Life Processes in Living Organisms Part – 2
Solutions
Question 1.
Complete the following chart.
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| 1. Reproduction that occurs with the help of somatic cells is called asexual reproduction. | 1. __________________________________________ ____________________________________________ |
| 2. __________________________________________ ____________________________________________ | 2. Male and female parent are necessary for sexual reproduction. |
| 3. This reproduction occurs with the help of mitosis only. | 3. __________________________________________ ____________________________________________ |
| 4. __________________________________________ ____________________________________________ | 4. New individual formed by this method is genetically different from parents. |
| 5. Asexual reproduction occurs in different individuals by various methods like binary fission, multiple fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation, spore production, etc. | 5. __________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ |
Answer:
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| 1. Reproduction that occurs with the help of somatic cells is called asexual reproduction. | 1. Reproduction that occurs due to fertilization of gametes is called sexual reproduction. |
| 2. For asexual reproduction only one parent is necessary. | 2. Male and female parents are necessary for sexual reproduction. |
| 3. This reproduction occurs with the help of mitosis only. | 3. This reproduction occurs with the help of both mitosis and meiosis. |
| 4. New individual formed by this method is genetically identical with parents. | 4. New individual formed by this method is genetically different from parents. |
| 5. Asexual reproduction occurs in different individuals by various methods like binary fission, multiple fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation, spore production, etc. | 5. Sexual reproduction occurs in two steps: First formation of haploid gametes by meiosis and then fertilization of these haploid gametes to form diploid zygote. There are no subtypes in the sexual reproduction. |
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks.
a. In humans, sperm production occurs in the organ …………
(a) prostate gland
(b) testis
(c) ovaries
(d) Cowper’s gland
Answer:
(b) testis
b. In humans, …………. chromosome is responsible for maleness.
(a) X
(b) Y
(c) Z
(d) O
Answer:
(b) Y
c. In male and female reproductive system of human, …………. gland is same.
Answer:
There is no similar gland in male and female reproductive system. There may be some homologies but there is no similarity.
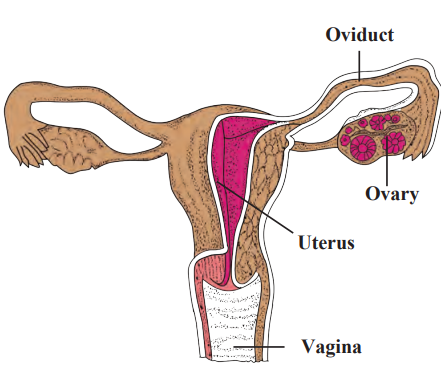
d. Implantation of embryo occurs in …………
(a) ovaries
(b) fallopian duct
(c) uterus
(d) vagina
Answer:
(c) uterus
e. …………type of reproduction occurs without fusion of gametes.
(a) Asexual
(b) sexual
(c) Fertilization
(d) Gamete formation
Answer:
(a) Asexual
f. Body breaks up into several fragments and each fragment begins to live as a new individual.
This is ………. type of reproduction.
(a) regeneration
(b) fragmentation
(c) binary fission
(d) budding
Answer:
(b) fragmentation
g. Pollen grains are formed by division in locules of anthers.
(a) meiosis
(b) mitosis
(c) amitosis
(d) binary
Answer:
(a) meiosis
Question 3.
