Secondary Economic Activities
Solutions
Exercise
Q. 1) Complete the chain:
Answer:
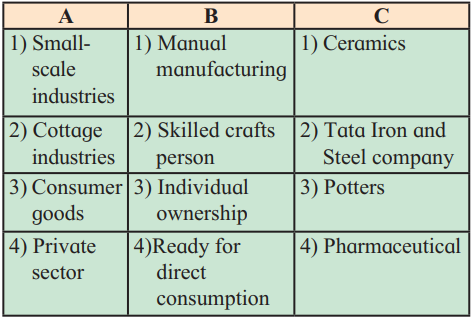
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| 1) Small scale industries | 1) Manual manufacturing | 1) Ceramics |
| 2) Cottage industries | 2) Skilled crafts person | 2) Tata Iron and Steel company |
| 3) Consumer goods | 3) Individual ownership | 3) Potters |
| 4) Private sector | 4) Ready for direct consumption | 4) Pharmaceutical |
Q. 2) Identify the correct correlation: A: Assertion; R: Reasoning
1. A: The humid climate of Mumbai offered great scope for the development of cotton textile industries.
R: Industries require ample amount of water.
Answer: 3) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Mumbai’s humid climate prevents cotton threads from breaking during spinning, and the cotton textile industry requires water for processing, making both statements correct with R explaining A.
A: In India, industries are found concentrated in few areas are available.
R: India is predominantly agrarian country.
Answer: 4) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Industries in India are concentrated in specific regions (e.g., Mumbai-Pune corridor) due to factors like raw material availability and infrastructure, not directly because India is agrarian. Both statements are true, but R does not explain A.
Q. 3) Give geographical reasons:
1. Distribution of industries is uneven.
Industries are concentrated in areas with favorable physical factors (e.g., availability of raw materials, water, and power) and economic factors (e.g., proximity to markets, capital availability).
Harsh climates, like extreme heat or cold, discourage industrial setup in certain regions (e.g., Northwest India).
Infrastructure, such as transportation and communication, is better developed in specific pockets, leading to industrial agglomeration in those areas.
2. Iron and steel industries are found in mineral-rich area of Dhanbad.
Dhanbad is rich in coal and iron ore, essential raw materials for iron and steel production.
These industries are weight-losing, requiring large quantities of bulky raw materials, so they are located near mineral sources to reduce transportation costs.
Proximity to coal fields provides a cheap and abundant energy source for smelting processes.
3. Fruit-processing industries are found in Ratnagiri and Sindhudurg districts of Konkan region.
These districts are known for producing perishable fruits like mangoes and cashews, which require immediate processing to prevent spoilage.
Proximity to raw material sources reduces transportation costs and ensures fresh produce for processing.
The coastal location facilitates export of processed fruit products, enhancing market access.
4. Industrial growth in southern America is limited.
Southern America has rugged terrain, including the Andes Mountains, which hinders infrastructure development.
The region lacks large reserves of industrial minerals like coal and iron compared to North America or Europe.
Sparse population and limited market size reduce the economic viability of large-scale industries.
Q. 4) Short notes:
1. Footloose industries:
Footloose industries have no strong locational preference as their raw materials and finished products are lightweight and easily transportable. Examples include watch-making and diamond cutting. They can be set up in various locations due to low dependence on specific resources or markets, often leveraging advanced communication technologies for flexibility.
2. Public sector industries:
These are industries owned and managed by the government, with all investments and marketing controlled by state agencies. Examples include Bharat Heavy Electrical Limited (BHEL). They aim to serve public welfare, promote economic development in backward regions, and ensure equitable distribution of resources.
3. Economies of scale:
Economies of scale occur when industries concentrate in a region, reducing production costs due to shared infrastructure, skilled labor, and market access. This leads to agglomeration, attracting more industries, as seen in the Mumbai-Pune corridor, where complementary industries (e.g., automobiles and ancillary units) benefit from proximity.
4. Role of transportation in industries:
Transportation reduces economic distance by facilitating the movement of raw materials and finished goods. Low-cost transport is crucial for heavy, bulky, or perishable materials, influencing industry location (e.g., sugar mills near sugarcane fields). Efficient transport networks, like ports and railways, enhance market access and reduce costs, as seen in coastal industrial regions.
