Disaster Management
Solutions
Question 1.
Complete the table.
(Motor accident, land sliding, forest fire, theft, riot, war, epidemic, drought, locust attack, financial crisis, flood, famine)
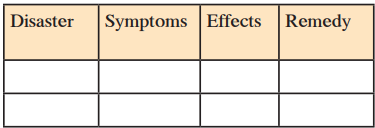
| Disaster | Symptoms | Effects | Remedy |
| Motor accident | Rash driving, drink and drive, ignorance to safety rules | Loss of life, loss of property | Following traffic rules, avoid driving if tipsy |
| Land sliding | New cracks or bulges in the ground, street or sidewalks, sunken road beds | Loss of property, loss of life, adverse impact on environment | Give help to clear debris, call ambulance to send victims to hospitals |
| Forest fire | Lightning, human activities involving smoke and fire near forests areas | Impact on environment, loss of lives of animals | Call fire brigade, give first aid to animals which survived the burns |
| Theft | Sheer carelessness towards property and wealth | Tension and loss of property | Informing police, giving emotional support |
| Riot | Opinion differences, political influence | Loss of life and property | Give shelter to innocent victims, provide food and clothing and first-aid to the victims |
| War | Transgressing, opinion differences between countries | Loss of life and property, Impact on the country and its economy | Give shelter to innocent victims, provide food, clothing and first-aid to the victims |
| Epidemic | Spreading of viruses from different animals | Loss of life, health risks, impact on environment | Give proper medication to people, preparing antidotes against epidemic |
| Drought | No rainfall for long duration | Food and water crisis, loss of life | Donate food and water for victims, provide shelter and monetary help |
| Locust attack | Leaf distortion, chlorosis, yellow to brown spots, premature leaf drop | Crop destruction, scarcity in food | Spraying pesticides |
| Financial crisis | Bankrupt, loss in business or services in individual case | Impact on the country and its economy, impact on individual | Giving support to friends and family, asking support from other countries when crises happens in a country |
| Flood | Cloudburst, heavy rainfall | Health risks, loss of property, food and water crisis, loss of life | Donate food and clothing for flood victims, stay at some height if possible |
| Famine | Heavy rainfall, drought | Food and water crisis, displacement of people, loss of life | Donate food and water for victims, provide shelter and monetary help |
Question 2.
Write notes.
a. Disaster Management Authority.
Answer:
Disaster Management Authority is the body that works at the level of government from national level to village level. This work is basically about management of any disaster and tackling the problems of the affected people. At National level there is National Disaster Management Authority for which the Prime Minister is the chairman. For every state there is State Disaster Management Authority, where the chief minister of every state is the chairman. Under the state level, there are district level units where district collector is responsible for disaster management and implementation of rehabilitation schemes. Below district level authority there are Taluka and then Village Disaster Management Committees.
b. Nature of disaster management.
Answer:
Disaster management involves either prevention of disasters (Pre-disaster management) or creating preparedness to face them (Post-disaster management). The action plans are prepared for managing disasters. This is done after studying the different aspects such as preventive measures, rehabilitation and reconstruction plans. The disasters are tackled by executing action plans in the following steps: Preparation, redemption, preparedness, action during actual disaster, response, resurgence and restoration. At every level there are other voluntary organizations and Government meteorological institutions for their help.
c. Mock drill.
Answer:
- Mock drill is the practice to check whether there is preparedness for dealing with the sudden attack of disaster.
- For this purpose, virtual or apparent situations that simulate the disaster are created.
- The reaction time for any type of disaster is checked by such activity. In the presence of trained personnel, the execution of the rescue plans are observed.
- People also understand their responsibilities at the time of actual disaster.
- The experts also check execution of plan designed for disaster redressal.
- By such mock drills, the efficacy of the system can be understood. In future, when actual calamity strikes, there is already preparation for disaster redressal. Therefore, mock drill is useful.
d. Disaster Management Act, 2005.
Answer:
Government of India has made Disaster Management Act in 2005. The affected people are given all necessary help as per this act. With the humanitarian view, people are rehabilitated and helped them to come back to normalcy after the disaster.
