Tertiary Economic Activities
Introduction
- Economic Activities: Human activities that generate income are called economic activities. They are divided into:
- Primary Activities: Directly depend on nature (e.g., farming, fishing, mining).
- Secondary Activities: Process raw materials from primary activities to make finished goods (e.g., manufacturing, textile production).
- Tertiary Activities: Provide services to support primary and secondary activities (e.g., transport, trade, communication, tourism).
- Tertiary Activities: These are service-based activities that link primary and secondary sectors. Examples include transportation, trade, communication, banking, and tourism.
Case Study: Entrepreneurs and Their Ventures
Rohit (Farmer’s Son):
- Plans to grow export-quality crops like lilies, orchids, kiwis, and dragon fruits.
- Needs to modify farmland (control moisture, temperature, soil pH) and use special fertilizers.
- Requires a license, foreign transaction account, and saplings.
- Targets Gulf countries for export due to high demand and proximity (freshness maintained during air transport).
Sejal (Businessman’s Daughter):
- Wants to produce toothpaste (FMCG product) using an advanced formula for dental health.
- Needs machinery, labor, land, No Objection Certificates (NOCs), packaging industries, and advertising.
- Benefits from government start-up schemes for subsidized loans; her father provides land.
Asif (Hotel Owner’s Son):
- Plans to start an event management company.
- Requires services like catering, florists, hall rentals, and permissions from authorities.
- Sets up an office and uses brochures and visiting cards for marketing.
Key Points:
- All three engage in tertiary activities (services like trade, event management) but interact with primary (farming) and secondary (manufacturing) sectors.
- They need permissions from competent authorities (government bodies that issue licenses/NOCs).
Questions from the Case Study
Competent Authorities: Government officials or departments that grant permissions, licenses, or NOCs for businesses.
Economic Activities:
- Rohit: Primary (agriculture) and tertiary (export trade).
- Sejal: Secondary (toothpaste manufacturing) and tertiary (trade, advertising).
- Asif: Tertiary (event management services).
Interactions:
- Rohit interacts with agricultural officers (tertiary) and foreign vendors (tertiary).
- Sejal collaborates with pharmaceutical experts (tertiary) and packaging industries (secondary).
- Asif works with caterers, florists, and hall owners (tertiary).
Classification of Activities:
- Primary: Farming (Rohit’s crops).
- Secondary: Toothpaste production, packaging (Sejal).
- Tertiary: Export trade, event management, advertising, licensing, banking.
Understanding Tertiary Activities
Definition: Tertiary activities provide services to support primary and secondary sectors. They involve buying/selling goods, transportation, communication, banking, tourism, etc.
Examples:
- Trade (wholesale, retail).
- Transportation (road, rail, air, water).
- Communication (phone, internet, postal services).
- Services (banking, insurance, tourism, education).
Characteristics:
- Do not directly derive products from nature (unlike primary).
- May produce some goods (e.g., brochures in event management) but focus on services.
- Act as a link between primary and secondary activities.
Geographical Influence:
- Climate, topography, and location affect tertiary activities (e.g., ports need coastal areas, airports need flat land).
- Markets are located near human settlements, influenced by geographical factors.
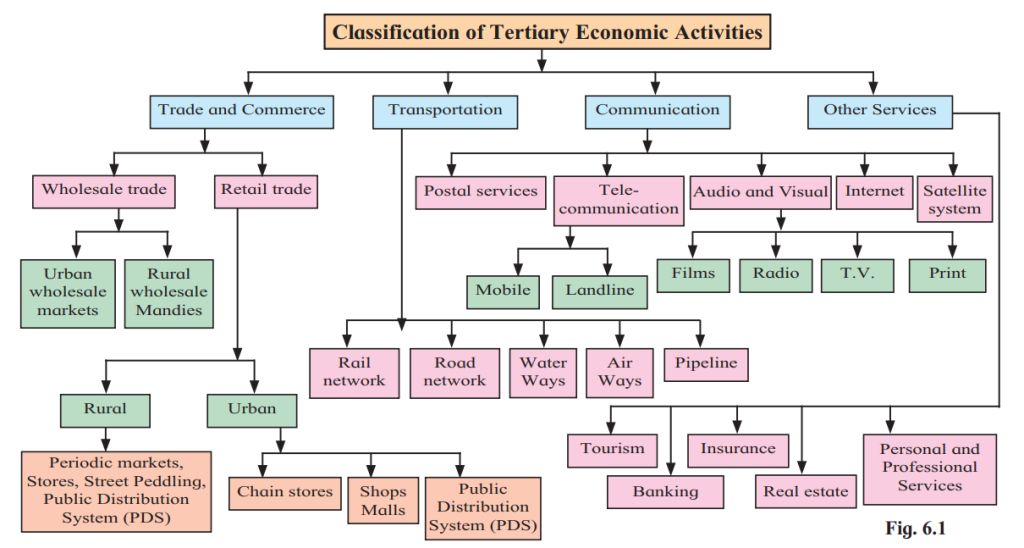
Classification of Tertiary Activities (Fig. 6.1)
Trade and Commerce:
- Wholesale (urban/rural markets, mandies).
- Retail (shops, chain stores, malls, street peddling).
- Public Distribution System (PDS).
Transportation:
Rail, road, waterways, airways, pipelines.
Communication:
Postal services, telecom (landline, mobile, internet), media (TV, radio, films, print).
Other Services:
- Tourism, banking, insurance, real estate, personal/professional services.
- Dependent on Geography: Waterways, ports, tourism (e.g., coastal areas for ports, scenic areas for tourism).
- Not Dependent on Geography: Banking, telecom, retail (can function anywhere with infrastructure).
