Human Nutrition – Solutions
1. Choose correct option
A. Acinar cells are present in ………..
a. liver b. pancreas
c. gastric glands d. intestinal glands
Answer: b. pancreas
- Explanation: Acinar cells are part of the exocrine pancreas, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes.
B. Which type of teeth are maximum in number in human buccal cavity?
a. Incisors b. Canines
c. Premolars d. Molars
Answer: d. Molars
- Explanation: In an adult human, there are 12 molars (3 per quadrant), making them the most numerous type of teeth.
C. Select odd one out on the basis of digestive functions of tongue.
a. Taste b. Swallowing
c. Talking d. Mixing of saliva in food
Answer: c. Talking
- Explanation: Taste, swallowing, and mixing of saliva with food are digestive functions of the tongue, while talking is not related to digestion.
D. Complete the analogy: Ptyalin: Amylase : : Pepsin : …………….. .
a. Lipase b. Galactose
c. Proenzyme d. Protease
Answer: d. Protease
- Explanation: Ptyalin is a type of amylase (carbohydrate-digesting enzyme), and pepsin is a type of protease (protein-digesting enzyme).
2. Answer the following questions
A. For the school athletic meet, Shriya was advised to consume either Glucon-D or fruit juice but no sugarcane juice. Why it must be so?
Answer: Sugarcane juice primarily contains sucrose, a complex sugar that requires digestion to be broken down into glucose and fructose, which delays energy release. Glucon-D and fruit juice contain readily absorbable simple sugars (like glucose and fructose) that provide quick energy, essential for athletic performance.
B. Alcoholic people may suffer from liver disorder. Do you agree? Explain your answer.
Answer: Yes, I agree. Alcoholism can cause liver disorders such as steatosis (fatty liver), alcoholic hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Excessive alcohol consumption damages liver cells, impairs bile production, and disrupts metabolic functions, leading to these conditions.
C. Digestive action of pepsin comes to a stop when food reaches small intestine. Justify.
Answer: Pepsin is active in the acidic environment of the stomach (pH 1.8). In the small intestine, bile and pancreatic juices neutralize the acidic chyme, creating an alkaline environment (pH ~7-8). This pH is unsuitable for pepsin activity, causing it to stop functioning.
D. Small intestine is very long and coiled. Even if we jump and run, why it does not get twisted? What can happen if it gets twisted?
Answer: The small intestine is held in place by mesenteries, which are connective tissues that anchor it to the abdominal wall, preventing twisting during movement. If it gets twisted (a condition called volvulus), it can lead to intestinal obstruction, impaired blood flow, severe pain, and potential tissue damage, requiring medical intervention.
3. Write down the explanation
A. Digestive enzymes are secreted at appropriate time in our body. How does it happen?
Answer: Digestive enzyme secretion is regulated by neurohormonal mechanisms. The sight, smell, or thought of food triggers saliva secretion via the nervous system. The vagus nerve (tenth cranial nerve) stimulates gastric juice secretion in the stomach, and gastrin hormone enhances this process. In the small intestine, hormones like secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK), and gastric inhibiting peptide (GIP) regulate the release of bile, pancreatic juice, and intestinal juice. These hormones ensure enzymes are secreted at the right time and place for efficient digestion.
B. Explain the structure of tooth. Explain why human dentition is considered as thecodont, diphyodont, and heterodont.
Answer:
- Structure of Tooth: A tooth consists of a crown (visible part above the gum), a root (embedded in the gum), and a neck (junction between crown and root). The crown is covered by enamel, the hardest substance made of calcium phosphate and carbonate. Dentin, a calcified connective tissue, forms the bulk of the tooth and encloses the pulp cavity, which contains nerves and blood vessels. The pulp cavity extends into the root canal. The root is covered by cementum, anchoring it to the gum socket.
- Thecodont: Each tooth is fixed in a socket in the jawbone by a gomphosis joint, making human dentition thecodont.
- Diphyodont: Humans have two sets of teeth in their lifetime—milk (deciduous) teeth and permanent teeth—hence diphyodont.
