Tertiary Economic Activities
Solutions
Exercise
Q. 1) Complete the chain :
Answer:
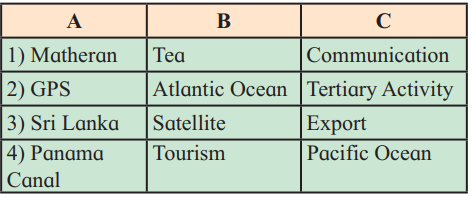
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Matheran | (1) Tourism | (1) Tertiary Activity |
| (2) GPS | (2) Satellite | (2) Communication |
| (3) Sri Lanka | (3) Tea | (3) Export |
| (4) Panama Canal | (4) Atlantic Ocean | (4) Pacific Ocean |
2. Choose the correct option.
1. Tertiary activities include
(a) Use of natural resources
(b) Finished product
(c) Raw material
(d) Transportation
Answer:
(d) Transportation
2. Natural ports
(a) Kochi
(b) JNPT
(c) Delhi International Terminal
(d) Nagpur Cargo Hub (MIHAN)
Answer:
(a) Kochi
3. Trans-Australian Railway connects
(a) Perth – Sydney
(b) Perth – Vladivostok
(c) Sydney – Vancouver
(d) Vancouver – Vladivostok
Answer:
(b) Perth – Vladivostok
3. Give geographical reasons.
1. Tertiary activities include both services and exchapge.
Answer:
Transportation, communication, trade and commerce are the main tertiary activities.
Road, rail and airways are the important modes of transportation, which help in exchange of goods and services. Therefore, it is a service activity.
Transportation provides facilities for the movement of goods from areas of surplus to areas of scarcity produced in primary and secondary activities.
Credit facilities, banking facilities, marketing are also tertiary activities, they provide services to people.
Postal services, shopkeepers, vegetable sellers, fruit sellers, etc., are also included in service activities.
2. The proportion of airways as means of transportation is increasing.
Answer:
Air transport is an important enabler to achieve economic growth and development.
In the global world, there is exchange of goods between countries. Therefore, there is more use of air transport to carry perishable, valuable and light goods from surplus areas to scarcity areas.
It facilitates integration into global economy and provides vital connectivity on a national, regional and international scale.
Nowadays tourism is the fastest growing industry; air transport is more used for international tourism.
Therefore, the proportion of airways as means of transportation is increasing.
3. Geographical diversity is responsible for trade to occur.
Answer:
The geographical diversity is the set of physical, human and cultural elements differentiated from each other that converge in the relatively small geographic space that is part of the same zone, region or country.
If you take into consideration natural regions of the world, each region is different from another.
The natural resource available in one country will be different from the ones available in different regions.
There is variation in climate, soil, minerals, forest, relief, water supply etc.
Depending upon the availability of geographical factors, there is specialisation of certain economic activities in certain areas and there is trade from surplus areas to scarcity areas. For example, in one region, plenty of oil is available while in another region no oil reserves are available.
This variation in distribution of oil will be responsible for the development of trade between oil rich and oil poor countries.
Thus, geographical diversity is responsible for trade to occur.
Q. 4) Short Notes:
1) Importance of Satellites as Means of Communication
Satellites are critical for modern communication, enabling global connectivity by transmitting signals for television, radio, internet, and mobile networks. They provide real-time data on weather, geographical locations, and natural phenomena like cyclones, aiding in disaster management and regional planning. Satellites facilitate navigation through GPS, support international trade by ensuring accurate logistics, and enable remote areas to access information, fostering economic and social development. Their ability to operate continuously makes them indispensable for communication and data collection.
2) Role of Transportation in Trade
Transportation is the backbone of trade, facilitating the movement of goods and services between producers and consumers. It connects regions and countries, enabling the exchange of raw materials, finished products, and perishable goods like agricultural produce. Efficient transportation systems, including roads, railways, waterways, and airways, reduce costs and time, enhancing trade competitiveness. Ports and airports are crucial for international trade, with sea and air routes handling significant global cargo. For instance, canals like Suez and Panama have revolutionized maritime trade by shortening routes, boosting economic efficiency.