Complete the paragraph with the help of words given in the bracket:
(Luteinizing hormone, endometrium of uterus, follicle stimulating hormone, estrogen, progesterone, corpus luteum)
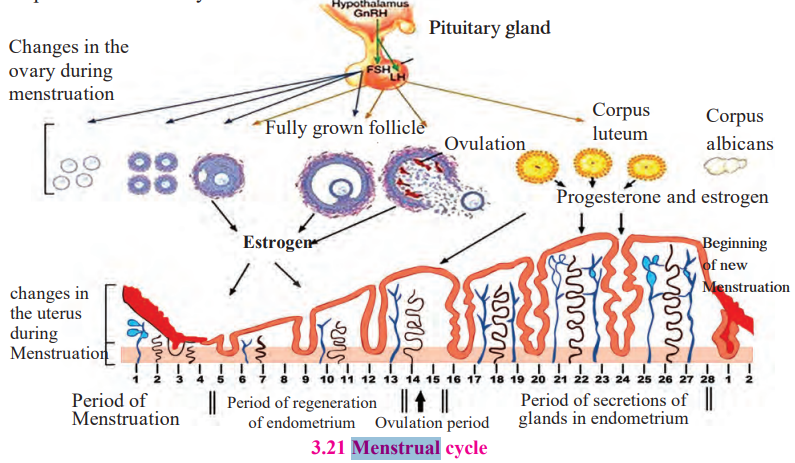
Growth of follicles present in the ovary occurs under the effect of follicle stimulating hormone. This follicle secretes estrogen. Ovarian follicle along with oocyte grows/regenerates under the effect of estrogen. Under the effect of Luteinizing hormone, fully grown up follicle bursts, ovulation occurs and corpus luteum is formed from remaining part of follicle. It secretes estrogen and progesterone. Under the effect of these hormones, glands of endometrium of uterus are activated and it becomes ready for implantation.
Question 4.
Answer the following questions short.
a. Explain with examples types of asexual reproduction in unicellular organism.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction occurs in unicellular organisms through various methods. Some of these methods are as follows:
1. Binary Fission: In this method, the parent cell divides into two equal parts, resulting in the formation of two new daughter cells. This division occurs through mitotic division. Generally, binary fission occurs in favourable conditions when sufficient food is available. Bacteria, protozoa, mitochondria, and chloroplasts reproduce asexually through binary fission.
Depending on the axis of division, binary fission in different protozoa is classified as:
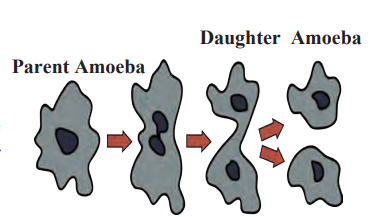
1. Simple Binary Fission: Since Amoeba does not have a definite shape, it can divide along any axis. Therefore, this type of fission is called simple binary fission.
Example: Amoeba
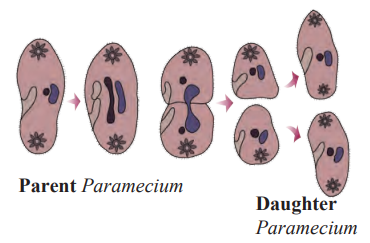
2. Transverse (Horizontal) Binary Fission: In Paramecium, division occurs along the transverse axis.
Example: Paramecium
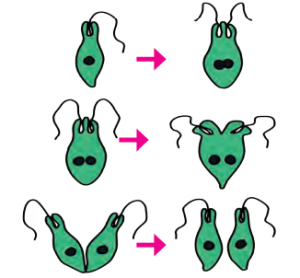
3. Longitudinal (Vertical) Binary Fission: In Euglena, division occurs along the longitudinal axis.
Example: Euglena
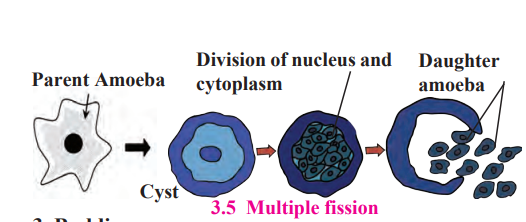
2. Multiple Fission: Amoeba and similar unicellular protozoa reproduce asexually through multiple fission in unfavourable conditions. When food is insufficient or environmental conditions become unfavourable, Amoeba stops moving and does not produce pseudopodia. It becomes spherical and forms a hard protective covering around itself, known as a “Cyst.”
Inside the cyst, the nucleus undergoes multiple mitotic divisions, resulting in the formation of several nuclei. Later, the cytoplasm also divides, producing multiple small Amoebae.
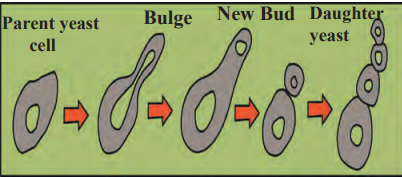
3. Budding: Yeast reproduces asexually through budding. First, mitotic division occurs in the parent cell, producing two daughter nuclei. A small outgrowth, called a “Bud,” appears on the parent cell. One of the daughter nuclei enters this bud. After growing sufficiently, the bud detaches from the parent cell and starts developing as an independent yeast cell.
b. Explain the concept of IVF.