As per this Act, National Disaster Response Force has been established. This force consists of 12 divisions in entire India which are attached with Indian Army. The headquarter is located in Delhi, but the action is taken all over the country with the help of army. As per the Act, in Maharashtra National Disaster Response Force is in action through State Reserve Polioe Force. The personnel of this force are trained accordingly, and they take part in the rescue work during different disasters.
Question 3.
Answer the following questions.
a. Explain the role of district disaster control unit after occurrence of any disaster.
Answer:
(1) District control unit looks after the ; disaster management of the district.
(2) It is immediately formed either after the impact of disaster or if warning is given about some upcoming disaster
District-wise Disaster Control Unit performs following role:
- The review of various aspects of disasters is done.
- Through the disaster control unit there is continuous contact established with various agencies like army, air force, navy, telecommunication department, paramilitary forces, etc. for obtaining help.
- The unit also coordinates with various voluntary organizations for their help in disaster management.
b. Give the reasons for increase in human disasters after the World War-II.
Answer:
- After Second World War, the feelings of peace and brotherhood among the global citizens were lost. The geographic, religious, racial and ethnic differences sprang up tremendously.
- Atrocities that Nazi has performed made deep impact on the minds of people. Terrorism, abduction, robberies and social unrest increased in almost all the countries.
- The financial losses had incurred in the World War II. The misuse of science and technology was done to retrieve these deficits.
- At the end of World War II, the atomic bombs were dropped in Japan. This has created health problems in the entire world.
- Social inequality, economic disparity, racial and religious differences were some adversaries that created unrest in the country.
- Later, the neighbouring nations kept on fighting. The geographical boundaries were changed. People always had feelings of insecurity. The terrorism flourished. All such instances gave rise to man-made disasters.
c. What are the objectives of disaster management?
(OR)
State any four objectives of disaster management.
Answer:
Objectives of disaster management:
- To save human life from disasters. To help them for moving away from the place of disasters by rapid action.
- To supply essential commodities to the affected people. This helps to reduce the gravity of disaster. People are given grains, water and clothes and other basic necessities under this objective.
- To bring back the conditions of affected people to normalcy.
- To rehabilitate the affected and displaced victims.
- To think and execute the protective measures in order to develop capability to face the disasters in future.
d. Why is it essential to get the training of first aid?
Answer:
When there is a disaster, we need to immediately help the victim. Till the medical help arrives, one should be in position to treat the injured and save his or her life. In such cases; knowing first- aid is essential. Such kind of a need may arise in case of our parents, our siblings at home or with friends in school. Those who are injured should be treated at once. If we know about techniques of first aid, we can save such person before the medical help arrives. Therefore, it is essential to get the training of the first aid.
e. Which different methods are used for transportation of patients? Why?
Answer:
For the transportation of patients following methods are used:
- Cradle method: This method is used for children and persons with less weight.
- Carrying piggy back: This method is useful in carrying the unconscious persons.
- Human crutch method: If one leg of the person is injured, then the victim is supported with minimum load on the other leg. This is called human crutch method.
- Pulling or lifting method: For carrying an unconscious person for a short distance this method is used.
- Carrying on four-hand chair: This method is used when the support is needed for a part below waist region.
- Carrying on two-hand chair: Patients that cannot use their hands but can hold their body upright, are carried by such method.
- Stretcher: By making temporary stretcher in case of emergency, the unconscious patient can be moved. Such temporary stretchers are made by using bamboos, blanket, etc.
Question 4.
On the basis of the structure of disaster management authority, form the same for your school.
Answer:
Students are expected to make the map based on their own.
Question 5.
Write down the reasons, effects and remedial measures taken for any two disasters experienced by you.
Answer:
Students are expected to write the answer based on their own experiences.
Question 6.
Which different aspects of disaster management would you check for your school? Why?
Answer:
For the pre-disaster management at school following aspects would be inspected.
- Are the telephones 6f the school working properly?
- Is there a first-aid box in each class?
- Are there any basic medicines in the school?
- Is the team ready for rescue of smaller children from lower classes?
