Human Settlements and Land Use
Exercise
Q. 1) Identify the correct correlation: A: Assertion; R: Reasoning
1) A: Settlements can be of various types. R: Various physical factors affect the growth of settlements.
Answer: 3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Settlements vary in types (e.g., compact, dispersed) due to physical factors like relief, water availability, and climate, which influence their growth and development.
2) A: When cities grow, their functions also grow. R: Cities can have only one function.
Answer: 1) Only A is correct.
Explanation: As cities grow, they take on multiple functions (e.g., administrative, commercial), but the reasoning is incorrect because cities typically perform multiple functions, not just one.
Q. 2) Give geographical reasons:
1. Not all rural settlements change into urban settlements.
Rural settlements may lack infrastructure, such as roads or industries, needed for urban growth.
Limited economic opportunities prevent population growth and urbanization.
Physical factors, like rugged terrain or poor water supply, may restrict development.
2. In rural settlements, land use is related to agriculture.
Rural areas have fertile soils and open land suitable for farming.
The economy in rural settlements is primarily agriculture-based, supporting crops and livestock.
Limited industrial or commercial activities focus land use on agricultural purposes.
3. Rural-urban fringes have the characteristics of both urban and rural settlements.
These areas are transitional, blending rural agricultural land with urban residential or industrial zones.
They feature mixed land use, including farms, housing, and small businesses.
Residents may commute to urban centers for work while living in less dense, rural-like settings.
4. Growth of urban areas is linked to land use.
Urban growth increases demand for residential, commercial, and industrial land.
Land use changes from agriculture to built-up areas as cities expand.
Infrastructure development, like roads and public buildings, drives urban land use patterns.
Q. 3) Write short notes on:
1) Interrelationship between rural and urban settlements
Rural and urban settlements are interdependent. Rural areas supply food, raw materials, and labor to urban centers, while urban areas provide markets, services, and manufactured goods to rural regions. Rural-urban migration drives urban growth, and urban sprawl often encroaches on rural land, creating fringes with mixed characteristics.
2. Problems of urban settlements
Urban settlements face issues like:
- Overcrowding: High population density strains resources.
- Traffic congestion: Increased vehicles cause delays and pollution.
- Housing shortages: Demand exceeds affordable housing supply.
- Environmental degradation: Pollution and waste management challenges arise.
- Unemployment: Rapid migration can outpace job creation.
3. Suburbs
Suburbs are smaller towns or cities on the outskirts of a major city, developed due to urban expansion. They offer less dense living environments with access to urban amenities. For example, Kalyan and Virar are suburbs of Mumbai, providing residential and commercial spaces for commuters.
4. Mixed land use
Mixed land use refers to areas where multiple activities—residential, commercial, and industrial—coexist. Common in urban settings, it integrates houses, shops, schools, and offices, enhancing convenience but potentially causing congestion or land use conflicts. Examples include city centers with diverse functions.
Q. 4) Answer the following questions:
1. Explain the characteristics of rural settlements.
Size and density: Small, with low population and sparse housing.
Land use: Primarily agricultural, focusing on farming and livestock.
Economic activities: Agriculture-based, with limited industrial or commercial functions.
Social structure: Close-knit communities with strong social bonds.
Infrastructure: Basic, with fewer roads, schools, or hospitals compared to urban areas.
Settlement patterns: Often dispersed or clustered, depending on terrain and resources.
2. What factors are responsible for development of various patterns in a settlement? Give examples.
Physical factors:
Water availability: Circular patterns form around lakes (e.g., settlements near Dal Lake).
Terrain: Linear patterns develop along flat riverbanks or roads (e.g., villages along the Ganges).
Economic factors:
Trade routes: Radial patterns emerge around market centers (e.g., towns around a trading post).
Social factors:
Security: Nucleated settlements form for protection (e.g., medieval villages).
Infrastructure:
Planned layouts: Rectangular patterns in modern cities (e.g., Chandigarh).
Cultural factors:
Religious sites: Settlements grow around temples or shrines (e.g., Varanasi).
Q. 5) Differentiate between:
1. Land use and Land cover
Land use: Describes how humans utilize land (e.g., agriculture, residential). Example: A park used for recreation.
Land cover: Refers to the physical surface of land (e.g., forest, water). Example: A park covered with grass or trees.
2. Barren and Non-agricultural land
Barren land: Uncultivable due to natural limitations like rocky terrain or deserts. Example: Ravines.
Non-agricultural land: Used for settlements, roads, or industries, not farming. Example: Urban housing areas.
