Development Administration
Exercise
1. State the appropriate concept for the given statement.
1. State that promotes economic and social well-being of its citizens
Answer: Welfare State
2. Unnecessary delays in administrative work is called
Answer: Red Tape
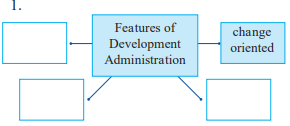
2. Complete the concept map.
Answer:
Features of Development Administration
- Change oriented
- Output-oriented
- Citizen participation
- Public commitment
3. State whether the following statements are true or false with reasons.
1. Change and growth-oriented approach is called Development Administration.
Answer: True
Reason: Development Administration is defined as an approach that focuses on bringing about change and achieving growth-oriented goals, such as economic, social, and political development, through planned and innovative administrative actions.
2. In post-independent India, government deliberately invested in public sector.
Answer: True
Reason: After independence, the Indian government deliberately invested in the public sector to promote industrialisation and development, as seen in projects like the Bhakra-Nangal Dam and Bhilai Steel Plant, which were referred to as the “Temples of Modern India” by Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru.
3. The 73rd amendment act gave constitutional status to municipalities.
Answer: False
Reason: The 73rd Amendment Act of 1992 gave constitutional status to Panchayati Raj institutions, not municipalities. The 74th Amendment Act of 1992 gave constitutional status to municipalities to strengthen urban local governments.
4. Explain the co-relation between the following.
Citizen participation and Development
Answer: Citizen participation is closely related to development in Development Administration. For development to be successful, active involvement of people is essential. When citizens participate in planning, implementing, and evaluating development programs, it ensures that the initiatives meet the actual needs of the community. In a diverse country like India, where needs vary across regions, participation ensures that programs are inclusive and effective. For example, the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts promoted grassroots participation through Panchayati Raj institutions and municipalities, enabling local people to contribute to development. This participation strengthens democracy and helps achieve developmental goals like poverty reduction and infrastructure improvement.
5. Answer the following.
1. Discuss any 4 areas of study in traditional public administration.
Answer: The four areas of study in traditional public administration are:
- Organisation of the governmental machinery: This focuses on the structure of government, including ministries, departments, and bodies like the UPSC and Election Commission.
- Management of different tasks: This involves leadership, planning, and coordination between departments, such as the role of NITI Aayog in planning.
- Personnel Administration: This covers recruitment, training, promotions, salaries, and pensions, for example, recruitment through UPSC or State Civil Service Commissions.
- Financial Administration: This deals with budget-making, parliamentary financial committees like the Public Accounts Committee, and auditing processes.
2. Write in brief about NITI Aayog.
Answer: NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) was established in 2014 to replace the Planning Commission. It serves as a think tank for the Government of India, promoting cooperative federalism and decentralized planning. Unlike the Planning Commission’s centralized approach, NITI Aayog focuses on grassroots planning, starting from villages, blocks, and districts, which is then harmonized at the state and national levels. It aims to foster sustainable development by involving states and local bodies in the planning process and addressing issues like poverty, agriculture, and infrastructure development.
6. Express your opinion of the following.
Citizen participation is necessary in development administration.
Answer: I believe citizen participation is essential in Development Administration because it ensures that development programs reflect the real needs and aspirations of the people. When citizens are involved in planning and implementing projects, it increases transparency, accountability, and the chances of success. For instance, in India, programs like the Community Development Programme and the 73rd and 74th Amendments have shown that involving people at the grassroots level leads to better outcomes in rural and urban development. Without citizen participation, development efforts may fail to address local issues, leading to inefficiency and wasted resources.

Leave a Reply