3) Tourism and GDP
Tourism significantly contributes to a country’s GDP by generating revenue through visitor spending on accommodation, transport, food, and attractions. In countries like the Maldives (38.92% GDP contribution in 2018) and Seychelles (25.73%), tourism is a major economic driver due to their natural beauty and favorable climates. It creates jobs, supports local businesses, and stimulates infrastructure development. Tourism also promotes cultural exchange and preserves natural and historical sites, indirectly boosting economic growth. However, its contribution varies based on geographical factors and government policies.
Q. 5) Differentiate Between:
1) Secondary Economic Activities vs. Tertiary Economic Activities
| Aspect | Secondary Economic Activities | Tertiary Economic Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Involve processing raw materials into finished goods. | Involve providing services to consumers and businesses. |
| Nature | Manufacturing and industrial activities. | Service-oriented activities. |
| Examples | Textile production, food processing, car manufacturing. | Transportation, trade, communication, banking, tourism. |
| Dependency | Dependent on primary activities for raw materials. | Links primary and secondary activities through services. |
| Output | Tangible products (e.g., clothes, machinery). | Intangible services (e.g., delivery, consultation). |
2) Quaternary vs. Quinary Activities
| Aspect | Quaternary Activities | Quinary Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Involve knowledge-based services like research, education. | Involve high-level decision-making and policy-making. |
| Nature | Intellectual and information-based services. | Administrative and executive functions. |
| Examples | Software development, teaching, financial planning. | Senior executives, government officials, judges. |
| Scope | Focus on innovation & research. | Focus on strategic leadership and governance. |
| Level of Responsibility | Moderate, involves specialized skills. | High, involves critical decision-making. |
3) Waterways vs. Airways
| Aspect | Waterways | Airways |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Transport via rivers, canals, seas, and oceans. | Transport through the air using aircraft. |
| Speed | Slower, suitable for bulk cargo. | Faster, ideal for perishable goods and passengers. |
| Cost | Cost-effective for heavy goods (e.g., cotton, coal). | Expensive, used for high-value or urgent shipments. |
| Geographical Constraints | Limited to coastal areas, rivers, or canals. | Requires airports but can connect distant locations. |
| Examples | Suez Canal, Panama Canal, Mumbai Port. | Delhi International Airport, transatlantic air routes. |
Q. 6) Answer in Detail:
1) Explain the Factors Affecting Trade Between Two Countries
Trade between countries is influenced by several geographical and economic factors:
- Difference in Natural Resources: Countries trade based on resource availability. For example, Gulf countries export oil but import grains due to limited agricultural land.
- Climate: Climate determines the types of products a country can produce. Tropical countries like Sri Lanka export tea, while snow-covered regions export meat or wool.
- Population Factors: Densely populated countries may focus on domestic needs, while less populated ones rely on trade. Skilled populations, like India’s IT workforce, drive service exports.
- Culture: Unique cultural products, such as Kashmiri shawls or Chinese porcelain, create trade demand due to their global appeal.
- Economic Cost: If importing is cheaper than producing locally, trade occurs. For instance, countries without tea plantations import from tea-producing nations.
- Specialization: Countries with specialized skills or products, like Israel’s dry farming expertise, export these services, fostering trade.
- Government Policies: Free trade policies encourage trade, while restrictions can limit it. Bilateral agreements also promote trade for diplomatic reasons.
2) Development of Transportation is Dependent on Geographical Factors. Explain.
Geographical factors significantly influence transportation development:
- Relief: Flat terrains facilitate the construction of roads, railways, and pipelines, while hilly or mountainous regions, like parts of Africa, pose challenges.
- Climate: Favorable climates support year-round transport operations, but fog, snow, or heavy rainfall can disrupt airways or roadways.
- Location: Coastal areas with broken coastlines are ideal for ports and harbors, as seen with Kochi Port. Inland locations may rely on rail or road networks.
- Natural Features: Rivers and canals (e.g., Suez and Panama Canals) enhance water transport, while dense forests or deserts hinder road and rail construction.
- Technology Adaptation: Advanced technology overcomes some geographical barriers, like building airports in flat areas or tunnels through mountains, but physical constraints still dictate feasibility. These factors determine the mode, cost, and efficiency of transportation systems, shaping their development.
3) Why is Transportation System Important in the Development of Any Nation?
The transportation system is vital for national development due to:
- Economic Growth: It enables the movement of goods, connecting producers to markets, which boosts trade and industrial growth. For example, efficient ports like Mumbai facilitate exports.
