Primary Economic Activities
Solutions
Exercise
Q. 1) Choose the correct option and complete the sentence:
1. Gathering of various products from the forests for livelihood is mainly carried in:
Answer: d) Equatorial evergreen forests
(Explanation: Gathering is prevalent in equatorial forests where tribes collect fruits, roots, and other forest products.)
2. Ideal location for fishing:
Answer: b) shallow seas, confluence of warm and cold ocean currents, growth of planktons, cold climate
(Explanation: These conditions, as seen near Japan, support abundant fish populations.)
3. Primary economic activity not related directly to latitudinal locations:
Answer: c) mining
(Explanation: Mining depends on the presence of minerals, not latitude, unlike agriculture or lumbering.)
4. Characteristics of extensive commercial agriculture:
Answer: b) monoculture, use of machinery, tropical, cereal production
(Explanation: Extensive agriculture involves large-scale monoculture with mechanization, often for cereals in tropical or temperate regions.)
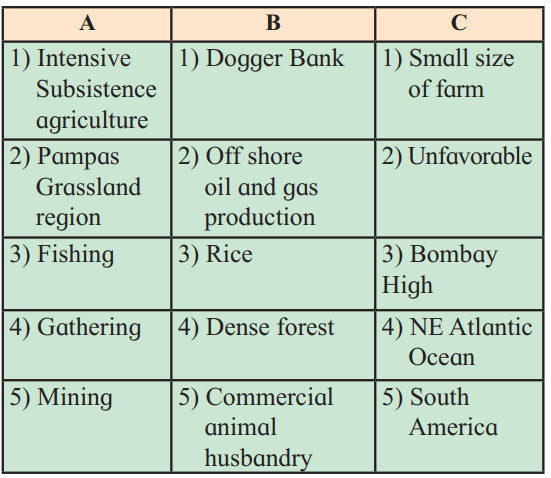
Q. 2) Complete the chain:
Answer:
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Intensive subsistence agriculture | (1) Rice | (1) Small size of farm |
| (2) Pampas grassland region | (2) Commercial animal husbandry | (2) South America |
| (3) Fishing | (3) Dogger bank | (3) NE Atlantic Ocean |
| (4) Gathering | (4) Dense forest | (4) Unfavourable Climate |
| (5) Mining | (5) Off shore oil and gas production | (5) Bombay high |
Q. 3) Write short notes on:
1. Plantation agriculture:
Plantation agriculture is a type of commercial farming practiced in tropical regions, focusing on a single crop like tea, coffee, rubber, or sugarcane. It requires large estates, significant capital investment, and a warm, humid climate with fertile soils. Plantations often use advanced technology and employ local labor, with products mainly exported to developed countries. Examples include tea plantations in India and rubber plantations in Malaysia.
2. Physical factors and fishing:
Physical factors influencing fishing include wide continental shelves with shallow waters (e.g., Dogger Bank), confluence of warm and cold ocean currents (e.g., Kuroshio and Oyashio near Japan), and abundant plankton growth, which supports fish populations. Cold climates aid natural fish preservation, while broken coastlines provide ports. These factors make areas like the North-West Pacific ideal for fishing.
3. Lumbering on a commercial scale:
Commercial lumbering involves large-scale tree felling for timber, primarily in coniferous forests of mid-latitudes (e.g., Canada, Russia). These forests have tall, single-species trees suitable for timber. Advanced machinery and transportation facilitate the industry. However, tropical forests are less viable due to dense, mixed hardwood species. Overexploitation has led to deforestation concerns.
4. Hunting and loss of ecosystem:
Hunting, once a subsistence activity, has caused significant ecosystem damage. Large-scale hunting has led to the extinction or endangerment of species like certain mammals and birds. This disrupts food chains, reduces biodiversity, and affects forest regeneration. Tribes like the Bushmen still hunt for livelihood, but commercial hunting is banned globally to protect ecosystems.
Q. 4) Give geographical reasons:
1. Agriculture is done on a large scale in India:
India’s large-scale agriculture is due to its vast fertile plains (e.g., Indo-Gangetic), favorable monsoon climate, and high population providing labor. Diverse crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane are grown to meet food demands.
2. Mining is developed in the Chhota Nagpur plateau of India:
The Chhota Nagpur plateau is rich in minerals like coal, iron ore, and bauxite. Its geological structure, coupled with proximity to industrial centers and transportation networks, supports large-scale mining.
3. Lumbering is developed on a large scale in Canada:
Canada’s vast coniferous forests, with tall, single-species trees, are ideal for commercial lumbering. Cold climates, advanced technology, and access to global markets via ports enhance the industry.
4. Extensive agriculture is a commercial type of agriculture:
Extensive agriculture involves large land areas with low labor input, using machinery for monoculture crops like wheat or maize. It aims for high yields for commercial markets, as seen in the Prairies or Steppes.
5. Lumbering is practised more in coniferous region than in tropical region:
Coniferous forests have uniform, tall trees suitable for timber, while tropical forests have dense, mixed hardwood species, making commercial lumbering difficult. Accessibility and market demand further favor coniferous regions.
6. Hunting has been banned:
Hunting is banned to prevent species extinction, protect biodiversity, and maintain ecological balance. Overhunting has depleted wildlife, prompting global conservation laws like the Wildlife Protection Act.
Q. 5) Differentiate between:
1. Lumbering in equatorial forests and temperate forests:
- Equatorial Forests: Lumbering is limited due to dense, mixed hardwood species, difficult terrain, and humid climate. It’s mostly subsistence-based.
- Temperate Forests: Commercial lumbering thrives in coniferous forests with tall, uniform trees, using advanced machinery. Examples include Canada and Russia.
