Systematics of Living Organisms
Solutions
1. Choose correct option
A. Which of the following shows single stranded RNA and lacks protein coat?
a. Bacteriophage b. Plant virus
c. Viroid d. Animal virus
Answer: c. Viroid
- Explanation: Viroids are infectious agents consisting of single-stranded RNA without a protein coat.
B. Causative agent of red tide is _____________.
a. Dinoflagellate b. Euglenoid
c. Chrysophyte d. Lichen
Answer: a. Dinoflagellate
- Explanation: The document mentions Gonyaulax, a dinoflagellate, (Kingdom Protista, Dinoflagellates).
C. Select odd one out for Heterotrophic bacteria.
a. Nitrogen fixing bacteria
b. Lactobacilli
c. Methanogens
d. Cyanobacteria
Answer: d. Cyanobacteria
- Explanation: Cyanobacteria are primarily autotrophic (photosynthetic), while the others (nitrogen-fixing bacteria, lactobacilli, methanogens) are heterotrophic or have heterotrophic modes, (Kingdom Monera).
D. Paramoecium : Ciliated Protist Plasmodium : ____________
a. Amoeboid protozoan b. Ciliophora
c. Flagellate protozoan d. Sporozoan
Answer: d. Sporozoan
- Explanation: The document states that Plasmodium is a sporozoan protozoan (Kingdom Protista, Animal-like Protists).
2. Answer the following
A. What are the salient features of monera?
Answer: The salient features of Monera, are:
- Unicellular organisms with prokaryotic cellular organization.
- Omnipresent, found in diverse environments, including extreme conditions.
- Nutritionally, they can be photoautotrophs, chemoautotrophs, or heterotrophs (mostly heterotrophic).
- Lack a well-defined nucleus; DNA is present as a nucleoid (circular, double-stranded).
May have plasmids (extra-chromosomal DNA). - Cell wall is made of peptidoglycan (murein), except in Archaebacteria.
- Lack membrane-bound organelles (e.g., mitochondria, chloroplasts).
- Ribosomes are smaller (70S).
- Reproduce asexually by binary fission or budding; rarely sexually by conjugation.
- Morphologically categorized as coccus, bacillus, vibrio, or spirillum.
B. What will be the shape of bacillus and coccus type of bacteria?
Answer:
- Bacillus: Rod-shaped.
- Coccus: Spherical.
C. Why is binomial nomenclature important?
Answer: Binomial nomenclature is:
- It provides a universal, systematic, and standardized naming system for organisms, facilitating international communication.
- It overcomes the limitations of vernacular/common names, which vary by region and language, causing confusion.
- It consists of two parts (genus and species epithet), ensuring specificity and clarity.
- It follows rules set by the International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (ICNAFP), ensuring consistency.
- It often includes the author’s name, providing credit and historical context.
3. Write short notes
A. Useful and harmful bacteria.
Answer: Useful Bacteria:
- Decomposers: Heterotrophic bacteria break down large molecules into simpler ones, aiding nutrient recycling .
- Nitrogen Fixation: Bacteria like Azotobacter fix nitrogen, enriching soil fertility.
- Industrial Uses: Lactobacilli help in milk curdling (e.g., yogurt production). Streptomyces produces antibiotics.
- Biogas Production: Methanogenic bacteria produce methane in biogas plants.
- Oil Degradation: Some bacteria assist in composting and degrading oil spills.
Harmful Bacteria:
- Pathogens: Cause diseases like typhoid, cholera, tuberculosis, and tetanus in humans.
- Mycoplasma: Lacks a cell wall, is pathogenic, and is resistant to common antibiotics.
