Biomolecules – Solutions
1. Choose correct option
A. Sugar, amino acids and nucleotides unite to their respective subunits to form——–
a. bioelements b. micromolecules
c. macromolecules d. each of these
Answer: c. macromolecules
- Explanation: (Sugar, amino acids, and nucleotides form polysaccharides, polypeptides, and polynucleotides, respectively, which are macromolecules.)
B. Glycosidic bond is found in —————.
a. Disaccharide b. Nucleosides
c. Polysaccharide d. each of these
Answer: d. each of these
- Explanation: (Glycosidic bonds are found in disaccharides, polysaccharides, and nucleosides.)
C. Amino acids in a polypeptide are joined by —————bond.
a. Disulphide b. glycosidic
c. hydrogen bond d. none of these
Answer: d. none of these
- Explanation: (Amino acids in a polypeptide are joined by peptide bonds.)
D. Lipids associated with cell membrane are ————.
a. Spingomyelin b. Isoprenoids
c. Phospolipids d. Cholesterol
Answer: c. Phospholipids
- Explanation: (Phospholipids are the primary lipids associated with cell membranes.)
E. Linoleic, Linolenic and ——————– acids are referred as essential fatty acids since they cannot be synthesized by the body and hence must be included in daily diet.
a. Arachidonic b. Oleic
c. Stearic d. Palmitic
Answer: a. Arachidonic
- Explanation: (Linoleic, linolenic, and arachidonic acids are essential fatty acids.)
F. Haemoglobin is a type of ————– protein, which plays indispensible part in respiration.
a. simple b. derived
c. conjugated d. complex
Answer: c. conjugated
- Explanation: (Haemoglobin is a conjugated protein with a haem prosthetic group.)
G. When inorganic ions or metallo-organic molecules bind to apoenzyme, they together form——
a. isoenzyme b. holoenzyme
c. denatured enzyme d. none of these
Answer: b. holoenzyme
- Explanation: (Inorganic ions or metallo-organic molecules bind to apoenzyme to form holoenzyme.)
H. In enzyme kinetics, Km= Vmax/2. If Km value is lower, it indicates —————-
a. Enzyme has less affinity for substrate
b. Enzyme has higher affinity towards substrate
c. There will be no product formation
d. All active sites of enzyme are saturated.
Answer: b. Enzyme has higher affinity towards substrate
- Explanation: (A lower Km value indicates higher enzyme-substrate affinity.)
2. Solve the following questions:
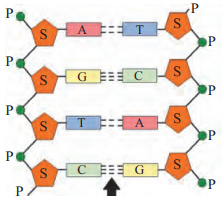
A. Observe the following figure and name nthe type of bond shown by arrow in the structure.
Answer: The hydrogen bond is indicated by the arrow. Phosphodiester bond between sugar and phosphate molecule and N-glycosidic link between nitrogenous base and sugar molecule are the other bonds seen in the structure.
3. Answer the following questions
A. What are building blocks of life?
Answer: Monosaccharides, amino acids, nucleotides, fatty acids, and glycerol are the basic units forming carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids.
B. Explain the peptide bond.
Answer: A covalent bond formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, linking amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
C. How many types of polysaccharides you know?
Answer: Two types – Homopolysaccharides (e.g., starch, cellulose, glycogen) and heteropolysaccharides (e.g., hyaluronic acid, heparin).
D. Enlist the significance of carbohydrates.
Answer: Provide energy (glucose for ATP synthesis), structural components (cellulose in cell walls), and storage (starch, glycogen).
E. What is a reducing sugar?
Answer: A sugar with a free aldehyde or ketone group that can reduce other compounds, e.g., glucose, maltose.
