Pillars of Democracy
Brainstorming – Solutions
(A1)
(i) Form groups and use the following topics for discussion. Take the help of your college library and your teacher.
Need for Democracy
- Democracy allows citizens to participate in governance through voting and representation.
- It ensures freedom, equality, and justice, giving everyone a voice in decision-making.
- It prevents power concentration, unlike autocracy, promoting fairness.
- Example: India’s democracy enables diverse groups to elect leaders, fostering unity.
- Discuss: How does democracy empower individuals compared to other systems?
Features of the Constitution of India
- The Constitution is a written document guiding India’s governance, drafted under Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
- It includes fundamental rights (e.g., right to equality) and directive principles for welfare.
- It establishes a federal structure with a balance between central and state powers.
- It promotes secularism, justice, and liberty for all citizens.
- Discuss: Why is the Constitution called the backbone of Indian democracy?
Freedom of Speech
- Freedom of speech, a fundamental right, allows citizens to express opinions freely.
- It strengthens democracy by enabling debate, criticism, and transparency.
- Example: Media exposes government flaws, ensuring accountability.
- It must be used responsibly to avoid harm or misinformation.
- Discuss: How can freedom of speech be balanced with social harmony?
Dictatorship vs. Democracy
- Democracy involves elected governments accountable to people; dictatorship concentrates power in one ruler.
- Democracy ensures equality and freedom; dictatorship often suppresses rights.
- Example: India’s democratic elections vs. authoritarian regimes like North Korea.
- Dictatorship may lead to efficiency but risks oppression; democracy prioritizes fairness.
- Discuss: Which system better ensures citizen welfare and why?
Qualities of an Ideal Politician
- An ideal politician is honest, transparent, and committed to public welfare.
- They listen to people’s needs and work for equality and justice.
- They avoid hero-worship and prioritize constitutional values.
- Example: Leaders like Dr. Ambedkar focused on uplifting the marginalized.
- Discuss: What traits make a politician trustworthy in a democracy?
Equality Before Law
- Equality before law ensures no one is above the legal system, regardless of status.
- It is enshrined in the Indian Constitution under Article 14.
- It prevents discrimination based on caste, religion, or wealth.
- Example: Courts treat all citizens equally, ensuring justice.
- Discuss: How does equality before law strengthen democracy?
(ii) State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statements.
(a) There is nothing wrong in being grateful to great men.
- True.
- Explanation: Dr. Ambedkar states there is nothing wrong in being grateful to great men for their contributions, but gratitude should not compromise liberty or lead to hero-worship.
(b) Hero-worship leads to dictatorship.
- True.
- Explanation: Ambedkar warns that excessive hero-worship in politics can lead to degradation and dictatorship, as it undermines critical thinking and democratic principles.
(c) Liberty cannot be divorced from equality.
- True.
- Explanation: Ambedkar emphasizes that liberty and equality are interconnected; without equality, liberty becomes superficial, as social and economic inequalities limit true freedom.
(d) One man one vote and one vote one value.
- True.
- Explanation: This principle, highlighted by Ambedkar, is fundamental to political democracy, ensuring every citizen’s vote has equal weight in elections.
(e) Fraternity means common sense.
- False.
- Corrected Statement: Fraternity means a sense of common brotherhood among all people.
- Explanation: Ambedkar defines fraternity as a sense of unity and solidarity among Indians, essential for social stability, not merely common sense.
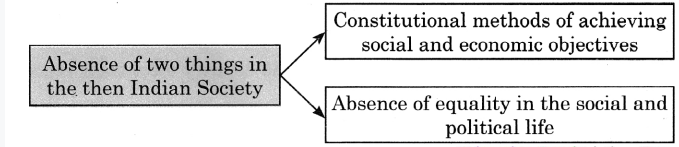
(iii) In his speech, Dr. B. R. Ambedkar has expressed his deep concern over the absence of two things in the then Indian society. Discuss with your partner and complete the web.