Answer:
- It is also known as in-vitro fertilization.
- In this process, sperm is collected from the father or any male donor and similarly, an ovum is collected from the mother or any female donor, then this is fertilized in the laboratory using sterilizing conditions.
- Now when the embryo is formed, it is transferred to the mother or the surrogate.
- Embryo up to 8 blastomere stage is transferred in the fallopian tube whereas blastomere more than 8 blastomeres is transferred in the uterus.
- The process is carried out in a laboratory along with high precision and a sterilized environment and these methods are a part of Assisted Reproductive Technology(ART).
- Though these processes are difficult and high precision should be maintained they have many helped many couples who were unable to conceive.
c. Which precautions will you follow to maintain the reproductive health?
Answer:
The cleanliness of body is very essential but keeping the mind clean is also important to maintain good reproductive health. One should be careful about sexual relationships. These things should not be experimented in young age. Mistakes committed like these can change the sexual health forever. The cleanliness and hygiene during menstruation, the cleanliness of genitals and other private parts are the aspects of personal hygiene. When living in a society, one should always be away from cross-infections of venereal type.
d. What is menstrual cycle? Describe it in brief.
Answer:
- Human females menstruate once every 28 to 29 days. The menstrual cycle refers to the order of events that occur between each menstruation.
- In the middle of the menstrual cycle, one ovum is discharged (ovulation).
- The menstrual cycle begins with the break down of the uterus endometrium, which lasts 3–5 days. Blood vessels in liquid form leave the body, however this only happens when the ovum is not fertilized.
- It is followed by the follicular phase. During this phase, the main follicles develop into Graafian follicles. This leads to uterine regeneration, follicular growth, and the production of estrogen by the developing follicles.
- During the 14th day of the cycle, the LH and FSH levels peak, leading to Graafian follicle rupture and ovulation. This phase is known as the ovulatory phase.
- In the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum declines, resulting in endometrial break down and the beginning of a new cycle.
Question 5.
In case of sexual reproduction, newborn show similarities about characters. Explain this statement with suitable examples.
Answer:
(1) Sexual reproduction occurs due to two different gametes. One male gamete is from father while the other female gamete is from mother.
(2) Both the gametes are produced by meiosis.
(3) When the gametes unite it is called process of fertilization which produces diploid zygote.
(4) Due to the chromosomes of parents, their DNA pass to the next generation through such fertilization. Therefore, the characters of newborn show similarities with parents.
Question 6.
Sketch the labelled diagrams.
a. Human male reproductive system.
Answer:
b. Human female reproductive system.
Answer:
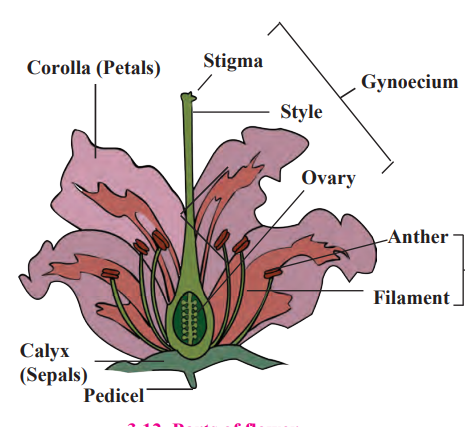
c. Flower with its reproductive organs.
Answer:
d. Menstrual cycle.
Answer:
Question 7.
Give the names.
a. Hormones related with male reproductive system.
Answer:
Follicle stimulating hormone and ICSH or Luteinizing hormone secreted by pituitary gland, testosterone secreted by testis.
b. Hormones secreted by ovary of female reproductive system.
Answer:
Estrogen and progesterone.
c. Types of twins.
Answer:
Monozygotic twins, Siamese twins and Dizygotic twins.
d. Any two sexual diseases.
Answer:
Gonorrhea and Syphilis.
e. Methods of family planning.
Answer:
Copper T, condoms, oral contraceptive pills.
Question 8.