F. What is the basic difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid?
Answer:
| Saturated fats | Unsaturated fats | |
| 1. | They contain single chain of carbon atoms with single bonds. | They contain chain of carbon atoms with one or more double bonds. |
| 2. | They are solid at room temperature. | They are liquid at room temperature |
| 3. | They increase blood cholesterol level by depositing it in the inner wall of the arteries. | They lower the blood cholesterol level and have many health benefits. |
| 4. | They do not get spoiled. | They get spoiled easily. |
| 5. | Saturated fats are obtained from animal fats, palm oil, etc. | Unsaturated fatty acids are obtained from plant and vegetable oil, etc. |
G. Enlist the examples of simple proteins and give their significance.
Answer: Examples of simple proteins are: E.g.: Albumins and histones.
Significance:
Albumin:
a. It is the main protein in the blood.
b. It maintains the pressure in the blood vessels.
c. It helps in the transportation of substances like hormone and drugs in the body.
Histones:
a. It is the chief protein of chromatin.
b. They are involved in the packaging of DNA into structural units called nucleosomes.
H. Explain the secondary structure of protein with examples.
Answer:
- There are two types of the secondary structures of protein: α-helix and β-pleated sheets.
- The polypeptide chain is arranged in a spiral helix. These spiral helices are of two types: α-helix (right-handed) and β-helix (left-handed).
- This spiral configuration is held together by hydrogen bonds.
- The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain determines the location of its bend or fold and the position of formation of hydrogen bonds between different portions of the chain or between different chains. Thus, peptide chains form an α-helix structure.
- Example of α-helix structure is keratin.
- In some proteins two or more peptide chains are linked together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Such structures are called β-pleated sheets.
- Example of a β-pleated sheet is silk fibres.
- Due to the formation of hydrogen bonds peptide chains assume a secondary structure.
I. Explain the induced fit model for mode of enzyme action.
Answer: The induced fit model shows that enzymes are flexible structures in which the active site continually reshapes by its interactions with the substrate until the time the substrate is completely bound to it. It is also the point at which the final form and shape of the enzyme are determined.
J. What is RNA? Enlist types of RNA.
Answer:
- RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid. It is a long single-stranded polynucleotide chain that helps in protein synthesis, functions as a messenger and translates messages coded in DNA into protein.
- There are three types of RNA:
mRNA (messenger RNA), rRNA (ribosomal RNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA).
K. Describe the concept of metabolic pool.
Answer: A reservoir of biomolecules in the cell, acted upon by enzymes to produce needed products, allowing interconversion (e.g., carbohydrates to fats).
L. How do secondary metabolites are useful for mankind?
Answer:
- Drugs developed from secondary metabolites have been used to treat infectious diseases, cancer, hypertension, and inflammation.
- Morphine, the first alkaloid isolated from Papaver somniferum is used as a pain reliver and cough suppressant.
- Secondary metabolites like alkaloids, nicotine, cocaine and the terpenes, cannabinol are widely used for recreation and stimulation.
- Flavours of secondary metabolites improve our food preferences.
- Tannins are added to wines and chocolate for improving astringency.
4. Solve the following questions:
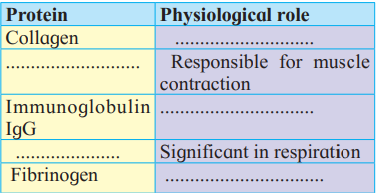
A. Complete the following chart.
Answer:
| Protein | Physiological role |
| Collagen | Provides strength and plays a structural role |
| Myosin & Actin | Responsible for muscle contraction |
| Immunoglobulin IgG | Protects the body from infection |
| Haemoglobin | Significant in respiration |
| Fibrinogen | Responsible for normal clotting of blood. |
B. Answer the questions with reference to the following figure.
i. Name the type of bond formed between two polypeptides.
ii. Which amino acid is involved in the formation of such bond?
iii. Amongst I, II, III and IV structural levels of protein, which level of structure includes such bond?
Answer:
i. Disulfide bond
ii. Cysteine
iii. Tertiary structure.