Q. 5) Differentiate between :
1) Weight-losing vs. Weight-gaining Industries
| Aspect | Weight-losing Industries | Weight-gaining Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw materials are bulky, but finished products are lighter. | Raw materials are lighter, but finished products are heavier/bulkier. |
| Location | Near raw material sources to reduce transport costs. | Near markets to minimize transport costs of bulky products. |
| Examples | Sugar mills, iron and steel industries. | Bakery, soft drink industries. |
2) Primary vs. Secondary Activities
| Aspect | Primary Activities | Secondary Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Direct extraction of resources from nature. | Processing of raw materials into finished products. |
| Examples | Agriculture, mining, fishing. | Manufacturing, construction, food processing. |
| Output | Raw materials (e.g., sugarcane, ores). | Finished goods (e.g., sugar, steel). |
3) Basic Industries vs. Consumer Industries
| Aspect | Basic Industries | Consumer Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Produce materials for other industries. | Produce goods for direct consumption. |
| Examples | Iron and steel, petrochemicals. | Textiles, electronics, pharmaceuticals. |
| Output | Raw materials for further manufacturing (e.g., steel). | Ready-to-use products (e.g., clothes, medicines). |
Q. 6) Answer the following:
1. Explain the physical factors affecting location of industries:
Answer:
- Climate: Moderate climates are ideal for industries, as harsh conditions (e.g., extreme cold or heat) hinder operations. For example, Mumbai’s humid climate supports cotton textiles.
- Availability of raw materials: Industries like sugar or jute mills are located near raw material sources (e.g., sugarcane fields) to minimize transport costs, especially for perishable or bulky materials.
- Water and power supply: Industries require water for processing (e.g., cooling, washing) and power (e.g., coal, electricity). They are often located near rivers or coal mines.
- Labour: Availability of skilled or semi-skilled labor influences location, with labor colonies often near large industries like textiles or mining.
- Transportation: Low-cost transport is key for moving heavy or perishable goods. Industries like cotton textiles may locate near ports for cheaper waterway transport.
- Site/land availability: Flat land with good transport connectivity is preferred. High land costs in urban areas push industries to rural areas like Chakan, Pune.
2. Explain the factors affecting location of sugar industries:
Answer:
- Proximity to raw materials: Sugarcane is perishable and loses weight and sugar content post-harvest, so sugar mills are located near sugarcane fields to reduce transport time and costs.
- Transportation: Efficient transport (e.g., roads or railways) is needed to move sugarcane quickly to mills, as seen in Solapur district’s sugar industries.
- Water supply: Sugar production requires water for processing and cleaning, so mills are often near rivers or canals.
- Market access: While secondary to raw material proximity, nearby markets for sugar and by-products (e.g., molasses) reduce distribution costs.
- Labour: Semi-skilled labor is required for harvesting and processing, often available in rural sugarcane-growing areas.
- Government policies: Subsidies, land grants, or incentives in regions like Maharashtra’s cooperative sector encourage sugar mill setups.
3. Describe the factors that are responsible for less development of industries in central Australia:
Answer:
- Harsh climate: Central Australia’s arid desert climate is unsuitable for industrial activities, lacking water for processing and cooling.
- Lack of raw materials: The region has limited mineral or agricultural resources compared to coastal areas, discouraging resource-based industries.
- Sparse population: Low population density means a small labor force and limited local markets, reducing industrial viability.
- Poor transportation: Remote areas lack developed road, rail, or port infrastructure, increasing transport costs for raw materials and goods.
- Land suitability: The rugged, arid terrain is unsuitable for large industrial setups, unlike the flat, accessible coastal regions.
- Economic focus: Australia’s economy prioritizes mining and agriculture, with industrial development concentrated in coastal cities like Perth and Sydney.
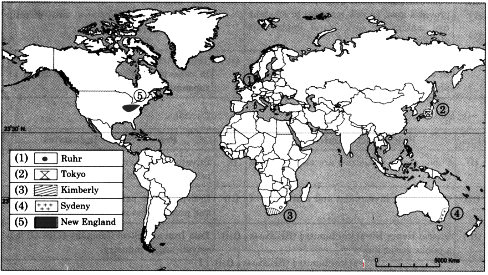
Q. 7) Show the following on a map of the world with suitable index :
1) Ruhr industrial region
2) An industrial region in Japan
3) An industrial region in South Africa
4) An industrial region in Australia
5) Industrial region near Great Lakes
Answer:

Leave a Reply