Transportation
Definition: A tertiary activity that moves people, goods, or industrial products from one place to another.
Importance:
- Essential for trade and economic development.
- Connects production areas to markets.
Types:
- Land: Roads, railways, pipelines.
- Water: Sea routes, canals (e.g., Suez, Panama).
- Air: Airways for fast transport.
Geographical Factors:
- Relief: Flat areas are easier for roads/railways; rugged terrains (mountains, forests) are challenging.
- Climate: Fog, snow, or high peaks can hinder air transport.
- Location: Coastal areas favor ports; inland areas need roads/railways.
Examples:
- Suez Canal: Connects Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- Panama Canal: Links Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
- Airways: Used for perishable goods like grapes; sea transport for bulk goods like cotton.
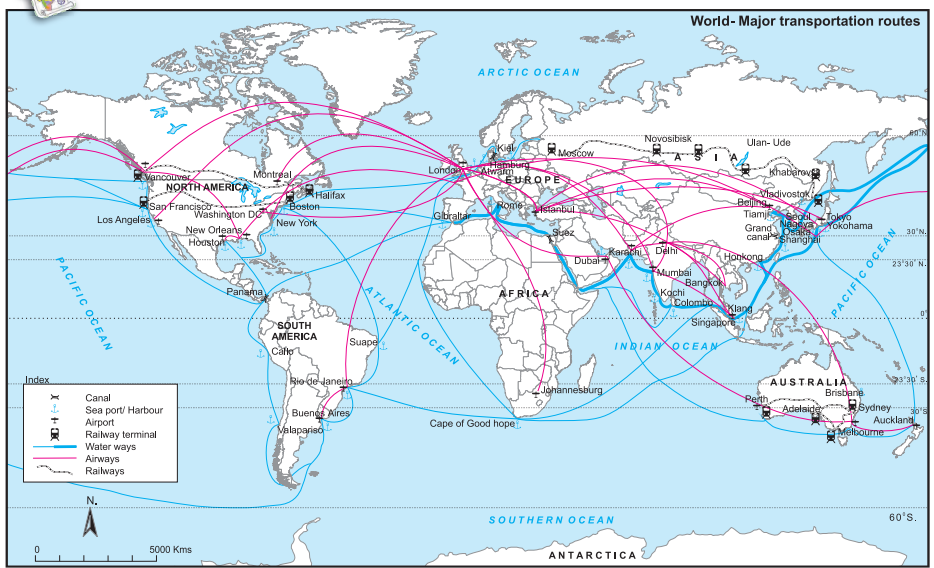
Map-Based Questions (Fig. 6.2)
- Transportation Means: Railways, airways, waterways.
- Higher Flow: Between North America and Europe (dense trade routes).
- Canals: Suez and Panama; they shorten sea routes for trade.
- Indian Cities: Mumbai and Delhi (international airports).
- Less Air Routes: Africa and South America (less developed infrastructure).
- Less Rail Routes: Africa and Australia (sparse population, rugged terrain).
- Intercontinental Rail: Trans-Siberian Railway (Asia to Europe).
- Australia’s Routes: Southern parts are more populated, so more routes; northern parts are arid.
- No Continuous Rail in Africa: Dense forests, deserts, and political instability.
Trade
- Definition: Voluntary exchange of goods and services between parties (individuals, countries).
- Types:
- Bilateral: Trade between two countries.
- Multilateral: Trade among multiple countries.
- Internal: Trade within a country.
- Factors Affecting Trade:
- Natural Resources: Uneven distribution (e.g., Gulf countries export oil, import grains).
- Climate: Affects crop/animal production (e.g., tropical countries export tea, coffee).
- Population: Dense populations need more imports; skilled populations (e.g., IT in India) drive service exports.
- Culture: Unique products (e.g., Kashmiri shawls, Chinese porcelain) have global demand.
- Economic Cost: Importing is cheaper than producing if conditions are unfavorable.
- Specialization: Countries export specialized goods/services (e.g., Israel’s dry farming).
- Government Policies: Free trade policies promote trade; restrictions limit it.
- Example:
- Country A (500 tons wheat, 200 laborers) vs. Country B (1000 tons wheat, 300 laborers): Trade may occur if B is more efficient.
- Country C (tea) and D (coffee): Trade occurs due to specialization.
- Country E (water engineering) and F (metro-making): Trade in services due to expertise.
Tourism
- Definition: A tertiary activity where people travel for leisure, culture, or adventure, contributing to a country’s economy.
- Importance:
- Contributes to GDP and employment (e.g., Maldives: 38.92% GDP, Aruba: 29.91% employment).
- Boosts local businesses (hotels, transport, guides).
- Geographical Factors:
- Physical: Climate, biodiversity, scenic beauty, beaches, mountains.
- Human: Transport, lodging, cultural diversity, government policies.
- Examples:
- Island countries (Maldives, Seychelles) thrive on tourism due to beaches and climate.
- Low tourism in countries like Congo (0.66% GDP) due to political instability, dense forests, and poor infrastructure.
- Planning in Tourism:
- Needed to manage resources, reduce negative impacts (e.g., environmental damage), and boost positive impacts (e.g., employment).
- Involves communities for sustainable development.
- Long-term process to improve infrastructure and attractiveness.
Communication
- Definition: A tertiary activity that involves sharing information through various means.
- Evolution:
- Past: Smoke signals, horsemen, telegrams.
- Present: Telephones, mobiles, internet, satellites.
- Importance:
- Satellites provide data on weather, minerals, and navigation.
- Drives regional development and global connectivity.
- Examples:
- Postal services, TV, radio, internet, mobile apps.
- Maps and GPS are communication tools (e.g., used in geography practicals).

Leave a Reply