Ocean Resources – Solutions
Q. 1) Complete the chain :
Answer:
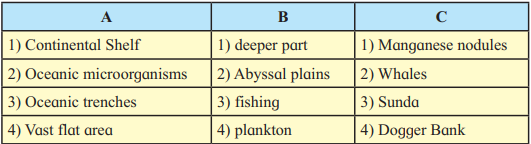
| A | B | C |
| (1) Continental Shelf | (1) Fishing | (1) Dogger Bank |
| (2) Oceanic Microorganisms | (2) Plankton | (2) Whales |
| (3) Oceanic Trenches | (3) Deeper Part | (3) Sunda |
| (4) Vast Flat Area | (4) Abyssal Plains | (4) Manganese Nodules |
Q. 2) Identify the correct correlation :
A : Assertion; R : Reasoning
1) A : Continental shelf is a storehouse of mineral oil and natural gas.
R : Continental shelf receives large quantities of load from continental areas.
1) Only A is correct
2) Only R is correct
3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
4) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer: 4) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- Explanation: The continental shelf is indeed rich in mineral oil and natural gas (e.g., Mumbai High), and it receives sediment loads from continents. However, the presence of oil and gas is due to geological processes, not directly due to sediment load.
2) A: More deposition occurs in the continental slope.
R: The slope is steeper here.
1) Only A is correct
2) Only R is correct
3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
4) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer: 2) Only R is correct.
- Explanation: The continental slope is steeper (2° to 5° gradient), but deposition is limited due to the steepness, contrary to the assertion. Most deposition occurs on the continental shelf or abyssal plains.
3) A : The islands are actually peaks of submerged mountains
R : Some peaks of submerged mountains come above the sea level
1) Only A is correct
2) Only R is correct
3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
4) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer: 3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Explanation: Islands, such as volcanic or continental islands, are often peaks of submerged mountains (e.g., Hawaiian Islands), and their emergence above sea level explains their formation as islands.
4) A: The abyssal plains are the deepest parts of the ocean
R: They lie at the bottom of the ocean
1) Only A is correct
2) Only R is correct
3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
4) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer: 1) Only A is correct.
- Explanation: Abyssal plains are not the deepest parts; oceanic trenches (e.g., Mariana Trench) are deeper. The reasoning is too vague and does not clarify the assertion.
5) A : Sodium chloride and potassium are parts of inorganic oceanic resources.
R : Salt extraction is a major activity in coastal areas.
1) Only A is correct
2) Only R is correct
3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
4) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer: 3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Explanation: Sodium chloride (common salt) and potassium are inorganic resources found in oceans, and salt extraction in coastal areas is a direct utilization of these resources.
Q. 3) Give geographical reasons.
1) Fishing has developed in continental shelves.
Answer:
- The continental shelf is shallow (up to 180-200 m), allowing sunlight to penetrate, which supports plankton growth, a primary food source for fish.
- Rich fishing grounds, like Grand Banks and Georges Bank, are located here due to abundant fish populations.
- The accessibility of shallow waters makes fishing easier and economically viable.
2) Our knowledge regarding the oceanic trenches is limited.
Answer:
- Oceanic trenches are extremely deep (e.g., Mariana Trench, ~11 km), making exploration difficult with current technology.
- Their remoteness and high-pressure environments limit human access, with only three humans having visited below 6,000 m.
- Exploration has been restricted to limited sampling campaigns, such as those in the 1950s.
3) The ocean is a storehouse of minerals.
Answer:
- Continental shelves contain oil, gas, and minerals like diamonds, chromite, and phosphorite.
- Abyssal plains have manganese nodules with iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper.
- Oceanic waters yield sodium chloride, potassium, and gypsum, supporting industries like salt extraction and construction.
4) Like the land, there are landforms below the ocean too.
Answer:
- The ocean floor features continental shelves, slopes, abyssal plains, trenches, ridges, and plateaus, similar to terrestrial plains, mountains, and valleys.
- Submarine canyons (e.g., Congo Canyon) and seamounts resemble terrestrial canyons and hills.
- These features are formed by tectonic, volcanic, and erosional processes, akin to landform formation on land.
Q. 4) Write short notes on:
1) EEZ
Answer:
- An EEZ extends 200 nautical miles from a country’s coast, as defined by the UNCLOS (1982).
- Within this zone, the country has exclusive rights to exploit resources like fish, minerals, and energy (e.g., India’s right to mine manganese nodules).
- Beyond the EEZ, oceanic resources are considered international and regulated by global institutions.
2) Oceanic tourism
Answer:
- Oceanic tourism includes activities like cruises, scuba diving, fishing, and beach tourism.
- It is growing popular, with developments like resorts and marinas, boosting local economies.
- However, it can harm marine ecosystems, requiring sustainable practices to minimize environmental impact.
3) Abundance of minerals in oceans
Answer:
- Continental shelves hold oil, gas, and minerals like diamonds, gold, and phosphorite.
- Abyssal plains contain manganese nodules with iron, nickel, and cobalt.
- Oceanic waters provide sodium chloride, potassium, and gypsum, used in industries like construction and salt production.
4) Deposition and continental slope
Answer:
- The continental slope, with a steep gradient (2° to 5°), experiences limited sediment deposition due to its incline.
