Morphology of Flowering Plants
1. Choose correct option
A. Which one of the following will grow better in moist and shady region?
a. Opuntia
b. Orchid
c. Mangrove
d. Lotus
Answer: (b) Orchid
B. A particular plant had a pair of leaves at each node arranged in one plane. What is the arrangement called?
a. Alternate phyllotaxy
b. Decussate phyllotaxy
c. Superposed phyllotaxy
d. Whorled phyllotaxy
Answer: (c) Superposed phyllotaxy
C. In a particular flower the insertion of floral whorls was in such a manner, so the ovary was below the level other three whorls, but its stigma was taller than other three whorls. What will you call such flower?
a. Hypogynous
b. Perigynous
c. epigynous
d. Half superior – half inferior
Answer: (c) Inferior ovary
D. Beet and Arum both store food for perennation. Do these examples represent two different types?
a. Beet is a stem but Arum is a root
b. Beet is a root but Arum is a stem
c. Beet is a stem but Arum is a leaf
d. Beet is a stem but Arum is an inflorescence
Answer: (b) Beet is a root but Arum is a stem
2. Answer the following questions
A. Two of the vegetables we consume are nnothing but leaf bases. Which are they?
Answer: Onion, Garlic
B. Opuntia has spines but Carissa has thorns. What is the difference?
Answer:
- In Opuntia, stem is modified into leaf like photosynthetic organ known as phylloclade.
- Spines growing on phylloclade of Opuntia are leaves, modified to reduce the loss of water through transpiration.
- Thoms in Carissa are modified apical buds. They provide protection against browsing animals.
- Thus, spines in Opuntia and thorns in Carissa have different origin and function.
C. Teacher described Hibiscus as solitary Cyme. What it means?
Answer: A solitary cyme in Hibiscus means a single flower that appears as a cymose inflorescence.
3. Write notes on
A. Fusiform root.
Answer: A fusiform root is a tap root that is thick in the middle and tapers at both ends, resembling a spindle. It stores food, e.g., radish.
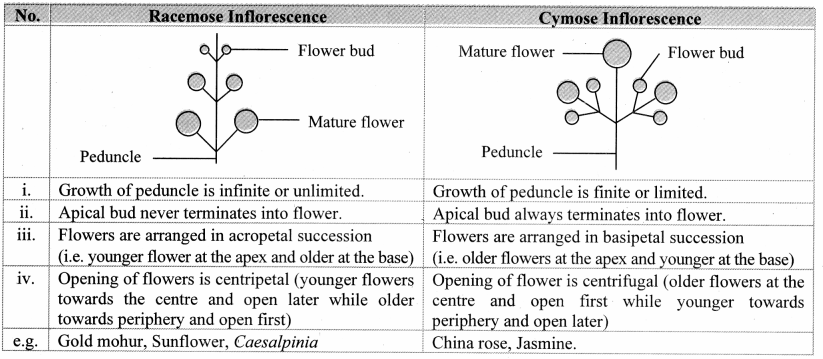
B. Racemose inflorescence
Answer: Racemose inflorescence is an indeterminate type where the main axis grows indefinitely, producing flowers laterally in acropetal order (younger at top), e.g., mustard.
C. Fasciculated tuberous roots
Answer: Fasciculated tuberous roots are adventitious roots that arise in clusters from the stem base, swollen to store food, e.g., dahlia.
D. Region of cell maturation
Answer: The region of cell maturation in roots is where cells differentiate into specialized tissues, forming structures like root hairs for absorption.
E. Rhizome
Answer: A rhizome is a horizontal underground stem that stores food and aids in vegetative propagation, e.g., ginger.
F. Stolon
Answer: A stolon is a horizontal above-ground stem that grows along the soil, producing new plants at nodes, e.g., strawberry.
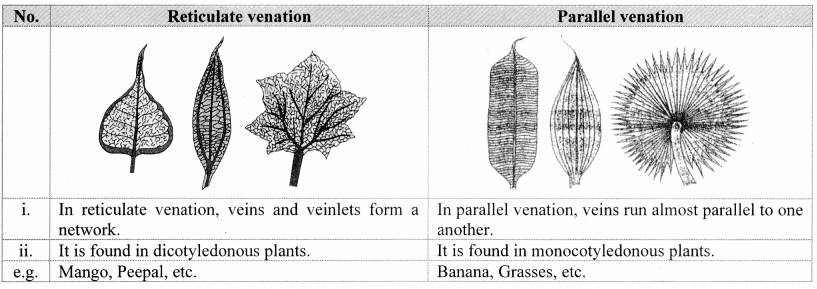
G. Leaf venation
Answer: Leaf venation is the pattern of veins in a leaf, either reticulate (net-like, e.g., dicots) or parallel (straight, e.g., monocots).
