Second Urbanisation in India – Solutions
Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative and write the complete sentences.
(1) Ashmaka is the name inlanguage.
(a) Pali (b) Sanskrit
(c) Ardhamagadhi (d) Prakrit
Answer: (b) Sanskrit
(2) The capital of Kashi mahajanapada was .
(a) Gorakhpur (b) Chandanagar
(c) Rajagriha (d) Varanasi
Answer: (d) Varanasi
(3) Gautama Buddha was born in .
(a) Kushinagara (b) Sarnath
(c) Lumbini (d) Pataliputra
Answer: (c) Lumbini
(4) The river was the natural boundary between Uttara Panchala nand Dakshina Panchala.
(a) Yamuna (b) Bhagirathi
(c) Ganga (d) Niranjana
Answer: (b) Bhagirathi
(B) Find the incorrect pair from set B and write the correct ones.
| Set ‘A’ | Set ‘B’ |
| (1) Kosala | Shravasti |
| (2) Anga | Champa |
| (3) Matsya | Mathura |
| (4) Gandhara | Taxila |
Answer: (c) Matsya – Virat Nagar
Q.2 Choose the correct reason and complete the sentence.
Gautama Buddha travelled continuously for 45 years….
(a) in the search of a Guru
(b) to practice austerities
(c) to preach dhamma
(d) to attain enlightenment
Answer: (c) to preach dhamma
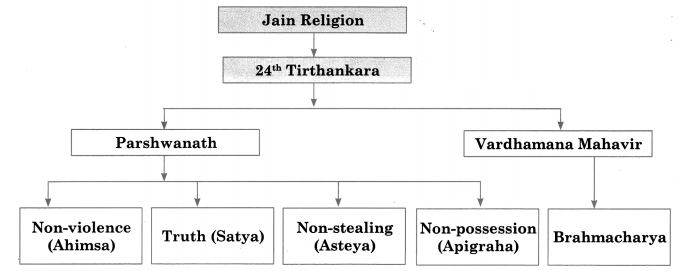
Q.3 Complete the concept map given below.
Answer:
Q.4 Explain the statements with reasons.
(1) Rise of mahajanapadas came into being.
Answer: The rise of mahajanapadas occurred due to the ambition of territorial expansion among janapadas, leading to conflicts. Stronger janapadas conquered and annexed weaker ones, expanding their territories. By 600 B.C.E., sixteen mahajanapadas emerged, from the northwest to Magadha, as a result of these conquests and the establishment of large empires like Magadha.
(2) The process of Second urbanisation began in ancient India.
Answer: The second urbanisation began due to the prosperity of trade and the establishment of powerful mahajanapadas with defined geographic boundaries and administrative systems. The capital cities of these mahajanapadas, such as Champa, Rajagriha, Shravasti, Saketa, Kushambi, and Varanasi, flourished as administrative and trade centers, fostering urban development by the 6th century B.C.E.
(3) Vardhamana Mahavira and Gautama Buddha attracted a large number of followers.
Answer: Vardhamana Mahavira and Gautama Buddha attracted numerous followers because their teachings addressed social disparities caused by the varna and caste system. Their philosophies, Jainism and Buddhism, rejected Vedic authority and rituals, appealing to people from all strata of society. Their use of common languages (Ardhamagadhi and Pali) and emphasis on ethical living and liberation resonated with the masses.
Q.5 Explain the following concepts.
(1) Nastik Darshan
Answer: Nastik Darshan refers to philosophical schools in ancient India that reject the authority of the Vedas and Vedic rituals. Jainism and Buddhism are considered nastik schools because they do not accept Vedic supremacy or the existence of a supreme deity as propagated by Vedic traditions. These schools focus on ethical conduct, liberation, and rational inquiry rather than ritualistic practices.
(2) The eightfold path preached by Gautama Buddha
Answer: The eightfold path, also known as the Ashtangika Marga or Madhyama Pratipada, is a core teaching of Gautama Buddha to overcome sorrow (dukkha) by following a balanced path. It includes:
- Samyak Drishti: Right understanding, accepting natural laws.
- Samyak Sankalp: Right determination or intention.
- Samyak Vacha: Right speech, truthful and kind.
- Samyak Karmanta: Right behavior or actions.
- Samyak Aajiva: Right livelihood, ethical means of living.
- Samyak Vyayam: Conscious avoidance of harmful actions.
- Samyak Smriti: Right mindfulness, awareness of thoughts and actions.
- Samyak Samadhi: Right concentration, achieving mental equanimity.
This path guides individuals toward enlightenment by cultivating ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom.
Q.6 Describe the administrative system of the mahajanapadas with the help of the following points.
(a) Terms showing types of states
Answer: The administrative system of mahajanapadas included various terms for types of states, such as Rajya (kingdom ruled by a Raja who performed the Rajasuya sacrifice), Saamrajya (empire ruled by a Saamraj who performed the Vajapeya sacrifice), Svaarajya, Bhaujya, Vairajya, Maharajya, and Parmeshthya. These terms indicate different levels of sovereignty and territorial control, with Saamrajya being a higher status than Rajya.
(b) King’s installation
Answer: The king, typically a Kshatriya, was installed through a coronation ceremony, often involving sacrifices like Rajasuya or Vajapeya. The position was generally hereditary, passed to the king’s son, though in some cases, kings were elected by the people. The first wife, known as Rajmahishi, was crowned alongside the king, signifying her role in the royal administration.
(c) Authority of the king
Answer: The king held absolute authority over his subjects, deciding taxation and land distribution. He could donate land at his discretion and performed sacrifices like Ashvamedha to assert supremacy. However, his power was not entirely unrestricted, as he relied on advisors like Purohita (priest), Senani (military commander), Amatya (minister), and Gramani (village head) for governance.
(d) Decision-making
Answer: Decision-making involved consultation with advisors and officials. Additionally, assemblies of people from all classes could participate in discussions, influencing decisions. These assemblies had significant power, as they could even force a king to step down. The king’s decisions were thus shaped by both his advisors and public opinion, ensuring a balance in governance.


Leave a Reply