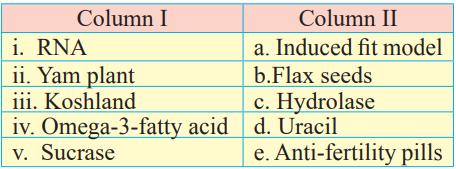
C. Match the following items given in column I and II.
Answer:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | RNA | d. | Uracil |
| ii. | Yam plant | e. | Anti-fertility pills |
| iii. | Koshland | a. | Induced fit model |
| iv. | Omega-3-fatty acid | b. | Flax seeds |
| v. | Sucrase | c. | Hydrolase |
5. Long answer questions
A. What are biomolecules? Explain the building blocks of life.
Answer: Biomolecules are organic molecules essential for life, including carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Building blocks: monosaccharides (e.g., glucose), amino acids (e.g., glycine), nucleotides (e.g., adenine), fatty acids, and glycerol.
B. Explain the classes of carbohydrates with examples.
Answer: Classes of Carbohydrates:
- Monosaccharides: Simple sugars, e.g., glucose, fructose.
- Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides, e.g., sucrose (glucose + fructose).
- Polysaccharides: Polymers, e.g., starch (storage), cellulose (structural).
C. Describe the types of lipids and mention their biological significance.
Answer: Types of Lipids and Significance:
- Simple lipids: Fats, waxes (energy storage, insulation).
- Compound lipids: Phospholipids, glycolipids (membrane structure).
- Derived lipids: Sterols, e.g., cholesterol (hormone synthesis).
- Significance: Energy reserve, membrane formation, hormone production.
D. Explain the chemical nature, structure and role of phospholipids in biological membrane.
Answer: Composed of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group with a nitrogenous compound. They form a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails, creating a lipid bilayer in cell membranes, regulating substance passage.
E. Describe classes of proteins with their importance.
- Simple: Yield only amino acids, e.g., albumin (transport).
- Conjugated: Contain non-protein groups, e.g., haemoglobin (oxygen transport).
- Derived: Formed by hydrolysis, e.g., peptones.
- Importance: Structural support, catalysis, transport, immunity.
F. What are enzymes? How are they classified? Mention example of each class.
Answer: Enzymes are protein catalysts. Classes:
- Oxidoreductases: e.g., alcohol dehydrogenase.
- Transferases: e.g., glucokinase.
- Hydrolases: e.g., sucrase.
- Lyases: e.g., histidine decarboxylase.
- Isomerases: e.g., xylose isomerase.
- Ligases: e.g., pyruvate carboxylase.
G. Explain the properties of enzymes.
Answer: Proteinaceous, specific 3D conformation, catalytic (unchanged post-reaction), substrate-specific, sensitive to temperature and pH with optimal conditions.
H. Describe the factors affecting enzyme action.
Answer: Factors Affecting Enzyme Action:
- Substrate concentration: Increases rate until saturation.
- Enzyme concentration: Proportional to reaction rate.
- Temperature: Optimal at 37°C, denatures above 40°C.
- pH: Specific optimum, e.g., pepsin at pH 2.
- Other substances: Co-enzymes/activators enhance, inhibitors retard.
I. What are nucleic acids? Enlist the point of differences among DNA and RNA.
Answer: Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of many small units or monomers called nucleotides.
DNA:
- It is the genetic material of the majority of the organisms.
- It is double-stranded.
- Deoxyribose sugar is present.
- Nitrogen bases like Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine are present.
- Specific base pairing is observed.
- Total number of purines is equal to the total number of pyrimidine. Thus, the purine to pyrimidine ratio is 1:1.
- It is present in the nucleus.
- It is responsible for determining hereditary characters and for formation of RNA.
RNA:
- It is a genetic material only of some viruses.
- It is single-stranded.
- Ribose sugar is present.
- Nitrogen bases like Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil are present.
- Nitrogen bases do not form pairs.
- The amount of purine and pyrimidine may or may not be equal.
- It is present in the nucleus and cytoplasm.
- It takes part in protein synthesis.
J. What are the types of RNA? Mention the role of each class of RNA.
Answer: There are three types of cellular RNAs:
- messenger RNA (mRNA),
- ribosomal RNA (rRNA),
- transfer RNA (tRNA).