- Has monitor or prefect participated in a mock drill? Does he/she know about first aid?
- Is the contact of parent representative available in emergency situations?
- Is the Medical Officer/Doctor present on the school campus?
- Is there enough drinking water and some dry snacks available in the school?
- Are the staircases and corridors suitable for quick evacuation of the children?
Question 7.
Identify the type of disaster.
a. Terrorism.
Answer:
Man-made, intentional.
Due to the activities of terrorism, many innocent lives are lost. Many are seriously injured. Some become crippled for their entire life. Buildings, monuments, vehicles everything is completely destroyed. There is rift between different religions or sects. The peaceful atmosphere is disturbed. The entire society is under the constant fear of insecurity.
b. Soil erosion.
Answer:
Natural, geophysical, geological.
When the upper fertile layer of soil is lost, it becomes barren. The trees are uprooted. The fertility of the area is lost. The land becomes unsuitable for cultivation or farming. Due to wind, flowing water or grazing animals the naturally occurring soil erosion becomes hazardous for the environment.
c. Hepatitis.
Answer:
Natural, biological, animal-origin.
Hepatitis is a viral disease which spreads through the contaminated food and water. The outburst of epidemic of hepatitis is difficult to control. As in big cities the quality of road side food is often consumed, the spread of hepatitis is. fast. People suffer due to hepatitis.
d. Forest fire.
Answer:
Natural, biological, plant-origin.
Due to heat and wind, the dry grass and the shrubs catch fire in the forests, resulting in forest fires. Such rapidly spreading forest fire can finish the biodiversity within a very short span of time. It is difficult to extinguish the naturally lit forest fires. Many trees and other vegetation, animals and birds along with their habitats are destroyed due to forest fire. The smoke emanating causes the air pollution.
e. Famine.
Answer:
Natural, climatic.
Due to famine there is severe water scarcity. In absence of water, the fields and farms become barren as the crops cannot grow without water. There is shortage of food grains. The cattle dies due to want of water and grass. Local people have to migrate in search of food, water and shelter.
f. Theft.
Answer:
Man-made, intentional.
Theft causes economic loss for the one whose money or valuables are looted. The person who suffers the loss also undergo mental and emotional shock. Sometimes the thief may also cause physical harm. It may cost on life too.
Question 8.
Some symbols are given below. Explain those symbols. Which disasters may occur if those symbols are ignored?
Answer:
The above signs are warning symbols which should never be ignored.
The meaning of each is given below. They are giving warnings about explosive, inflammable, oxidizing, compressed gas, corrosive, toxic, irritant, environmentally hazardous and health hazard.
(1) Explosive: Some materials are explosive. While handling such materials care should be taken. We should not take anything that would cause fire leading to explosion. If explosion occurs, there would be a major disaster causing great loss of life and property. Thus if this sign is seen, great care has to be taken.
(2) Inflammable: Similar to explosive substances, the inflammable materials can also catch fire easily. Therefore, to warn people such sign is given on materials that can cause hazard by burning.
(3) Oxidizing: Some chemical substances are oxidizing. They carry out chemical reactions with a rapid speed. E.g. If potassium permanganate falls on the cloth, it starts the reaction on its C-C bonds. Due to such property of carrying out reactions, the cloths may catch fire. Therefore, oxidizing substances should be handled with care.
(4) Compressed: Compressed substances are filled under pressure in some container. If mishandled, they can come out of the container by bursting it open. This can cause some injuries.
(5) Corrosive: The corrosive substances are very reactive. The mere touch of corrosive substances can cause destruction of skin, eyes, respiratory passages, digestive organs, etc. rapidly. Just touching or smelling of such substances can cause major injury and thus warning sign of corrosive substance should never be ignored.
(6) Toxic: To taste a toxic substance or even to smell it, can lead to death. The packing of these substances are therefore marked as dangerous. They should be avoided as far as possible.
(7) Irritant: When skin or any delicate part of the body comes in contact with the irritant substance, it can cause harmful reaction. Especially, eyes, nasal mucosa and skin are affected by contact with corrosive substances.