- Regional Connectivity: Transportation links rural and urban areas, promoting balanced development by providing access to resources, jobs, and services.
- Employment Generation: Transport infrastructure projects and operations create jobs, from construction workers to logistics professionals.
- Social Integration: It facilitates the movement of people, fostering cultural exchange and national unity.
- Global Competitiveness: Efficient transport systems reduce costs and time, making a nation’s products competitive in international markets.
- Infrastructure Development: Transportation drives the need for roads, railways, airports, and ports, spurring overall infrastructure growth. Without a robust transportation system, economic activities like trade, tourism, and industry would stagnate, hindering national progress.
4) Tertiary Activities are Expanding Day-by-Day. Explain the Statement.
Tertiary activities, encompassing services like transportation, communication, trade, and tourism, are expanding due to:
- Technological Advancements: Innovations like satellites, the internet, and mobile networks have revolutionized communication and logistics, increasing the scope of tertiary services.
- Globalization: Increased international trade and travel demand efficient transport, banking, and marketing services, expanding the tertiary sector.
- Urbanization: Growing urban populations require more services, such as retail, healthcare, and public transport, driving tertiary growth.
- Rising Standards of Living: Higher disposable incomes lead to increased demand for tourism, entertainment, and professional services.
- Specialization: The emergence of quaternary (research, IT) and quinary (policy-making) activities reflects the diversification of tertiary services to meet complex societal needs.
- Government Support: Policies promoting tourism, trade, and digital infrastructure further fuel the growth of tertiary activities. This expansion is evident in the increasing contribution of tertiary activities to GDP, as seen in countries like the USA (77.4% in 2018).
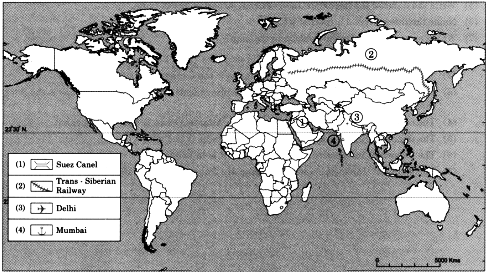
Q. 7) On an outline map of the world, show the following with the help of suitable index :
1) A canal bringing radical change in sea transport.
2) Railway connecting two continents.
3) An international airport in India.
4) An important port in India.
Answer:
Q. 8) Read the Given Passage and Answer the Following Questions:
1) Why Does the Tourism Sector Need Planning?
Answer: The tourism sector needs planning because it involves multiple industries (transport, hospitality, etc.) working together in a complex manner, requiring coordination to maximize output, income, and employment. Planning ensures limited resources are allocated efficiently, addresses development choices, and promotes sustainable growth by minimizing negative impacts on the environment and culture.
2) What is the Importance of Communities in Planning?
Answer: Communities are the basic elements of tourism, as their acceptance and involvement are essential for successful tourism development. Local communities provide cultural authenticity, support services, and hospitality, which enhance tourist experiences. Their participation in planning ensures that tourism aligns with their values, reduces negative socio-cultural impacts, and fosters community support for sustainable tourism.
3) Explain Any Two Benefits of Planning.
Answer: Maximizing Economic Benefits: Planning allocates resources to optimize income, employment, and GDP contribution by prioritizing high-potential tourism sectors.
Sustainable Development: It reduces negative environmental and socio-cultural impacts while enhancing positive outcomes, ensuring long-term viability of tourism destinations.
4) What Factors Affect the Economy of the Host Community?
Answer: The economy of the host community is affected by:
Tourism Revenue: Spending by tourists on lodging, food, and activities boosts local businesses and income.
Job Creation: Tourism generates employment in hospitality, transport, and guiding services.
Infrastructure Development: Tourism drives investment in roads, hotels, and utilities, benefiting the local economy.
Environmental and Cultural Impacts: Negative impacts, like resource depletion or cultural erosion, can harm economic stability if not managed.
5) Why is Planning a Long-Term Task?
Answer: Planning is a long-term task because tourism development is a continuous process that involves preparing, upgrading, and improving destinations to meet evolving tourist needs and global trends. It requires ongoing efforts to maintain infrastructure, adapt to environmental changes, engage communities, and balance economic, social, and environmental goals for sustainable growth over time.

Leave a Reply