Answer:-
(A2)
(i) Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar has cited the quotes by John Stuart Mill and Daniel O’Connel. Go through the lesson and write down 4 to 5 lines for each of them.
John Stuart Mill
- John Stuart Mill, a philosopher, cautioned against giving too much power to any individual.
- Dr. Ambedkar cites him to warn against laying liberties at the feet of a great man.
- Such unchecked power can enable someone to subvert democratic institutions.
- This emphasizes the need to protect democracy by limiting excessive authority.
- Example: A leader with absolute power may undermine democratic checks and balances.
Daniel O’Connel
- Daniel O’Connel, an Irish patriot, stated, “No man can be grateful at the cost of his honour, no woman at the cost of her chastity, and no nation at the cost of its liberty.”
- Ambedkar uses this to highlight that gratitude to leaders should not compromise liberty.
- Excessive devotion to individuals risks a nation’s freedom and democratic values.
- This warns against hero-worship, which can lead to degradation and dictatorship.
- Example: Blind loyalty to a leader can erode a nation’s independence.
(ii) Discuss with your partner and make a list of steps that you feel are essential to unite the people of different castes, races, religions, and languages in India.
- Promote Education: Educate people about unity and respect for diversity to reduce prejudice.
- Encourage Interfaith Dialogue: Organize events where people from different religions share values.
- Celebrate Cultural Diversity: Hold festivals showcasing traditions of various castes and communities.
- Enforce Anti-Discrimination Laws: Strictly implement laws to prevent caste or racial discrimination.
- Youth Engagement: Involve youth in community projects to foster brotherhood across groups.
- Media Campaigns: Use media to promote messages of unity and fraternity among all Indians.
- Equal Opportunities: Ensure equal access to jobs and education for all communities.
(iii) Write your views/opinions in brief on the following topics.
(a) We must always cast our vote.
- Voting is a fundamental right and duty in a democracy.
- It ensures citizens’ voices shape the government and policies.
- Not voting allows others to decide the nation’s future.
- Example: Low voter turnout can lead to unrepresentative governments.
- Casting votes strengthens democracy and accountability.
(b) Liberty, equality, and fraternity lead to an ideal nation.
- Liberty ensures freedom of thought, speech, and action for all.
- Equality provides equal opportunities, preventing discrimination.
- Fraternity fosters unity and brotherhood among diverse groups.
- Together, these principles create a just, inclusive, and stable nation.
- Example: India’s Constitution embodies these for an ideal society.
(c) Steps to be taken to eradicate inequality.
- Implement strict laws against discrimination based on caste, gender, or religion.
- Provide equal access to education and employment opportunities.
- Promote awareness campaigns to challenge stereotypes and biases.
- Ensure economic policies uplift marginalized communities.
- Encourage inclusive representation in governance and institutions.
(d) Role of youth in creating social awareness.
- Youth can use social media to spread awareness about social issues.
- They can organize campaigns to promote equality and unity.
- Participating in community service fosters empathy and understanding.
- Example: Youth-led movements can challenge caste or gender discrimination.
- Their energy and innovation drive positive social change.
(A3)
(i) Let’s use the Thesaurus. Along with your partner, go to library or search the internet for a standard Thesaurus to complete the following table. One is done for you.
| Sr. No. | Word | Type | Synonym | Antonym |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | observe | verb | notice, discern, detect, mark | ignore, overlook |
| 2. | abandoned | verb | deserted, forsaken, left | occupied, retained |
| 3. | grateful | adjective | thankful, appreciative, obliged | ungrateful, unappreciative |
| 4. | initiative | noun | drive, enterprise, leadership | passivity, inertia |
| 5. | peril | noun | danger, risk, hazard | safety, security |
| 6. | separation | noun | division, parting, detachment | union, connection |
(ii) Homograph: Homograph is a word spelt and pronounced like another word but with a different meaning.