(8) Environmentally hazardous: Many sub¬stances cause harm to the environment due to their toxicity. Air, water or soil can be polluted due to such pollutants. When environment is affected, ultimately these hazardous effects come back to human species. Therefore, such substances should be carefully used. Their use should be judicious and controlled.
(9) Health hazard: The substances that can cause hazard to our health should always be distanced from us. Such substances should not be kept in proximity. As far as possible they should be kept away and handled with great care if needed for any work. Materials marked with health hazard can cause severe toxicity.
Question 9.
Explain that why is it said like that?
a. Mock drill is useful.
Answer:
It is very correct to say that mock drills are very important and useful. These drills should be conducted at every work places, schools, public places etc. These drills ensure a way of checking the preparedness of facing a disaster. Through mock drills,
- we can evaluate the response or reaction time to a disaster
- we can identify our own abilities
- coordination between various departments of disaster control can be improved
- we can check the competency of the planned actions
- we can identify the possible errors and risks
b. Effective disaster management makes us well prepared for future.
Answer:
We know that disasters are sudden and unplanned and thus can’t be avoided in most cases. But if effective disaster management is employed and exercised, then we would certainly achieve the abilities to face the adverse effects of disasters. Hence, through effective disaster management, we actually make ourselves prepared for future. Through effective disaster management,
- we can supply essential commodities to the people after or before disaster
- we can arrange rescue for the affected
- we can rehabilitate and rebuild the affected area in short span of time
- we can minimise losses of life and property
- we can build tools to assess the damaged caused
Question 10.
Complete the following chart.
Answer:
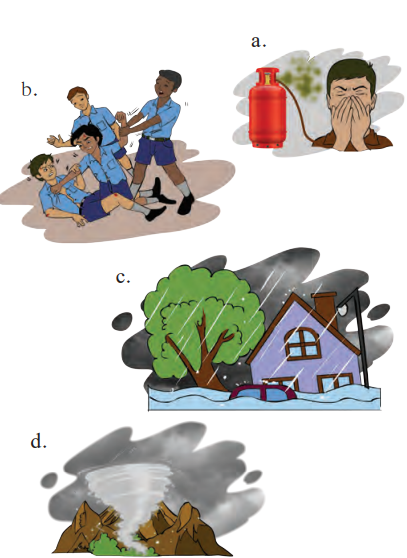
Question 11.
Following are the pictures of some disasters. How will be your pre and post-disaster management in case you face any of those disasters?
Answer:
In the pictures given, following disasters are shown:
a) The picture shows a gas leak from an LPG cylinder.
i. Pre-disaster management:
- The gas cylinder and the rubber tubes used must be certified.
- Gas cylinders must be properly checked for leakage from the pipe nozzle or any other part while installing.
ii. Post-disaster management:
- Do not try to turn ON or turn OFF any electrical appliances in the surrounding area.
- Put out all flames, incense sticks, etc.
- Turn off the LPG regulator and immediately put on the safety cap.
- Open all the windows and doors to ensure ventilation.
- Get in touch with the LPG cylinder dealer immediately.
b) The picture shows a fight between schoolboys in the playground.
Pre-disaster management:
- Discussing the problem with elders
- Trying to settle the dispute verbally
Post-disaster management:
- Identifying any serious injuries that occurred to oneself or the counterpart. Getting proper medication for the same
- Apologizing to each other.
Pre-disaster management:
- Keep an emergency kit. This kit should consist of portable lights, medicines, etc.
- Keep extra dry food and portable water
- Move to higher floors if possible
- Switch off all the electrical appliances
Post-disaster management:
- Avoid going to water flooded areas as there are chances of harmful insects being present there
- Check for the casualties around
- Help the victims in need
d) The picture shows a cyclone.
Pre-disaster management:
- Keep an emergency kit. This kit should consist of portable lights, medicines, etc.
- Keep extra dry food and portable water
- Move to locations that are less prone to cyclones
- Switch off all the electrical appliances
Post-disaster management:
- Clearing the debris left behind the cyclone
- Help the victims in need
- Check for ruptures or cracks on the wall of the house




Leave a Reply