- Heterodont: Humans have four types of teeth (incisors, canines, premolars, molars) with different shapes and functions, making dentition heterodont.
C. Explain heterocrine nature of pancreas with the help of histological structure.
Answer: The pancreas is a heterocrine gland with both exocrine and endocrine functions.
- Exocrine Part: Composed of acinar cells that secrete pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes (e.g., amylase, lipase, trypsinogen) into the duodenum via the pancreatic duct.
- Endocrine Part: Consists of islets of Langerhans, which include α-cells (secrete glucagon), β-cells (secrete insulin), and δ-cells (secrete somatostatin). These hormones are released into the bloodstream to regulate blood sugar and other metabolic processes.
- Histological Structure: The pancreas has acini (exocrine) and islets of Langerhans (endocrine) interspersed. Acinar cells form clusters around ducts, while islets are scattered between acini, containing hormone-secreting cells. This dual structure supports its heterocrine nature.
4. Write short note on
A. Position and function of salivary glands.
Answer:
- Position: There are three pairs of salivary glands: parotid (in front of the ear), submandibular (below the lower jaw), and sublingual (below the tongue). They open into the buccal cavity.
- Function: Salivary glands secrete saliva, which contains water (98%), electrolytes, mucus, and salivary amylase. Saliva moistens food, aids in bolus formation, and initiates starch digestion (amylase converts starch to maltose). Mucus lubricates food for swallowing, and lysozyme in saliva acts as an antibacterial agent.
B. Jaundice
Answer: Jaundice is a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin, conjunctiva, and whitish stool due to abnormal bilirubin metabolism. It occurs due to excessive red blood cell breakdown, elevated bilirubin levels beyond the liver’s processing capacity, or bile flow obstruction. Bilirubin, derived from hemoglobin breakdown, can be water-soluble or fat-soluble (toxic to the brain). Symptoms include yellowing and fatigue. There is no specific treatment; supportive care and rest are provided. Jaundice indicates underlying liver or bile duct issues, and serum bilirubin levels aid diagnosis.
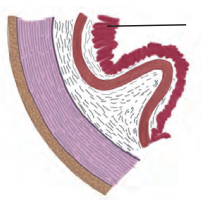
5. Observe the diagram. This is histological structure of stomach. Identify and comment on significance of the layer marked by arrow
Answer: The layer marked in the diagram represents glandular epithelium of mucosa.
Significance of the glandular epithelium of mucosa:
Goblet cells of the epithelial layer of a mucous membrane secrete mucus which lubricates the lumen of the alimentary canal. This helps in movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract.
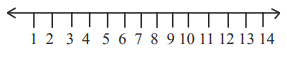
6. Find out pH maxima for salivary amylase, trypsin, nucleotidase and pepsin and place on the given pH scale
Answer:
Salivary amylase = 6.8
Trypsin = 8
Nucleotidase = 7.5
Pepsin = 2
7. Write the name of a protein deficiency disorder and write symptoms of it.
Answer: Protein Deficiency Disorder: Kwashiorkor
Symptoms:
- Underweight and stunted growth
- Poor brain development
- Loss of appetite
- Anaemia
- Protruding belly
- Slender legs
- Bulging eyes
- Oedema of lower legs and face
- Change in skin and hair colour
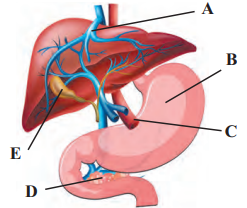
8. Observe the diagram given below label the A, B, C, D, E and write the function of A, C in detail.
Answer: A- Bile duct, B- Stomach, C- Common hepatic duct, D- Pancreas, E- Gall Bladder
Functions of A- Bile duct and C- Common hepatic duct:
Bile duct:
- It carries bile from the gall bladder and empties it into the upper part of the small intestine.
Common hepatic duct:
- It drains bile from the liver. It helps in transportation of waste from liver and helps in digestion by releasing bile.

Leave a Reply