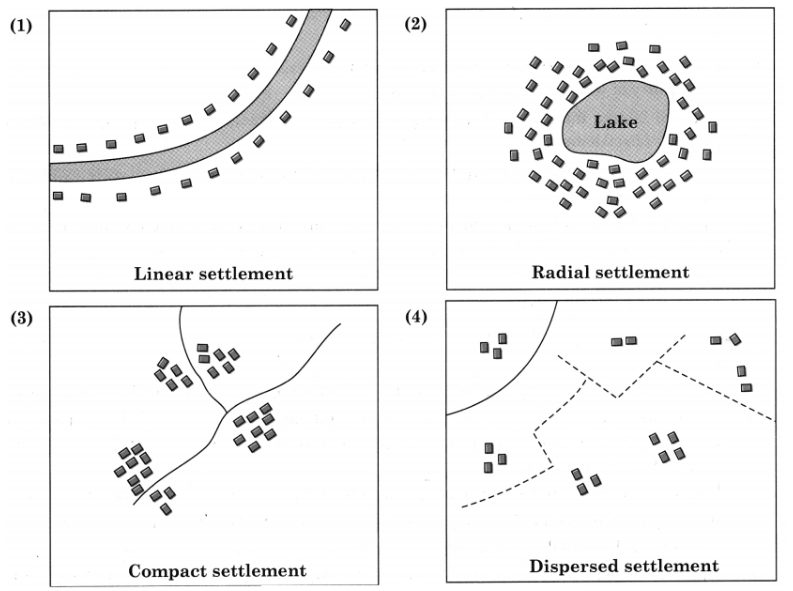
3. Radial pattern and Circular pattern
Radial pattern: Settlements radiate from a central point (e.g., market or temple). Example: A town around a plaza.
Circular pattern: Settlements encircle a feature like a lake, driven by water availability. Example: Villages around a pond.
4. Nucleated and Dispersed settlement
Nucleated settlement: Houses are closely packed in a cluster, often for security or resource access. Example: Villages in Rajasthan.
Dispersed settlement: Houses are spread out, typically in areas with extensive agriculture. Example: Farmsteads in Punjab.
Q. 6) Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram for :
1) Linear settlement
2) Radial settlement
3) Compact settlement
4)Dispersed settlement
Answer:
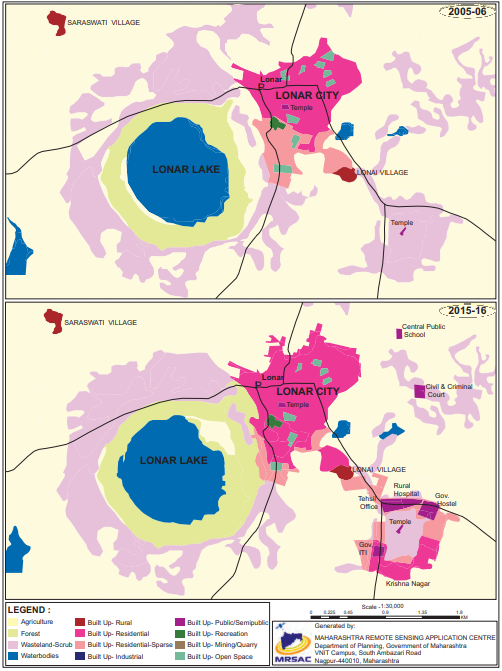
Q. 7) Write a note in your own words about how land use in Lonar city has evolved over time.
Answer:
Two maps of Lonar city are given. One map is of the year 2005-06 and another is of 2015-16.
These two maps show the changes in land use that have taken place in the span of 10 years.
The following changes have been registered.
There is no change in the size of Lonar lake.
The area occupied by Lonar city has increased substantially.
Forest area around the lake has increased.
An area under waste land/ scrubs have increased.
Around the temple in the southeast, on the waste scrub land a new rural hospital, government hostel, government ITI, Tahsil office etc., has been developed. This newly developed area has been named as Krishna Nagar, which is not in 2005-06 map.
To the north-east of the Lonar city two more building have been constructed. One is central public school and another is civil and criminal court.
To the south of the temple in the heart of Lonar city built up residential area is spreading over built up residential sparse.
Overall built up residential sparse is increasing in all directions around Lonar lake and south-eat of the Lonar city and thus there is encroachment over agricultural land.
Q. 8) Read the given passage and answer the following questions:
1. Which human settlements are mentioned in the passage above?
Answer: Hamlets, villages, small towns, large towns, isolated places, cities, and conurbations.
2. On what basis are urban and rural areas classified?
Answer: Urban and rural areas are classified based on population size, density, and access to services, as per precise definitions (e.g., by the U.S. Census Bureau).
3. What functions are carried out in rural settlements?
Answer: Rural settlements focus on functions like farming, fishing, and mining, often tied to natural resources.
4. Explain the difference between low-order service and high-order service settlements.
Answer:
Low-order service settlements: Small settlements (e.g., villages) with limited services, like one or two general stores, serving basic needs.
High-order service settlements: Larger settlements (e.g., cities) with higher populations, greater density, and specialized services, like chain stores and advanced facilities.

Leave a Reply