Biomes – Solutions
Q. 1. A) Complete the chain :
Answer:
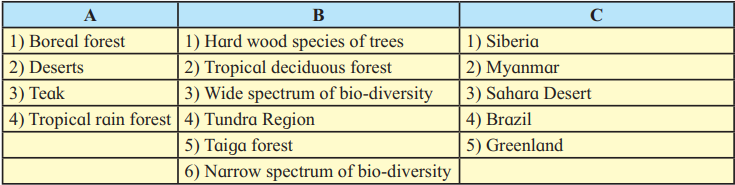
| A | B | C |
| (1) Boreal forest | (1) Taiga forest | (1) Siberia |
| (2) Deserts | (2) Narrow spectrum of bio-diversity | (2) Sahara Desert |
| (3) Teak | (3) Tropical deciduous forest | (3) Myanmar |
| (4) Tropical rainforest | (4) Hardwood species of tree | (4) Brazil |
Q. 1 B) Fill in the blanks with appropriate alternatives given below and rewrite the sentences.
1) Ecosystem consists of interaction between ……………….. and abiotic factors.
a) Biotic factors b) Animals
c) Human beings d) Plants
Answer: a) Biotic factors
- Explanation: An ecosystem involves the interaction between biotic factors (plants, animals, bacteria, etc.) and abiotic factors (soil, water, sunlight, nutrients).
2) The original meaning of savanna is……………….
a) Land with many trees.
b) Extensive perennial grass land.
c) Land which is full of trees with much grass.
d) land which is without trees but with much grass.
Answer: b) Extensive perennial grassland
- Explanation: Savanna is characterized by continuous cover of perennial grass, as described in the document.
3) In Africa tropical evergreen forest is predominantly found in ……………….. .
a) Amazon basin
b) Sahara desert
c) Congo basin
d) Savanna
Answer: c) Congo basin
- Explanation: Tropical evergreen forests in Africa are primarily located in the Congo basin, not the Amazon, Sahara, or Savanna regions.
4) Mediterranean forest is also known as ………………….. forests.
a) Hard wood
b) Chaparral
c) Man made
d) Soft wood
Answer: b) Chaparral
- Explanation: Mediterranean forests are referred to as Chaparral forests due to their specific vegetation type.
Q.2 A) Arrange the given statements as per given instructions.
1) Arrange the following biomes in proper order from Equator to Pole.
a) Tundra b) Tropical rain forest
c) Boreal forest d) Sahara desert
Answer: Tropical rainforest, Sahara desert, Boreal forest, Tundra
Explanation:
- Tropical rainforest (0° to 10° N and S, near the equator).
- Sahara desert (20° to 30° N and S, tropical desert biome).
- Boreal forest (50° to 65° N, also known as Taiga).
- Tundra (65° to 90° N, closest to the poles).
Q. 2. B) Select the inappropriate factor or statement
1) Trees in the tropical rain forest-
a) Mahogany b) Ebony
c) Pine d) Rosewood
Answer: c) Pine
- Explanation: Tropical rainforests have trees like Mahogany, Ebony, and Rosewood, but Pine is characteristic of coniferous forests like the Taiga, not tropical rainforests.
2) Temperate grasslands in the world.
a) Prairies – North America
b) Steppes – Eurasia
c) Downs – Africa
d) Pampas – South America.
Answer: c) Downs – Africa
- Explanation: The Downs are located in Australia, not Africa. The correct temperate grasslands include Prairies (North America), Steppes (Eurasia), and Pampas (South America).
4) Major hot deserts in the world are-
a) Gobi – Asia
b) Kalahari – Africa
c) Atacama – South America
d) Arabian – Asia
Answer: Gobi – Asia
- Explanation: Gobi Desert is a cold desert, not a hot desert, as it is located in Central Asia and has a much colder climate compared to tropical deserts.
Q. 3) Give geographical reasons:
1) The trees in the tropical rainforests are broad-leaved while those in the Taiga are coniferous.
Answer: Tropical rainforests, located near the equator (0° to 10° N and S), receive high rainfall and sunlight, supporting dense, broad-leaved trees that maximize photosynthesis. These leaves are evergreen to take advantage of the consistent climate. In contrast, the Taiga (50° to 65° N) experiences cold, harsh winters with snow. Coniferous trees with needle-like, waxy leaves and a conical shape are adapted to reduce water loss, withstand snow accumulation, and survive the cold climate.