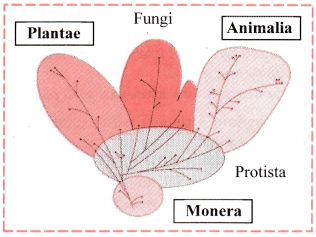
B. Five Kingdom system
Answer: The Five Kingdom system, proposed by R.H. Whittaker in 1969, classifies organisms based on phylogenetic relationships into:
- Monera: Unicellular, prokaryotic organisms (e.g., bacteria, cyanobacteria). Lack a defined nucleus, have peptidoglycan cell walls (except Archaebacteria).
- Protista: Unicellular, eukaryotic organisms (e.g., diatoms, amoeba). Show plant-like (chrysophytes), animal-like (protozoans), or fungi-like (myxomycetes) traits.
- Plantae: Multicellular, autotrophic eukaryotes with chlorophyll and cellulosic cell walls (e.g., plants, some insectivorous like Venus flytrap).
- Fungi: Eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms with chitinous cell walls (e.g., mushrooms, yeast). Reproduce sexually or asexually.
- Animalia: Multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with holozoic nutrition, no cell wall, and determinate growth (e.g., animals).
- This system improves upon Linnaeus’s two-kingdom classification by accommodating organisms like bacteria and fungi that don’t fit neatly into Plantae or Animalia.
C. Useful Fungi
Answer:
- Food: Mushrooms (Agaricus) are consumed as food, and morels/truffles are delicacies.
- Industrial Uses: Saccharomyces (yeast) is used in bakery (bread) and breweries (alcohol production).
- Medicinal Uses: Penicillium produces antibiotics (e.g., penicillin). Neurospora is used in genetic and biochemical research.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Fungi form lichens with algae, aiding in soil formation, and mycorrhiza with plant roots, enhancing nutrient absorption.
- Decomposition: Saprophytic fungi break down organic matter, recycling nutrients.
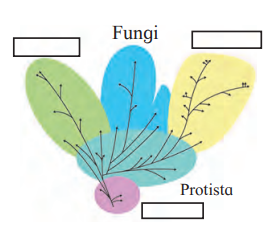
4. Complete tree diagram in detail
Answer:
5. Draw neat labelled diagrams
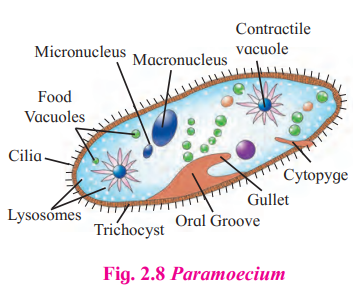
A. Paramoecium
Answer:
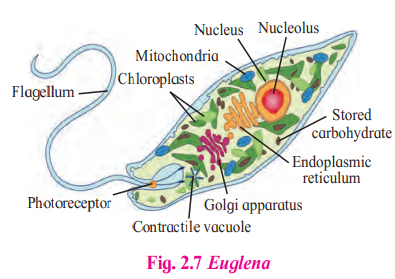
B. Euglena
Answer:
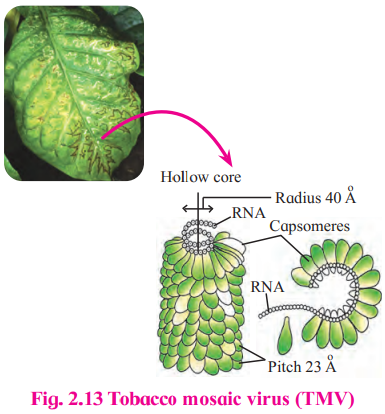
C. TMV
Answer:
6. Complete chart and explain in your words
Answer:
7. Identify the following diagrams, label them and write detail information in your word
A
Answer:
- Euglena is the given organism.
- It’s a Protista with flagellated flagella. It is a member of the Euglenoids group.
- Euglenoids are heterotrophic flagellates that can also function as autotrophs.
- It has two flagella, one of which is short and the other of which is long.
- Due to the presence of photoreceptors and photosynthetic pigments, it can perform photosynthesis in the presence of light.
