Kingdom Animalia – Solutions
1. Choose correct option
A. Which of the following belongs to a minor phylum?
a. Comb jelly b. Jelly fish
c. Herdmania d. Salpa
Answer: a. Comb jelly
- Explanation: Comb jellies belong to the Phylum Ctenophora, which is considered a minor phylum due to its limited number of species.
B. Select the animal having venous heart.
a. Crocodile b. Salamander
c. Rohu d. Toad
Answer: c. Rohu
- Explanation: Pisces (fishes like Rohu) have a venous heart, which contains deoxygenated blood.
C. In Ascaris, __________________.
a. mesoglea is present
b. endoderm is a discontinuous layer
c. mesoderm is present in patches
d. body cavity is absent
Answer: c. mesoderm is present in patches
- Explanation: Ascaris is pseudocoelomate, meaning the body cavity is not fully lined by mesoderm, and the mesoderm is present in patches.
D. Which of the following is incorrect in case of birds?
a. Presence of teeth
b. Presence of scales
c. Nucleated RBCs
d. Hollow bones
Answer: a. Presence of teeth
- Explanation: Birds have jaws modified into beaks without teeth, making the presence of teeth incorrect.
E. Chitinous exoskeleton is a characteristic of ___________.
a. Dentalium b. Antedon
c. Millipede d. Sea urchin
Answer: c. Millipede
- Explanation: Phylum Arthropoda (which includes millipedes) has a chitinous exoskeleton.
2. Answer the following questions
A. Reptiles are known for having three chambered heart. Which animal shows a near four chambered condition in reptiles?
Answer: Crocodile
- Explanation: Reptiles generally have a three-chambered heart, but crocodiles have an incompletely partitioned ventricle, making it a near four-chambered condition.
B. The circulatory system has evolved from open to closed type in Animal kingdom. Which Phylum can be called first to represents closed circulation?
Answer: Annelida
- Explanation: Phylum Annelida has a closed circulatory system, which is the first phylum to exhibit this feature in the animal kingdom.
C. Pinna is part of external ear and it is found in mammals. Do aves and reptiles show external ear in any form?
Answer: No, aves and reptiles do not show an external ear (pinna) in any form.
- Explanation: Mammals have an external ear (pinna), but aves and reptiles lack this structure. Aves have a tympanum representing the ear, and reptiles also have a tympanum but no external ear.
D. Fish and frog can respire in water. Can they respire through their skin? If yes, why do they have gills?
Answer: Yes, both fish and frogs can respire through their skin. Frogs have moist skin that allows cutaneous respiration, and some fish can also use their skin for gas exchange. However, they have gills because gills are more efficient for extracting oxygen from water, especially in aquatic environments where oxygen levels are lower than in air.
E. Birds need to keep their body light to help in flying. Hence, they show presence of some organs only on one side. How their skeleton helps in reducing their weight?
Answer: Birds have hollow (pneumatic) bones with air cavities, which significantly reduce their body weight, aiding in flight.
F. Cnidarians and Ctenophorans are both diploblastic. Which other character do they have in common, which is not found in other Phyla?
Answer: Both Cnidarians and Ctenophorans exhibit a blind-sac body plan.
G. Crab and Snail both have a protective covering. Is it made up of the same material?
Answer: No, the protective covering of crabs and snails is not made of the same material. Crabs (Arthropoda) have a chitinous exoskeleton, while snails (Mollusca) have a calcareous shell.
H. Sponge and sea star show calcareous protective material. Do they belong to the same Phylum?
Answer: No, sponges and sea stars do not belong to the same phylum. Sponges belong to Phylum Porifera, and sea stars belong to Phylum Echinodermata.
I. Fish and snake both have scales. How do these scales differ from each other?
Answer: Fish scales are dermal (bony or cartilaginous, e.g., placoid in Chondrichthyes, cycloid/ctenoid in Osteichthyes), originating from the skin’s dermal layer. Snake scales are epidermal, made of keratin, and are shed periodically.
J. Lower Phyla like Arthropods and Cnidarians show metamorphosis. Is it also found in any class of Phylum Chordata?
Answer: Yes, metamorphosis is found in the class Amphibia of Phylum Chordata.
3. Draw neat labelled diagram
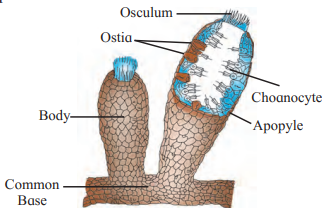
A. Sycon
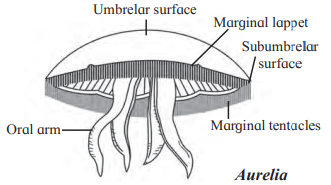
B. Aurelia
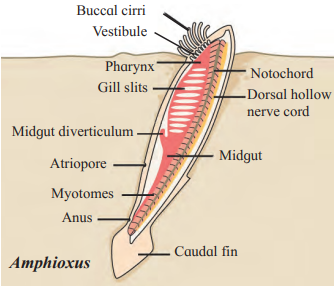
C. Amphioxus
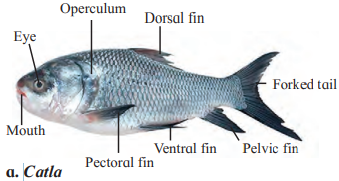
D. Catla
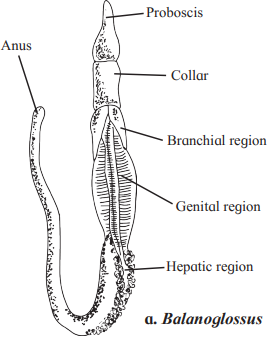
E. Balanoglossus
F. Scolidon
4. Match the following
| Phylum | Characters |
| i. Annelida | a. Tube feet |
| ii. Mollusca | b. Ostia |
| iii. Ctenophora | c. Radula |
| iv. Porifera | d. Parapodia |
| v. Echinodermata | e. Comb plates |
Answer:
| Phylum | Characters |
| 1. Annelida | (d) Parapodia |
| 2. Mollusca | (c) Radula |
| 3. Ctenophora | (e) Comb plates |
| 4. Porifera | (b) Ostia |
| 5. Echinodermata | (a) Tube feet |
5. Identify the animals given in pictures and write features of its phylum / class.
Answer: The given animal is Tomopteris. It belongs to the phylum Annelida.
