Animal Tissue – Solutions
1. Choose correct option
A. The study of structure and arrangement of tissue is called as _____________
a. anatomy b. histology
c. microbiology d. morphology
Answer: b. histology
- Explanation: Histology is defined as the study of the structure and arrangement of tissues.
B. ____________ is a gland which is both exocrine and endocrine.
a. Sebaceous b. Mammary
c. Pancreas d. Pituitary
Answer: c. Pancreas
- Explanation: The pancreas functions as both an exocrine gland (secreting digestive enzymes) and an endocrine gland (releasing hormones like insulin into the bloodstream).
C. _____________ cell junction is mediated by integrin.
a. Gap b. Hemidesmosomes
c. Desmosomes d. Adherens
Answer: b. Hemidesmosomes
- Explanation: Hemidesmosomes are mediated by integrins, allowing cells to adhere strongly to the basement membrane.
D. The protein found in cartilage is _______.
a. ossein b. haemoglobin
c. chondrin d. renin
Answer: c. chondrin
- Explanation: Chondrin is the protein found in the matrix of cartilage.
E. Find the odd one out
a. Thyroid gland b. Pituitary gland
c. Adrenal gland d. Salivary gland
Answer: d. Salivary gland
- Explanation: Thyroid, pituitary, and adrenal glands are endocrine glands, while the salivary gland is an exocrine gland.
2. Answer the following questions:
A. Identify and name the type of tissues in the following:
a. Inner lining of the intestine
Answer: Epithelial tissue (Columnar epithelium)
- Explanation: The inner lining of the intestine is composed of columnar epithelial tissue, which aids in secretion and absorption.
b. Heart wall
Answer: Muscular tissue (Cardiac muscle)
- Explanation: The heart wall contains cardiac muscles, which are striated, involuntary muscles forming the myocardium.
c. Skin
Answer: Epithelial tissue (Stratified epithelium)
- Explanation: The epidermis of the skin is made of stratified epithelial tissue, which provides protection.
d. Nerve cord
Answer: Nervous tissue
- Explanation: The nerve cord is composed of nervous tissue, consisting of neurons and neuroglial cells for impulse conduction.
e. Inner lining of the buccal cavity
Answer: Epithelial tissue (Ciliated epithelium)
- Explanation: The inner lining of the buccal cavity in some animals (e.g., frogs) contains ciliated epithelial tissue to move materials.
B. Why do animals in cold regions have a layer of fat below their skin?
Answer: Animals in cold regions have a layer of adipose tissue (fat) below their skin because it acts as a good insulator, helping to retain body heat. It also serves as a source of energy and a shock absorber.
C. What enables the ear pinna to be folded and twisted while the nose tip can’t be twisted?
Answer: The ear pinna contains elastic cartilage, which is flexible and allows folding and twisting while maintaining shape. The nose tip contains hyaline cartilage, which is less flexible and more rigid, preventing twisting.
D. Sharad touched a hot plate by mistake and took away his hand quickly. Can you recognize the tissue and its type responsible for it?
Answer: Nervous tissue (Multipolar neurons) and Muscular tissue (Skeletal muscles)
- Explanation: The quick withdrawal of the hand is a reflex action involving nervous tissue (multipolar neurons in the spinal cord and motor neurons) that detect the stimulus and conduct impulses, and skeletal muscles that contract to move the hand.
E. Priya got injured in an accident and hurt her long bone and later on she was also diagnosed with anaemia. What could be the probable reason?
Answer: The injury to Priya’s long bone likely damaged the bone marrow, specifically the red bone marrow in spongy bone, which is responsible for producing red blood cells. This damage could impair red blood cell production, leading to anaemia.
F. Supriya stepped out into the bright street from a cinema theatre. In response, her eye pupil shrunk. Identify the muscle responsible for the same.
Answer: Smooth muscle (Iris muscles)
- Explanation: The shrinking of the pupil is controlled by the smooth muscles in the iris, specifically the sphincter pupillae, which contract involuntarily to reduce pupil size in bright light.