2) Desert biomes have thorny vegetation.
Answer: Desert biomes (20° to 30° N and S) have extreme temperatures and very low rainfall, leading to sparse vegetation. Thorny plants like cacti, acacia, and khejari have thick, water-storing leaves or stems and thorns to reduce evaporation and protect against herbivores. These adaptations help them survive the arid conditions and limited water availability.
3) Lumbering activity has developed in Taiga forests.
Answer: The Taiga biome (50° to 65° N) is dominated by evergreen coniferous trees like spruce, fir, and pine, which provide softwood ideal for lumbering. The uniform tree species and soft wood make deforestation and processing easier. The sparse human population and vast forest cover support large-scale lumbering for sawmills, paper pulp, and furniture industries.
4) Mediterranean biome has proved to be a catalyst to the development of cinema industry.
Answer: The Mediterranean biome (30° to 40° N and S) has a pleasant climate, natural beauty, and diverse flora (citrus trees, colorful shrubs). These features attract filmmakers for outdoor shooting. The region’s tourism appeal, coupled with industries like fruit and flower processing, supports infrastructure for the cinema industry, making it an ideal location for film production.
Q. 4) Write short notes on:
1) Agriculture in temperate grassland biome
Answer: Temperate grasslands (40° to 55° N and S), such as Prairies, Steppes, Pampas, and Velds, have fertile soils and sufficient rainfall for extensive agriculture. Crops like maize and wheat are grown on large fields, often spanning hundreds of hectares, using advanced machinery. These regions are major exporters of grains due to high yields. Livestock raising for meat, milk, wool, and hides is also significant, with animals like Merino sheep in Australia being globally renowned.
2) Human life in Tundra biome
Answer: The Tundra biome (65° to 90° N) has a harsh, cold climate with permafrost, making human settlements sparse. Indigenous groups like Lapps, Samoyeds, and Eskimos live here, traditionally relying on hunting and fishing. Modern influences have introduced advanced tools, changing fishing methods and increasing exploitation. Global warming and improved transportation are affecting the biome, improving living standards but threatening biodiversity.
3) Animal adaptation in grasslands
Answer: Grasslands, including savanna (10° to 20° N and S) and temperate grasslands (40° to 55° N and S), support diverse herbivores like antelopes, zebras, and deer, adapted to feed on abundant grasses. Their seasonal color changes provide camouflage. Carnivores like lions, cheetahs, and coyotes thrive due to the high herbivore density. Animals have adaptations like strong hooves for mobility and keen senses to evade predators, ensuring survival in open landscapes.
4) Marine biomes
Answer: Marine biomes cover 70% of Earth’s surface, including oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries, divided into layers based on light penetration. The euphotic layer (up to 200 m) supports fish, turtles, and corals due to sunlight. The disphotic layer (up to 1000 m) has limited light, hosting squid and eels adapted to darkness. The aphotic layer (1000–4000 m) lacks light, with bioluminescent species like angler fish surviving on detritus. These biomes vary by salt content and support diverse aquatic life adapted to high pressure and cold.
Q. 5) Distinguish between :
1) Biome and ecosystem
Answer:
| Biome | Ecosystem |
| (i) An area where different types of flora and fauna live together in the same region in the same type of climatic conditions is called a biome. | (i) In a given region, the interaction between biotic and abiotic factors is known as ecosystem. |
| (ii) The boundaries of different biomes on land are determined mainly by climatic conditions like rainfall, temperature, humidity, amount of insolation received and soil conditions. | (ii) The biotic factors are plants, animals and bacteria. The abiotic factors consist of soil, water, sunlight and nutrients. |
| (iii) There can be many ecosystems in a biome. | (iii) There are different trophic levels in an ecosystem. |
2) Tropical and temperate grassland biomes.
