Equality and Justice – Solutions
Exercise
1. (A) Choose the correct alternative and complete the following statements.
1. The base of political equality is democracy. (democracy, dictatorship, military rule, monarchy)
2. John Rawls was an advocate of Distributive justice. (distributive, political, economic, gender based)
1. (B) State the appropriate concept for the given statement.
1. Principle of equality which states that each one should get an opportunity for development of their individual personality –
Answer: Natural Equality
Explanation: The document explains that natural equality means individuals should not be discriminated against based on their natural abilities and should have opportunities to develop their personality.
2. Type of equality which says that every citizen has an equal right to participate in affairs of the State –
Answer: Political Equality
Explanation: Political equality, as per the document, ensures that every citizen has an equal right to participate in state affairs, typically in a democracy.
3. Absence of economic exploitation –
Answer: Economic Equality
Explanation: The document describes economic equality as the absence of economic exploitation, providing equal opportunities for development and preventing wealth concentration.
(C) Complete the following sentence using appropriate reason.
In India, laws were made regarding abolition of untouchability. Because
(a) untouchability is a political concept
(b) untouchability is legal concept
(c) social inequality is controlled by State legislation
Answer: (c) social inequality is controlled by State legislation
Explanation: The document highlights that laws abolishing untouchability were made to ensure social equality, as social inequalities like untouchability are addressed through state legislation.
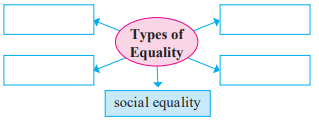
2. Complete the concept map/maps.
Answer:
Types of Equality
- Natural Equality
- Civil Equality
- Political Equality
- Economic Equality
- Social Equality
Explanation: The document lists five types of equality: Natural, Civil, Political, Economic, and Social, as shown in the concept map.
3. State whether the following statements are true or false with reasons.
1. Democracy denies equality.
Answer: False
Reason: Democracy promotes equality by ensuring equal rights to participate in state affairs, as mentioned in the document under political equality. It is based on principles like universal adult franchise.
2. Equality is a political goal.
Answer: True
Reason: The document states that equality is looked at as a political goal in modern times, aiming to reduce inequalities and ensure fairness in society.
3. Social democracy is a foundation of political democracy.
Answer: True
Reason: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar, as quoted in the document, emphasized that political democracy cannot last without social democracy, which recognizes liberty, equality, and fraternity.
4. Explain co-relation between the following.
1. Equality and Justice
Answer: Equality and justice are closely related concepts. Equality ensures that all individuals are treated fairly and have equal opportunities, which is a foundation for justice. The document explains that justice involves the equitable distribution of resources, which cannot be achieved without equality. For example, equality before the law ensures legal justice, while social equality supports social justice by reducing discrimination.
2. Legal Justice and Social Justice
Answer: Legal justice involves applying laws impartially to ensure fairness, while social justice focuses on equitable distribution of resources and opportunities, especially for weaker sections. The document notes that legal justice is a means to suppress injustice through laws, while social justice addresses broader societal inequalities, like those based on caste or gender. In India, both are ensured through constitutional measures like reservations and laws against discrimination.
5. Express your opinion of the following.
Casteism is a barrier to social equality.
Answer: I agree that casteism is a significant barrier to social equality. The document highlights that the caste system creates social inequalities by discriminating against certain groups, denying them equal status and opportunities. In India, casteism leads to practices like untouchability, which hinder social harmony and mutual respect. Efforts by thinkers like Mahatma Phule and Dr. Ambedkar to abolish caste-based discrimination show its negative impact on achieving social equality.
6. Answer the following.
Explain Indian concept of justice.
Answer: The Indian concept of justice, as per the document, addresses inequalities caused by systems like caste and patriarchy. Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar emphasized that true justice requires changing these structures and ensuring equitable resource distribution. The Indian Constitution promotes both procedural justice (fair legal processes) and social justice (uplifting weaker sections). This is achieved through policies like reservations, scholarships, and laws abolishing untouchability. Ambedkar’s vision of social democracy highlights justice as a way of life that upholds liberty, equality, and fraternity, ensuring dignity for all.

Leave a Reply