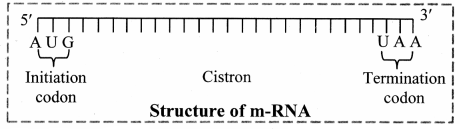
1. Messenger RNA (mRNA):
a. It is a linear polynucleotide.
b. It accounts 3% of cellular RNA.
c. Its molecular weight is several million. , d. mRNA molecule carrying information to form a complete polypeptide chain is called cistron.
e. Size of mRNA is related to the size of message it contains.
f. Synthesis of mRNA begins at 5’ end of DNA strand and terminates at 3’ end.
Role of messenger RNA:
It carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, which are the sites of protein synthesis.
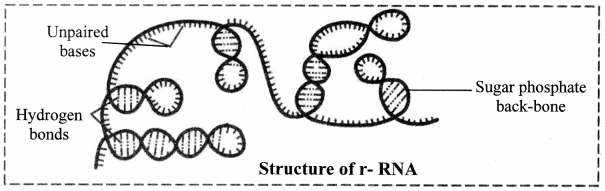
2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA):
a. rRNA was discovered by Kurland in 1960.
b. It forms 50-60% part of ribosomes.
c. It accounts 80-90% of the cellular RNA.
d. It is synthesized in nucleus.
e. It gets coiled at various places due to intrachain complementary base pairing.
Role of ribosomal RNA: It provides proper binding site for m-RNA during protein synthesis.
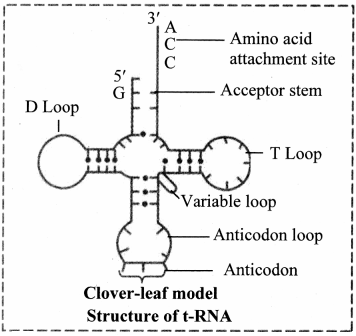
3. Transfer RNA (tRNA):
a. These molecules are much smaller consisting of 70-80 nucleotides.
b. Due to presence of complementary base pairing at various places, it is shaped like clover-leaf.
c. Each tRNA can pick up particular amino acid.
d. Following four parts can be recognized on tRNA
1. DHU arm (Dihydroxyuracil loop/ amino acid recognition site
2. Amino acid binding site
3. Anticodon loop / codon recognition site
4. Ribosome recognition site.
e. In the anticodon loop of tRNA, three unpaired nucleotides are present called as anticodon which pair with codon present on mRNA.
f. The specific amino acids are attached at the 3′ end in acceptor stem of clover leaf of tRNA.
Role of transfer RNA: It helps in elongation of polypeptide chain during the process called translation.
K. What is metabolism? How metabolic pool is formed in the cell.
Answer:
- Metabolism is the sum of the chemical reactions that take place within each cell of a living organism and provide energy for vital processes and for synthesizing new’ organic material.
- Metabolic pool in the cell is formed due to glycolysis and Krebs cycle.
- The catabolic chemical reaction of glycolysis and Krebs cycle provides ATP and biomolecules. These biomolecules form the metabolic pool of the cell.
- These biomolecules can be utilized for synthesis of many important cellular components.
The metabolites can be added or withdrawn from the pool according to the need of the cell.
6. If double stranded DNA has 14% C (cytosine) what is percentage of A (adenine), T(thymine) and G (gaunine) would you expect?
Answer: A purine always pairs with pyrimidine.
Adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine.
Therefore, as per the given data If cytosine = 14% then guanine = 14%.
According to Chargaff s rule,
(C+G) = 14+ 14 = 28%
Therefore, (A+T) = 72%
So, A= 36%, T= 36%, G = 14%.
7. Name
i. The term that describes all the chemical reactions taking place in an organism.
Answer: Metabolism: All chemical reactions in an organism.
ii. The form in which carbohydrate is transported in a plant.
Answer: Sucrose: Form in which carbohydrate is transported in plants.
iii. The reagent used for testing of reducing sugar.
Answer: Benedict’s reagent: Reagent used for testing reducing sugars.


Leave a Reply