal Advantages:
- Access to ports and trade.
- Fertile land and resources (e.g., minerals, coffee).
- Better transport and energy supply.
Interior Challenges:
- Dense forests and heavy rainfall (Amazon).
- Droughts in the northeast highlands.
- Poor infrastructure and limited resources.
Comparison of India and Brazil
Settlement Patterns
India:
- Location: Nucleated in northern plains, coastal cities; dispersed in Himalayas, deserts.
- Pattern: Compact in fertile areas; scattered in rugged regions.
- Types: Rural (villages), urban (cities), mixed in some areas.
- Density: High in plains (e.g., Ganga Basin); low in mountains.
Brazil:
- Location: Nucleated in southeast coast; dispersed in Amazon and highlands.
- Pattern: Dense along coasts; sparse in interiors.
- Types: Urban in coastal cities; rural in remote areas.
- Density: High in Sao Paulo, Rio; low in Amazonas.
Urbanization
India:
- Urbanization: 31.16% (2011), slow growth.
- Concentrated in southern states and Delhi.
- Driven by industrial growth and new towns.
- Challenges: Rural dominance, uneven development.
Brazil:
- Urbanization: 86%, rapid growth.
- Concentrated in southeast (Sao Paulo, Rio).
- Driven by industries, ports, and resources.
- Challenges: Overcrowding in coastal cities, underdeveloped interiors.
Policies
- India: “Go to Villages” policy promotes rural development to reduce urban pressure.
- Brazil: “Go West” policy encourages settlement in less populated western regions to balance development.



Leave a Reply