For example: the word ‘fast’ has two meanings. The different meanings arefast- hold firmly fast- to abstain from food fast- opposite of slow
The different meanings are fast- hold firmly, fast- to abstain from food, fast- opposite of slow. Go through the text again and make a list of meanings of all the homographs that are found in the text. Also make a list of such words that you know, have heard or read somewhere.
Lead
- Meaning 1: To guide or direct (e.g., “He was assigned the big and challenging task of framing the Constitution”).
- Meaning 2: A heavy metal (not directly in text but contextually possible).
Fair
- Meaning 1: Just or impartial (e.g., implied in “equality before law”).
- Meaning 2: A gathering or exhibition (not directly in text but contextually relevant).
Right
- Meaning 1: A legal entitlement (e.g., “fundamental rights” in the Constitution).
- Meaning 2: Correct or opposite of left (e.g., “right to equality”).
Cast
- Meaning 1: To throw or vote (e.g., implied in “we must always cast our vote”).
- Meaning 2: A group or social class (e.g., “castes are anti-national”).
Additional Homographs Known, Heard, or Read Somewhere
Bat
- Meaning 1: A flying mammal.
- Meaning 2: A piece of equipment used in sports like cricket.
Bank
- Meaning 1: A financial institution.
- Meaning 2: The side of a river.
Match
- Meaning 1: A contest or game.
- Meaning 2: A small stick used to create fire.
Wave
- Meaning 1: A movement of the hand as a greeting.
- Meaning 2: A surge of water or energy.
Tear
- Meaning 1: To rip something apart.
- Meaning 2: A drop of water from the eye
(A4)
(i) Go through the statement taken from the text – ‘The social democracy means a way of life which recognises liberty, equality and fraternity’.
(a) In Politics we will be recognizing the principle of ‘one man one vote’ and ‘one vote one value’.
- Which principle will we be recognizing in politics?
(b) The politically minded Indians preferred the expression ‘the Indian nation’.
- Which expression did the politically minded Indians prefer?
(c) Fraternity means a sense of common brotherhood of all Indians.
- What does fraternity mean?
(A5)
How to prepare a speech.
With the help of the steps given above, write speeches on the following topics.
• Duties of an ideal citizen
• Equality: A blessing
• Merits of democracy
• Freedom of speech
• Advantages of education
• Unity in Diversity
Speech 1: Duties of an Ideal Citizen
Greeting and Salutation:Respected Principal, teachers, and my dear friends,It is a matter of pride for me to share my views on “Duties of an Ideal Citizen” in front of this august gathering.
Introduction:Citizens are the backbone of a nation. An ideal citizen is not merely someone who enjoys rights, but someone who also performs their duties sincerely. Today, I would like to highlight the responsibilities that make one an ideal citizen.
Main Body:An ideal citizen obeys laws, respects the Constitution, and promotes harmony in society. They participate actively in civic duties, like voting. They contribute to cleanliness, save resources like water and electricity, and pay taxes honestly.As Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar said, “We must hold fast to constitutional methods of achieving our social and economic objectives.” Hence, every citizen should act within legal and moral boundaries.
Suggestions:Let’s educate people about their rights and duties. Let’s inculcate values of discipline, respect for diversity, and commitment to public service among youth.
Conclusion:Thank you for giving me this opportunity to express my thoughts. And thank you all for listening patiently.Remember: “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.” – John F. Kennedy
Speech 2: Equality – A Blessing
Greeting:Respected dignitaries and dear friends,It’s an honour to speak on the topic “Equality – A Blessing”.
Introduction:Equality is the soul of democracy. It means treating every individual with fairness and without discrimination. But is our society truly equal?
Main Body:Dr. Ambedkar rightly stated that in politics we have equality, but in social and economic life, inequality persists. Casteism, gender bias, and class differences still exist.Is it fair that two children with the same talent have unequal chances just because of their background?Equality is a blessing because it ensures that everyone gets equal rights, opportunities, and dignity.
Suggestions:We must remove social evils like caste discrimination and gender inequality. Promote inclusive education, reservation policies, and awareness campaigns. Respect every individual irrespective of their background.
