India and European Colonialism – Solutions
Exercise
Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the statement.
1. Vasco da Gama was a seafarer from Portugal.
(a) Poland (b) England (c) France (d) Portugal
Rewritten Statement: Vasco da Gama was a seafarer from Portugal.
2. The license was given by England to the East India Company to trade with the eastern countries by Queen Elizabeth.
(a) Sir George Oxenden (b) Queen Elizabeth (c) Princess Braganza (d) Homer
Rewritten Statement: The license was given by England to the East India Company to trade with the eastern countries by Queen Elizabeth.
(B) Find the incorrect pair from group ‘B’, and write the corrected one.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
|---|---|
| Arcebispo | Chief Executive Officer |
| Chancellor | Judge |
| Vedor da Fazenda | In-charge of Company’s possessions |
| Capitaon | Captain |
Answer:
Incorrect Pair: Arcebispo – Chief Executive Officer
Corrected Pair: Arcebispo – Archbishop of Goa
Explanation: The document specifies that the advisory board assisting the Vice-rei included the Archbishop (Arcebispo) of Goa, not a Chief Executive Officer.
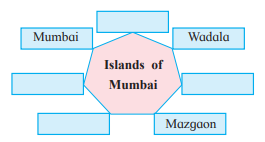
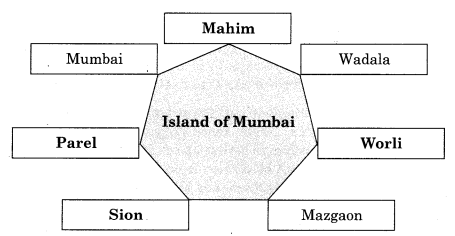
Q.2 Complete the concept map.
Answer:
Q.3 Explain the following statements with reasons.
1. The Indian rulers had to obtain cartaz.
Reason: The Portuguese established firm control over the Indian Ocean and made it mandatory for Indian rulers to obtain a license called a “Cartaz” to sail on the Indian Ocean. This document included details such as the ship’s name, captain, ports of departure and arrival, and weaponry for self-defense. If Indian rulers sailed without this license, their ships were either seized or sunk by the Portuguese naval forces. This system ensured Portuguese dominance over maritime trade and restricted the freedom of Indian rulers to conduct independent sea trade.
2. Indian rulers found it difficult to fight the Portuguese.
Reason: Indian rulers struggled to counter the Portuguese due to their superior naval strength and advanced war tactics. The Portuguese had a strong naval force equipped with cannons and used sudden sea-based attacks to devastate enemy territories. Most Indian rulers lacked a comparable naval force, making it challenging to compete with the Portuguese at sea. The document highlights that only Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj built his own navy, while others were unable to match the Portuguese. Additionally, the Portuguese established fortified colonies and used durable teakwood from India to build ships, further strengthening their position.
Q.4 Answer the following questions in detail.
1. Which are the places where the Portuguese established their colonies?
The Portuguese established their colonies at several locations along the Indian coasts, as follows:
- Western Coast: Diu, Daman, Chaul, Goa (including Sashti and Bardesh), Honnavar, Gangoli, Basrur, Mangalore, Kannur, Kodungallur, Cochi, and Kollam.
- Eastern Coast: Nagpattinam, Mylapore (also known as Sao Tome/San Thom), and Hugli in Bengal.
- Capital: The Portuguese Empire in India, known as Estado da India, had its capital at Goa.These colonies were strategically chosen to control maritime trade routes and were fortified with forts to protect against external attacks and ensure a steady supply chain via seaways.
2. What were the rights given to United East India Company by the Dutch government?
The Dutch government issued a license to the United East India Company in 1602, granting the following rights:
- Trading Rights: The company was authorized to conduct trade with eastern countries, enabling them to establish commercial operations across a vast region from the eastern coast of Africa to Japan.
- Staff Appointment: The company could appoint staff to manage its operations, including a Governor-General to oversee Indian affairs.
- Establishment of Factories: The company was permitted to build factories (emporiums) for buying, storing, and selling goods.
- Fort Construction: The company had the authority to construct forts, which were fortified with cannons and walls for security.
- Military Engagement: The company was allowed to engage in battles against eastern countries to protect its interests.
- Treaty-Making: The company could sign treaties with eastern rulers, as evidenced by their treaty with the king of Kochi for a monopoly in black pepper trade.These rights enabled the Dutch to establish a robust colonial presence, with factories and forts in places like Petapuli, Machilipatnam, Pulicat, Nagapattan, Kochi, and others, and to challenge other European powers like the Portuguese.

Leave a Reply