2. Plantation agriculture and extensive commercial agriculture:
- Plantation Agriculture: Focuses on a single tropical crop (e.g., tea, rubber) on large estates, export-oriented, labor-intensive.
- Extensive Commercial Agriculture: Involves large-scale monoculture (e.g., wheat) in temperate regions, mechanized, with low labor input.
3. Mining and Fishing:
- Mining: Involves extracting non-renewable minerals (e.g., coal, oil) from land or sea, dependent on geological deposits, capital-intensive.
- Fishing: Harvesting renewable marine resources, reliant on physical factors like currents and plankton, skill-based in coastal areas.
Q. 6) Answer the following questions:
1. What are the factors affecting commercial fishing?
Answer:
Physical Factors: Wide continental shelves, shallow waters, confluence of warm and cold currents (e.g., Kuroshio-Oyashio), and plankton growth.
Human Factors: Traditional fishing skills (e.g., Japanese), large populations relying on fish (e.g., Japan), technology (e.g., trawlers), broken coastlines for ports, and cold climates for preservation.
Economic Factors: Market demand and lack of alternative occupations in coastal regions.
2. Write a note on Intensive Subsistence agriculture:
Answer: Intensive subsistence agriculture involves small plots cultivated with high labor input to maximize yield for family sustenance. Practiced in densely populated regions like South Asia (e.g., India), it focuses on crops like rice and wheat. Farmers use traditional methods, limited mechanization, and rely on monsoon rains. It supports large populations but has low per-capita output.
3. Give the characteristics of Market Gardening:
Answer:
Small-scale, intensive cultivation of high-value crops like vegetables, fruits, and flowers.
Located near urban markets for quick delivery.
Uses advanced techniques like greenhouses and irrigation.
Labor-intensive with high capital investment.
Examples: Netherlands, peri-urban areas of cities.
4. Write a note on the areas in the world practicing commercial animal husbandry:
Answer: Commercial animal husbandry is practiced in temperate grasslands between 30°N–60°N and 30°S–55°S, notably in North America (USA, Canada), South America (Argentina), and Australia. These regions have vast grasslands, advanced technology, and large estates for cattle and sheep rearing. Products like beef, wool, and dairy are exported. Dense forests and equatorial regions are less suitable due to poor fodder and climate.
5. Mining is dependent on the extraction of naturally occurring minerals. Explain:
Answer: Mining involves extracting naturally occurring minerals like coal, iron ore, or oil from the earth’s crust. Its distribution is uneven, depending on geological formations, not latitude. Factors like mineral value, capital, technology, skilled labor, and transportation influence mining. For example, oil extraction in the Arabian Sea requires advanced offshore technology. Mining supports industries, boosting economic development, but causes environmental pollution.
6. Write in detail about the characteristics of primary economic activities:
Answer: Primary economic activities involve direct exploitation of natural resources and include hunting, gathering, agriculture, animal husbandry, fishing, lumbering, and mining. Their characteristics are:
- Nature-Dependent: Reliant on climate, soil, topography, and resource availability.
- Geographical Variation: Distribution varies (e.g., fishing in coastal areas, lumbering in coniferous forests).
- Subsistence to Commercial: Ranges from subsistence (e.g., tribal hunting) to commercial (e.g., Canadian lumbering).
- Environmental Impact: Overexploitation causes deforestation, species loss, and pollution.
- Mechanization: Modern technology enhances output (e.g., trawlers in fishing, machinery in mining).
- Economic Importance: Forms the base for industries and supports livelihoods, especially in developing countries.
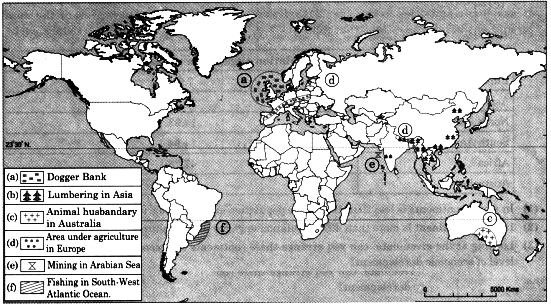
7. On an outline map of the world, show the following with appropriate symbols and prepare-an index.
(a) Dogger Bank fishing area.
(b) Area of lumbering in Asia.
(c) Area of animal husbandry in Australia.
(d) An area of agriculture in Europe.
(e) Mining area in Arabian Sea.
(f) Fishing area in South-West Atlantic Ocean.
Answer:
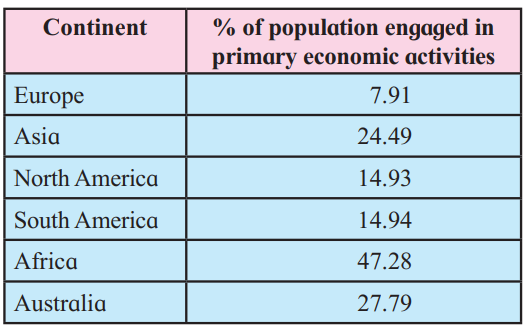
Q. 8) Given below is the data about the continentwise employment engaged in primary economic activities in the year 2018. Draw a suitable diagram to represent the data and answer the questions that follow :
1) In which continents is less than 10% of the population engaged in agriculture?
2) In which continent is more than 40% population engaged in agriculture?
3) Looking at the given data, can you arrange these continents in an ascending order on the basis of level of economic development?
Answer:
- In Europe, less than 10% population is engaged in agriculture.
- In Africa, more than 40% population is engaged in agriculture.
- Ascending order is as follows:
| Continent | % of Population |
|---|---|
| Africa | 47.28 |
| Australia | 27.79 |
| Asia | 24.49 |
| South America | 14.94 |
| North America | 14.93 |
| Europe | 7.91 |
Africa, Australia, Asia, South America, North America, Europe.

Leave a Reply