For features of Annelida,
- Animals belonging to the phylum Annelida are worms with annuli or rings.
- They are bilaterally symmetrical true coelomates showing metamerically segmented soft, elongated and cylindrical body.
- Digestive system is complete with a mouth and anus at opposite ends of the body.
- Locomotory organs are setae, parapodia, or suckers. They have well-developed layers of circular and longitudinal muscles which help in the movement of the body.
Answer: The organism in the given picture is Eel and it belongs to the phylum Chordata.
Features of phylum Chordata:
- Notochord present at least in early embryonic life.
- Nerve cord is single, dorsal and non-ganglionated.
- The heart is ventral in position.
- Pharyngeal gill slits are present at least in the embryonic stage.
- Post-anal tail is present at least in the embryonic stage.
Answer: The given organism in the given picture is Dolphin and it belongs to class Mammalia.
Features of class Mammalia:
- Special feature: Presence of mammary glands (milk-producing glands) for the nourishment of young ones. Mammary glands are modified sweat glands.
- Habitat: Mammals are omnipresent (present everywhere). These are mostly terrestrial, some are aquatic and a few are aerial and arboreal (living on trees).
- Locomotion: Limbs are the organs of locomotion and are modified for walking, climbing, burrowing, swimming, etc.
- Body division: Body is differentiated into head, neck, trunk, and tail. They have an external ear (pinna).
- Body temperature: Mammals are homeotherms or warm-blooded animals.
Answer: The given organism is Snake and it belongs to class Reptilia.
Features of class Reptilia:
- Habitat: They are crawling animals. They are the first true terrestrial vertebrates. Few may be aquatic or semi-aquatic and are also found in marshy areas.
- Locomotion: Locomotion occurs by limbs in most animals. The limbs are pentadactyl with clawed digits, which help the animal to walk, creep or crawl. Snakes are limbless and crawl on their belly.
- Body temperature: They are poikilotherms.
- Exoskeleton: Skin is dry, non-glandular and covered by an exoskeleton of epidermal scales or scutes, shields or plates. Lizards and snake shed their skin periodically.
Answer: The given organism is Sea urchin and belongs to the phylum Echinodermata.
Features of Phylum Echinodermata:
- Habitat: These are exclusively marine.
- Forms: Members of this phylum are solitary, sedentary or free-living and gregarious, benthic.
- Body symmetry: These animals are radially symmetrical with pentamerous symmetry.
- Shape: Members of Echinodermata are spherical, elongated or star-shaped.
Answer: The given organism is a flying lizard and belongs to class Reptilia.
Features of class Reptilia:
- Habitat: They are crawling animals. They are the first true terrestrial vertebrates. Few may be aquatic or semi-aquatic and are also found in marshy areas.
- Locomotion: Locomotion occurs by limbs in most animals. The limbs are pentadactyl with clawed digits, which help the animal to walk, creep or crawl. Snakes are limbless and crawl on their belly.
- Body temperature: They are poikilotherms.
- Ear: Tympanum is present
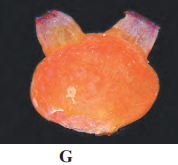
Answer: The organism is Herdmania and belongs to Phylum Chordata (Subphylum Urochordata).
Features of Phylum Chordata (Subphylum Urochordata):
- Habitat: They are exclusively marine.
- Body covering: Soft body is covered by ‘test’ or ‘tunic’ which is made up of tunicate.
- Notochord: Notochord is present only in the tail of the larva and is lost during metamorphosis. Hence, the name Urochordata.
- Respiration: Pharynx with many gill slits for respiration.
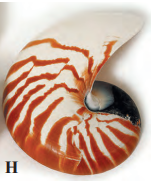
Answer: The organism in the given picture is Nautilus and it belongs to phylum Mollusca.
Features of phylum Mollusca:
- Habitat: They are aquatic or seen in marshy places. Few of them are terrestrial.
- Forms: Molluscs are either free-living or sedentary.
- Body plan: These are soft-bodied and show tube within a tube type of body plan.
- Body symmetry: Most of the Molluscs show bilateral symmetry but few are asymmetrical due to torsion (twisting).
Answer: The organism in the given picture is Amphioxus and it belongs to Phylum Chordata (Subphylum Cephalochordata).
Features of Phylum Chordata (Subphylum Cephalochordata):
- Notochord present at least in early embryonic life.
- Nerve cord is single, dorsal and non-ganglionated.
- The heart is ventral in position.
- Pharyngeal gill slits are present at least in the embryonic stage.
- The post-anal tail is present at least in the embryonic stage.
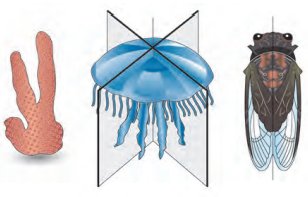
6. Observe and identify body symmetry of given animals
Answer:
i. represents asymmetry
ii. represents radial symmetry
iii. represents bilateral symmetry









Leave a Reply