Answer:
| Tropical Grassland Biome | Temperate Grassland Biome |
| (i) It is located between 10° to 20° N and S. | (i) It is located between 40° to 55° N and S. |
| (ii) It is characterised by a continuous cover of perennial grass that grows about 3 m to 6 m height, known as elephant grass and there are a few shrubs and trees. | (ii) Grass is a dominant vegetation. It is soft. Not many types of trees are found. The various species of grass include purple needle grass, blue grama, buffalo grass and galleta. |
| (iii) It is rich in herbivorous animals like rabbits, antelopes, buffaloes, zebras, rhinos, giraffes, elephants, warthogs, etc. It also supports a number of carnivores like lions, leopards, cheetah, wild dogs, jackals, hyenas, and birds like vultures, great Indian bustards, twitter and ostriches. | (iii) It is rich and varied in animal life. Herbivore animals include gazelles, zebras, wild horses, wolves, deer, rabbits, etc. In the veld grasslands, ostriches are found. In the Downs of Australia, kangaroos and dingoes are found. |
3) Human activities in tropical evergreen and Monsoon regions.
Answer:
| Human activities in Tropical Evergreen | Human activities in Monsoon Regions |
| (i) Human life is not very easy in this climate. | (i) Human life is easier than that in the rainforest. |
| (ii) Indigenous humans in these parts are still in their primitive stage. | (ii) Primary and secondary occupations based on forests are found here. |
| (iii) Indigenous tribes are Pygmies in Congo, Boro Indians in Amazon, Sentinels, Onges, Jarawahs, etc., in Andaman and Nicobar Islands in India. | (iii) Various tribal communities inhabit the regions under this biome. |
| (iv) They are engaged in primary activities like gathering of forest products, hunting, fishing, etc. Secondary activities are not developed. | (iv) Animal rearing for milk and meat production is carried out. Primary and secondary activities based on forest products are also developed. |
Q. 6) Answer in detail :
1) Give an account of the desert biome with the help of following points :
Answer:
a) Location: Tropical desert biomes are found at 20° to 30° N and S, including the Sahara (Africa), Arabian (Asia), and Atacama (South America). They are typically located in the western parts of continents due to dry trade winds and rain-shadow effects.
b) Plant Life: Vegetation is sparse due to low rainfall and extreme temperatures. Plants like date palms, acacia, khejari, and cacti have thick, water-storing leaves, thorny structures to reduce evaporation, and trunk-like leaves for photosynthesis, adapted to survive arid conditions.
c) Animal Life: Biodiversity is limited due to sparse vegetation. Small animals like camels, snakes, lizards, desert turtles, and mongoose are adapted to survive with minimal water, burrowing or staying in hideaways to avoid heat. Birds include ostriches and desert eagles, and insects like beetles and termites are common.
d) Human Life: Extreme temperatures make human life difficult. Settlements are sparse, concentrated near oases, and often nomadic (e.g., Bedouin tribes). Agriculture is limited but possible with irrigation, and date palms are a key food source. Mineral extraction is easier due to minimal vegetation, but desertification is spreading to nearby regions like the Nile valley.
2) Explain the reasons behind deforestation in your area. What measures will you suggest to minimize deforestation?
Answer: Reasons for Deforestation:
- Agriculture Expansion: Forests are cleared for crops and pastures, especially in tropical deciduous and temperate grassland biomes, to meet food demands.
- Industrialization: Urban sprawl and industries encroach on forests, particularly in Mediterranean and temperate deciduous biomes, for infrastructure and resources.
- Logging: Hardwood from tropical rainforests and softwood from Taiga are harvested for construction, furniture, and paper, leading to deforestation.
- Wildfires and Overgrazing: Frequent fires in savanna and overgrazing in grasslands reduce forest cover, increasing desertification risks.
Measures to Minimize Deforestation:
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Plant native trees to restore degraded areas and create new forests to replace lost cover.
- Sustainable Forestry: Promote selective logging and certify sustainable timber to reduce overexploitation.
- Protected Areas: Establish and enforce national parks and reserves to conserve biodiversity in threatened biomes like rainforests and Taiga.
- Regulation of Agriculture: Encourage sustainable farming practices, like agroforestry, to reduce forest clearing.
- Public Awareness: Educate communities about the importance of forests for biodiversity, climate regulation, and livelihoods to foster conservation efforts.
- Policy Enforcement: Implement strict laws against illegal logging and land conversion, with penalties for violations.

Leave a Reply