3. Answer the following quetions
A. What is cell junction? Describe different types of cell junctions.
Answer: Cell junctions are junctional complexes that connect epithelial cells laterally to each other and to the basement membrane, facilitating communication, adhesion, and tissue integrity.
Types of cell junctions:
- Tight Junctions (TJs): Maintain cell polarity and prevent lateral diffusion of proteins and ions.
- Gap Junctions (GJs): Allow passage of ions, small molecules, and chemical messages between cells.
- Hemidesmosomes (HDs): Mediated by integrins, they anchor cells to the basement membrane, maintaining tissue homeostasis.
- Desmosomes (Ds): Provide mechanical strength to epithelial tissue, cardiac muscles, and meninges.
- Adherens Junctions (AJs): Involved in signaling pathways and transcriptional regulation.
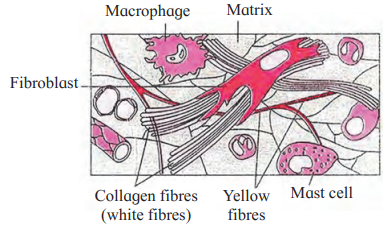
B. With help of neat labelled diagram, describe the structure of areolar connective tissue.
Answer: Areolar connective tissue is a type of loose connective tissue with a semisolid, jelly-like matrix made of gelatin. It contains:
- White fibres (collagen): Provide tensile strength.
- Yellow fibres (elastin): Provide elasticity.
- Cells:
- Fibroblasts: Large, flat cells with branching processes that produce fibres and matrix.
- Mast cells: Oval cells secreting heparin and histamine.
- Macrophages: Amoeboid, phagocytic cells.
- Adipocytes (fat cells): Store fat, with eccentric nuclei.
D. Distinguish between smooth muscles and skeletal muscles.
Answer:
| Feature | Smooth Muscles | Skeletal Muscles |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Walls of visceral organs, blood vessels | Attached to bones |
| Shape | Spindle-shaped, unbranched | Long, cylindrical, syncytial |
| Nucleus | Single, central nucleus | Multiple nuclei, peripheral |
| Striations | Absent (non-striated) | Present (striated) |
| Myofilaments | More actin, less myosin | Equal actin and myosin |
| Contraction | Slow, sustained, involuntary | Quick, strong, voluntary |
| Innervation | Autonomous nervous system | Somatic nervous system |
| Structure | No sarcomeres, simple myofibrils | Sarcomeres with A, I, H, Z bands |
| Example | Intestinal walls, blood vessels | Biceps, quadriceps |
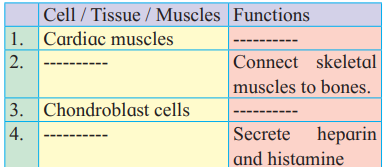
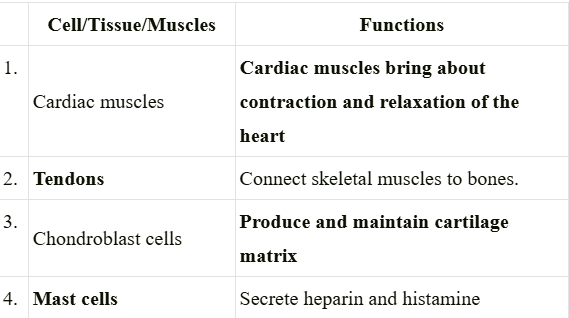
4. Complete the following table
Answer:
5. Match the following and rewrite:
| ‘A’ Group | B’ Group |
| 1. Muscle | (a) Perichondrium |
| 2. Bone | (b) Sarcolemma |
| 3. Nerve cell | (c) Periosteum |
| 4. Cartilage | (d) Neurilemma |
Answer:
| ‘A’ Group | B’ Group |
| 1. Muscle | (c) Periosteum |
| 2. Bone | (a) Perichondrium |
| 3. Nerve cell | (b) Sarcolemma |
| 4. Cartilage | (d) Neurilemma |

Leave a Reply