Conclusion:Thank you for the opportunity to voice this concern. Together, let us make equality not just a constitutional promise, but a reality in every home, school, and workplace.
Speech 3: Merits of Democracy
Greeting:Honourable Principal, respected teachers, and my dear friends,I feel proud to speak today on a topic that lies at the heart of our nation – “Merits of Democracy.”
Introduction:Democracy means government of the people, by the people, and for the people – as said by Abraham Lincoln. It gives citizens the power to participate in governance and ensures their rights and freedoms.
Main Body:One of the greatest merits of democracy is liberty – freedom to express, act, and believe. Second, democracy ensures equality – one person, one vote, one value. It promotes fraternity, encouraging unity and brotherhood.Unlike dictatorship, democracy promotes accountability, transparency, and peaceful change of power. Citizens can criticize the government and demand better policies.
Suggestions:Let’s not take democracy for granted. We must vote wisely, question injustice, and stand united for the democratic values of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Conclusion:Thank you for allowing me to speak on this powerful concept. As Dr. Ambedkar said, “Political democracy cannot last unless there lies at the base of it social democracy.”
Speech 4: Freedom of Speech
Greeting:Respected Principal, teachers, and dear classmates,It’s a privilege to present my thoughts on “Freedom of Speech” – a fundamental right and a cornerstone of democracy.
Introduction:Freedom of speech is the right to express our thoughts without fear. It empowers citizens, strengthens democracy, and fuels progress. But are we using it responsibly?
Main Body:Freedom of speech allows journalists to report truth, activists to demand justice, and citizens to express disagreement. However, this freedom should not be misused to spread hate or fake news.Dr. Ambedkar emphasized constitutional methods. Freedom comes with responsibility. Speech must never hurt others’ dignity or incite violence.
Suggestions:Let’s encourage healthy debates, critical thinking, and responsible use of social media. Freedom of speech must be preserved, but with respect for others’ rights and the unity of the nation.
Conclusion:Thanks to the organizers and all of you for your time. Let us pledge to use our voice not to divide, but to enlighten and uplift. “I disapprove of what you say, but I will defend to the death your right to say it.” – Voltaire
Speech 5: Advantages of Education
Greeting:Honourable dignitaries and dear audience,I am grateful for the chance to speak on a life-changing tool – “Advantages of Education.”
Introduction:Education is the most powerful weapon we can use to change the world – said Nelson Mandela. It shapes our personality, thinking, and future.
Main Body:Education teaches us to distinguish right from wrong, to question, and to innovate. It opens up opportunities, removes poverty, and empowers individuals, especially women.In a democracy, educated citizens can choose better leaders and resist injustice. Dr. Ambedkar himself rose through the power of education and uplifted an entire community.
Suggestions:We must ensure education reaches every child. Equal opportunity, skill-based training, and removal of gender disparity are vital.
Conclusion:Thank you for listening so attentively. Education doesn’t just build careers – it builds nations. Let’s cherish and spread its light everywhere.
Speech 6: Unity in Diversity
Greeting:Respected teachers and friends,Today I feel honoured to speak on the beautiful strength of our nation – “Unity in Diversity.”
Introduction:India is a land of different cultures, languages, and religions. Yet, we stand together as one – because our unity is stronger than our differences.
Main Body:Despite being home to thousands of castes, customs, and beliefs, India celebrates every festival, shares common history, and protects the spirit of democracy.Dr. Ambedkar rightly said that fraternity gives unity and solidarity to social life. But this unity doesn’t come automatically – it must be protected against hatred and division.
Suggestions:Let us rise above caste, religion, and language barriers. Promote intercultural understanding, and respect every Indian as a brother or sister. Unity ensures peace, progress, and pride.
Conclusion:Thank you for this opportunity. Let us remember: “We may have different religions, different languages, different coloured skin, but we all belong to one human race.”

Leave a Reply