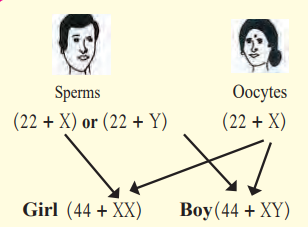
Gender of child is determined by the male? partner of couple. Explain with reasons whether this statement is true or false.
Answer:
Human females have two X chromosomes (XX) and human males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). Therefore, the eggs produced by females have only X chromosomes while the sperms produced by males can have either X or Y chromosome. If an unfertilised egg fuses with a sperm containing X chromosome, then it gives rise to a girl child having two X chromosomes. If an unfertilised egg fuses with a sperm containing Y chromosome, then it gives rise to a male child having one X and one Y chromosome.
Question 9.
Explain asexual reproduction in plants.
Answer:
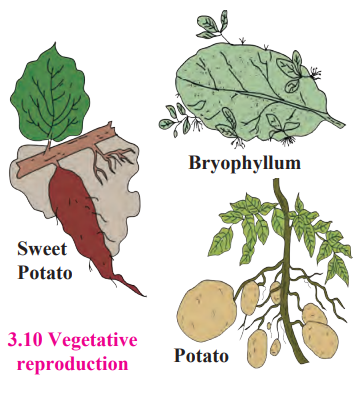
- Vegetative propagation is the method of asexual reproduction in plants.
- It takes place with the help of vegetative parts like root, stem, leaf and bud.
- Potato, suran (Amorphophallus) and other tubes propagate with the help of ‘eyes’ which are buds. These eyes are present on the stem tubers.
- In case of plants like sugarcane and grasses, buds present on nodes perform vegetative propagation.
- Plants like Bryophyllum performs vegetative propagation with the help of buds present on leaf margin.
Question 10.
Modern techniques like surrogate mother, sperm bank and IVF technique will help the human beings. Justify this statement.
Answer:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) – In this technique, fertilization is brought about in the test-tube and the embryo formed is implanted in uterus of woman at appropriate time.
- Surrogacy – Surrogacy is another method which is used for women who face problem in implantation of embryo in uterus. In this technique the donor of the oocyte is the women itself who has problem in implanting the embryo in the uterus. The collected oocyte is fertilized with the sperm of her husband in a test tube. The embryo which is obtained after fertilization is implanted in the uterus of another female who is called the surrogate mother.
- Sperm bank – It is a new concept which is similar to blood banks. Sperms are collected from the male donors after a thorough medical checkup and stored for future use. These sperms are used to fertilize the ovum of the women and then this fertilised ovum is implanted in the uterus of the same women.
Question 11.
Explain sexual reproduction in plants.
Answer:
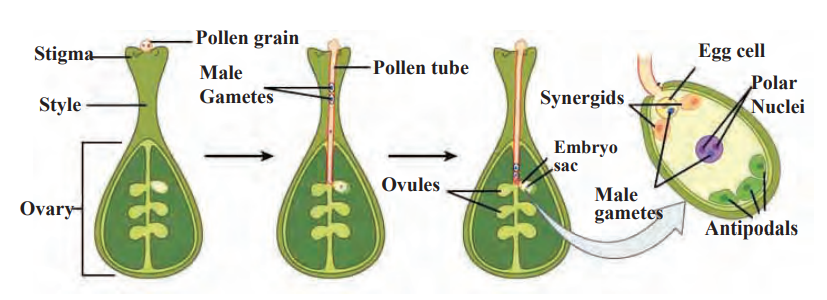
- In sexually reproducing plants, flowers function as the reproductive organs.
- In flowers, male organ is the stamen and female organ is the carpel.
- Flowers which have both the male and female organs i.e. stamens and carpels are called bisexual flowers whereas flowers which have either male or female organs are called unisexual.
- Male gametes called pollen grains are produced by stamen, and carpels produce female gametes called ovules or egg cells inside ovaries.
- Fertilization takes place in the ovule where the egg cell and pollen grain fuse.
- This fertilized egg cell later develops into an embryo and the entire ovule gets converted into a seed.
- Under favourable conditions, the seed germinates to give rise to a new plant.


Leave a Reply