- Sediments from the continental shelf may slide down, forming features like submarine canyons or avalanche fans (e.g., Congo Canyon).
- Methane hydrates are found here, but deposition is minimal compared to the shelf or abyssal plains.
Q. 5) Answer in detail:
1) The marine pollution is ultimately going to be harmful to the man himself. Discuss.
Answer:
- Sources of Pollution: Marine pollution arises from oil spills (e.g., from oil transport ships), industrial waste, radioactive waste, and river effluents carrying urban and industrial waste. Plastic pollution, like the 30-year-old plastic bag found in the Mariana Trench, is widespread, with microplastics constituting a third of ocean debris.
- Impact on Marine Ecosystems: Pollution threatens marine life by disrupting food chains (e.g., plankton and fish killed by desalination plants or plastic ingestion). Coral reefs, like the Great Barrier Reef, are at risk, reducing biodiversity.
- Human Consequences: Contaminated seafood affects human health, as pollutants accumulate in fish consumed by humans. Pollution disrupts fisheries, threatening food security and livelihoods. Coastal pollution degrades tourism and water quality, impacting economies.
- Long-term Risks: As human dependence on oceans for food, water, and minerals grows, pollution could limit resource availability, exacerbating global challenges like food insecurity by mid-21st century.
- Mitigation Needs: Sustainable practices, reduced waste disposal, and international.
2) There is similarity in the relief on the land surface and the ocean bottom.
Answer:
- Comparable Landforms: The ocean floor mirrors terrestrial relief with features like continental shelves (plains), slopes (escarpments), abyssal plains (flat plains), trenches (deep valleys), and oceanic ridges/plateaus (mountain ranges).
- Specific Examples: Submarine canyons (e.g., Congo Canyon) resemble terrestrial canyons, while seamounts are akin to hills or mountains. Oceanic islands (e.g., Hawaiian Islands) are peaks of submerged mountains, similar to mountain peaks on land.
- Formation Processes: Both land and ocean landforms result from tectonic activity (e.g., plate boundaries forming trenches or mountains), volcanic activity (e.g., seamounts or volcanic islands), and erosion/deposition (e.g., sediment fans on slopes or river deltas).
- Functional Similarity: Continental shelves support fishing, like fertile plains support agriculture. Trenches and deep valleys both represent extreme depths, while ridges and plateaus indicate elevated terrain.
- Significance: Understanding these similarities aids in mapping and exploiting ocean resources, as terrestrial geological knowledge can be applied to oceanic exploration.
3) Discuss how development of oceanic tourism should be carried out without disturbing marine life.
Answer:
- Sustainable Practices: Tourism activities like cruises and scuba diving should follow eco-friendly guidelines, such as limiting waste discharge and using biodegradable materials to reduce pollution (e.g., avoiding plastic debris).
- Protected Areas: Establish marine protected areas (MPAs) around sensitive ecosystems like coral reefs (e.g., Great Barrier Reef) to restrict tourism-related damage while allowing controlled access for education and research.
- Regulated Infrastructure: Resorts and marinas should be built with environmental impact assessments to minimize habitat destruction. Use eco-friendly designs, like floating structures, to avoid disturbing the ocean floor.
- Controlled Activities: Limit high-impact activities like overfishing or destructive diving practices. Promote low-impact tourism, such as snorkeling or wildlife observation, with trained guides to ensure minimal disturbance.
- Public Awareness: Educate tourists about marine conservation to foster respect for ecosystems. Encourage participation in clean-up drives or citizen science projects to monitor marine health.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: Regular monitoring of tourism impacts and strict enforcement of regulations by international and local authorities can ensure compliance, preserving marine biodiversity while supporting tourism growth.
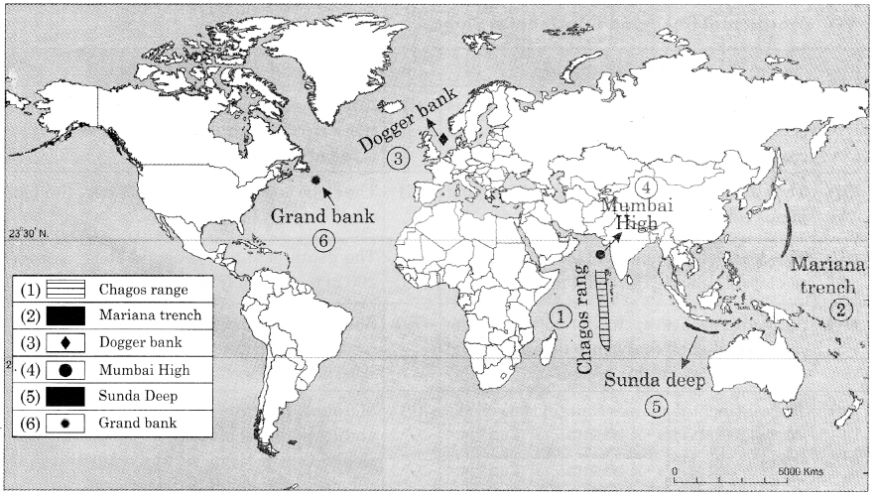
Q. 6) Show the following on the map of the World:
1) Chagos Range
2) Mariana Trench
3) Dogger Bank
4) Mumbai High
5) Sunda Deep
6) Grand Banks
Answer:

Leave a Reply