H. Cymose inflorescence
Answer: Cymose inflorescence is a determinate type where the main axis ends in a flower, with flowers in basipetal order (younger at base), e.g., jasmine.
I. Perianth
Answer: Perianth is the non-reproductive floral whorls (calyx and corolla) that protect reproductive organs, e.g., tepals in lilies.
J. Vexillary aestivation
Answer: Vexillary aestivation is a petal arrangement in Fabaceae where a large standard petal covers two wing petals, which enclose two keel petals.
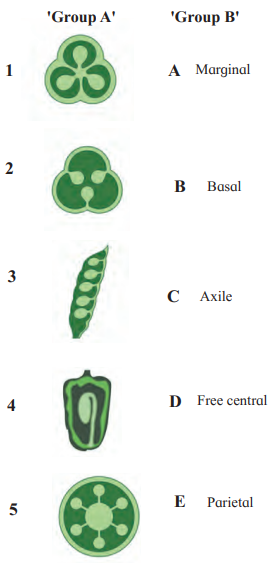
K. Axile placentation
Answer: Axile placentation is when ovules are attached to a central axis in a multilocular ovary, e.g., lemon.
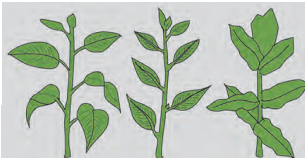
4. Identify the following figures and write down the types of leaves arrangement
Answer:
1. The given figures represent phyllotaxy. It is the arrangement of leaves on the stem and branches in a specific manner.
2. Figure ‘a’ and ‘b’ represents, alternate phyllotaxy. In this type of phyllotaxy, single leaf arises from each node of a stem. e.g. Mango
3. Figure ‘c’ represents opposite decussate phyllotaxy. In this type of phyllotaxy, a pair of leaf arise from each node and the consecutive pair at right angle to the previous one. e.g. Calotropis.
5. Students were on the excursion to a botanical garden. They noted following observation. Will you be able to help them in understanding those conditions?
A. A wiry outgrowth was seen on a plant arising from in between the leaf and stem.
Answer: This is an axillary bud or tendril.
B. There was a green plant with flat stem, but no leaves. The entire plant was covered by soft spines.
Answer: This is a cactus (e.g., Opuntia).
C. Many obliquely produced roots were given out from the lower nodes, apparently for extra support.
Answer: These are prop roots.
D. Many plants in the marshy region had upwardly growing roots. They could be better seen during low tide.
Answer: These are pneumatophores.
E. A plant had leaves with long leaf apex, which was curling around a support.
Answer: This is a leaf tendril.
F. A plant was found growing on other plant. Teacher said it is not a parasite. It exhibited two types of roots.
Answer: This is an epiphyte (e.g., orchid).
G. While having lunch, onion slices were served to them. Teacher asked which part of the plant are you eating?
Answer: Leaf bases.
H. Students observed large leaves of coconut and small leaves of Mimosa. Teacher asked it what way they are similar?
Answer: Both have compound leaves.
I. Teacher showed them Marigold flower and said it is not one flower. What the teacher meant?
Answer: Marigold is a composite inflorescence.
J. Students cut open a Papaya fruit and found all the seeds attached to the sides. Teacher inquired about the possible placentation of Papaya ovary.
Answer: Parietal placentation.
6. Match the following
Answer:
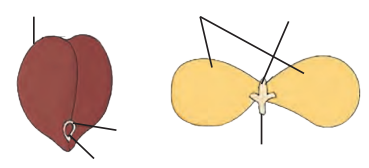
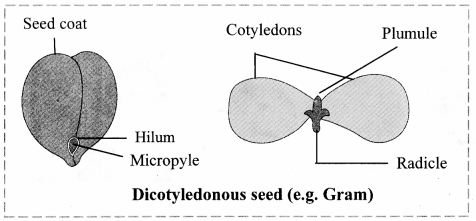
7. Observe the following figures and label the different parts.
8. Differentiate with diagramatic representation.
A. Racemose and cymose infloresance
B. Reticulate and parallel venation
C. Tap root and Adventitious root



Leave a Reply