Refraction of light
Short Questions
1. What is refraction of light?
Answer : Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one transparent medium to another.
2. State the first law of refraction.
Answer : The incident ray, refracted ray, and normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
3. What is the second law of refraction known as?
Answer : The second law of refraction is known as Snell’s law.
4. What is the refractive index of a medium?
Answer : It is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium.
5. What happens to light when it passes from a rarer to a denser medium?
Answer : Light bends towards the normal.
6. What happens to light when it passes from a denser to a rarer medium?
Answer : Light bends away from the normal.
7. What is the critical angle?
Answer : The angle of incidence for which the angle of refraction is 90°.
8. What is total internal reflection?
Answer : It occurs when light reflects entirely back into a denser medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.
9. What causes the twinkling of stars?
Answer : The twinkling of stars is due to the changing refractive index of atmospheric gases.
10. Why don’t planets twinkle?
Answer : Planets appear as a collection of point sources, so their average brightness remains constant.
11. What is dispersion of light?
Answer : Dispersion is the separation of light into its component colors while passing through a medium.
12. Which color of light bends the least in a prism?
Answer : Red light bends the least due to its longer wavelength.
13. Which color of light bends the most in a prism?
Answer : Violet light bends the most due to its shorter wavelength.
14. What is a mirage?
Answer : A mirage is an illusion of water caused by the refraction of light in varying air densities.
15. Why can we see the Sun slightly before sunrise?
Answer : Atmospheric refraction bends sunlight, making the Sun visible before it crosses the horizon.
Long Questions
1. Explain the phenomenon of refraction with an example from the given activities.
Answer : Refraction occurs when light changes direction while passing from one medium to another, like water to air. In Activity 1, a pencil in water appears thicker and bent due to refraction at the water-air interface. This happens because light slows down in water, bending towards the normal.
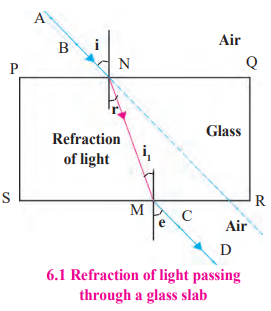
2. How do the laws of refraction apply to a light ray passing through a glass slab?
Answer : The first law states that the incident ray, refracted ray, and normal lie in the same plane. The second law (Snell’s law) states that the ratio of sine of the angle of incidence to sine of the angle of refraction is constant. In a glass slab, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray due to equal but opposite refractions at parallel surfaces.
3. What is the refractive index, and how is it related to the velocity of light?
Answer : The refractive index is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in a medium. It is calculated as n = v1/v2, where v1 is the speed in the first medium and v2 in the second. A higher refractive index indicates slower light speed in that medium.
4. Why does a rainbow form, and what processes are involved?
Answer : A rainbow forms due to dispersion, refraction, and total internal reflection in water droplets. Sunlight refracts and disperses into colors inside a droplet, reflects internally, and refracts again while exiting. This creates a spectrum of colors visible as a rainbow.
5. Why do stars twinkle but planets do not?
Answer : Stars twinkle because their light, from a point source, bends due to changing atmospheric refractive indices. Planets, appearing as a collection of point sources, have their brightness averaged out, preventing twinkling. Atmospheric turbulence affects starlight more due to their greater distance.
6. What is total internal reflection, and how does it contribute to optical phenomena?
Answer : Total internal reflection occurs when light in a denser medium hits a rarer medium at an angle greater than the critical angle, reflecting entirely back. This is crucial in phenomena like rainbows, where light reflects inside water droplets. It’s also used in optical fibers for efficient light transmission.
7. How does atmospheric refraction affect the apparent position of stars?
Answer : Atmospheric refraction bends starlight towards the normal as it enters denser air layers. This makes stars appear higher in the sky than their actual position. The changing refractive index due to air movement causes the twinkling effect.
8. Explain how a mirage is formed with reference to atmospheric conditions.
Answer : A mirage forms when light from a distant object bends due to varying air density near a hot surface. Hot air near the ground is rarer, causing light to bend upward, creating an illusion of water. This is due to continuous refraction as light passes through layers of increasing refractive index.
9. How does dispersion of light occur in a prism, and what is the result?
Answer : Dispersion occurs when white light passes through a prism, and different colors bend at different angles due to varying refractive indices. Red light bends the least, and violet the most, creating a spectrum. This separation of colors is visible as a rainbow-like band.
10. How can you demonstrate refraction using a glass slab as described in Activity 3?
Answer : In Activity 3, a light ray passing through a glass slab refracts at the air-glass interface, bending towards the normal. It refracts again at the glass-air interface, bending away, resulting in a parallel emergent ray. The activity shows the ray’s displacement and confirms the laws of refraction.

Leave a Reply