B
Answer:
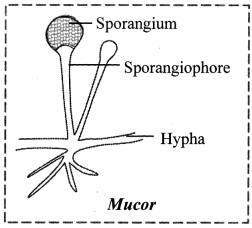
- Mucor is a fungus that belongs to the Kingdom Fungi and the class Phycomycetes.
- They are decomposers and thus thrive in damp, moist environments on decaying organic matter.
- The body is made up of horizontally spreading hyphae.
- Sporangiophore with sporangium at their tips can be seen on the hyphae.
- They release spores, which aid in the asexual reproductive process.
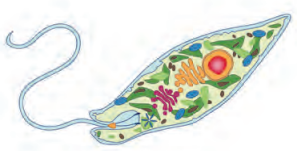
C
Answer:
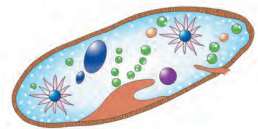
- Paramoecium is the organism shown.
- It is a member of the Kingdom Protista. It is a Protista that looks like an animal. Because cilia are used for locomotion, hence referred to as ciliate protozoans.
- On the cell surface, there is a gullet that opens.
- There are two nuclei present, one larger called the macronucleus and one smaller called the micronucleus.
- Osmoregulation is helped by the presence of large contractile vacuoles.
D
Answer:
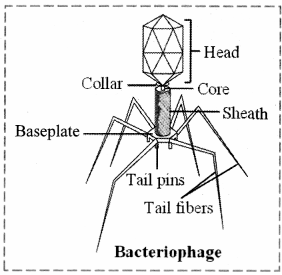
- Bacteriophage is a kind of bacteriophage. It’s an acellular organism that doesn’t belong to any of the kingdoms.
- This is a bacterial cell-infecting virus.
- They have a genetic material core that is wrapped by a protein shell called a capsid.
- The structure is made up of a head, a core, and a basal plate with tail fibres.
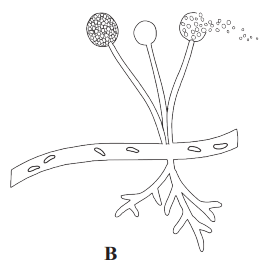
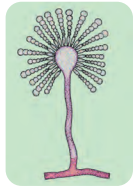
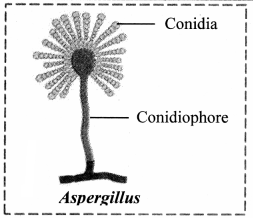
E
Answer:
- It belongs to class ascomycetes of the kingdom Fungi.
- It is multicellular.
- The hyphae are branched and septate.
- Aspergillus grows well in soil, decaying vegetation, hay, dung, on plants, etc.
- Asexual reproduction takes place by spores called conidia which are produced at the tip of hyphae called conidiophores.
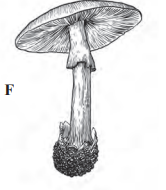
F
Answer:
- It belongs to class basidiomycetes of the kingdom Fungi.
- It has branched septate hyphae.
- It grows in soil, on rotten wood, etc.
- It is edible and rich in proteins.
- Vegetative reproduction takes place by fragmentation.
8. The scientific name of sunflower is given below. Identify the correctly written name.
A. Helianthus annuus L.
B. Helianthus Annuus l.
Answer: The correctly written scientific name of sunflower is Helianthus annuus L.
9. Match the following.
| Kingdom | Example |
| i. Monera | a. Riccia |
| ii. Protista | b. Cyanobacteria |
| iii. Plantae | c. Rhizopus |
| iv. Fungi | d. Diatoms |
Answer:
| Kingdom | Examples |
| 1. Monera | b. Cyanobacteria |
| 2. Protista | d. Diatoms |
| 3. Plantae | a. Riccia |
| 4. Fungi | c. Rhizopus |
10. Complete the following
A. Plant-like Protista – Diatoms
B. Animal like Protista – Entamoeba



Leave a Reply