Social Problems in India – Solutions
Q.1 (A) Complete the following statements by choosing the correct alternative given in the bracket and rewrite it.
(1) The Domestic Violence Act was passed in the year _____. (1995, 2005, 2011)
Answer: 2005
(2) One of the causes of farmer suicide is _____. (multi-cropping, indebtedness, climate change)
Answer: indebtedness
(B) Correct the incorrect pair and rewrite it.
(1) (i) Marijuana – Drug addiction
(ii) Violent films – Internet addiction
(iii) Selfitis syndrome – Substance addiction
(iv) Country liquor – Alcohol addiction
Answer:
Incorrect Pair: Selfitis syndrome – Substance addiction
Correct Pair: Selfitis syndrome – Mobile (Social media) addiction
(C) Identify the appropriate term from the given options in the box and rewrite it against the given statement.
(1) A problem faced by transgender persons: Gender discrimination
(2) It can lead to physical health problems: Narcotic drugs
(D) Correct the underlined words and complete the statement.
(1) Alcoholic Anonymous helps drug addicts.
Answer: Several government and private organizations (NGOs)/Narcotics Anonymous
(2) Ageing is an artificial process.
Answer: natural
Q.2 Write short notes.
(1) Effects of addiction
Answer: Addiction, whether to substances (alcohol, drugs, tobacco), the internet, or mobile phones, has profound effects on individuals and society:
- Psychological Impact: Addicts develop dependency, leading to anxiety, depression, or aggression when access to the substance or device is restricted.
- Impact on Family: Addiction disrupts family harmony, potentially causing domestic violence or emotional isolation due to lack of communication.
- Health Consequences: Physical health deteriorates (e.g., cancer from tobacco, liver damage from alcohol), and mental health suffers from stress and anxiety.
- Workplace Issues: Addiction reduces productivity, increases absenteeism, and may lead to workplace harassment or exploitation.
- Economic Drain: Addictions are costly, with expenses on substances, internet, or devices, and treatment costs further strain finances.
- Social Isolation: Addicts often withdraw from real-world interactions, preferring virtual or substance-induced experiences.
(2) Measures to tackle the problem of ageing.
Answer: To address the challenges faced by the ageing population, several measures can be implemented:
- Government Role: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment formulates policies like the National Policy on Older Persons (NPOP, 1999) to provide shelters, healthcare, and protection for the elderly.
- NGO Contributions: Organizations like HelpAge India and Dignity Foundation offer support through care services and online communities.
- Education: Schools can promote awareness through community service projects and NSS programs to instill respect and empathy for the elderly.
- Family Support: Families should create an inclusive environment, valuing the elderly’s wisdom and involving them in activities.
- Healthcare Access: Improving access to medical facilities for physical and mental health issues, including specialized care for diseases like Alzheimer’s, is crucial.
- Old Age Homes: Increasing the availability of affordable, well-equipped homes for the elderly can provide a supportive living environment.
Q.3 Write differences.
(1) Social problem and Individual problem
Answer:
| Aspect | Social Problem | Individual Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A condition affecting a significant number of people, deviating from social norms. | A problem experienced by an individual, not necessarily felt by others. |
| Scope | Impacts a large group or society, requiring collective action. | Limited to the individual, often resolvable by personal effort. |
| Cause | Rooted in societal structures, norms, or external conditions (e.g., unemployment). | May stem from personal traits, habits, or circumstances (e.g., laziness). |
| Solution | Requires collective efforts, policy changes, or social movements. | Often solved through self-motivation or support from family/friends. |
| Example | Domestic violence, farmers’ suicides. | Personal loneliness, low academic performance. |
(2) Mobile addiction vs. Drug addiction
Answer:
| Aspect | Mobile Addiction | Drug Addiction |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Psychological dependence on mobile devices for social media, gaming, etc. | Physical and psychological dependence on chemical substances (e.g., alcohol, narcotics). |
| Health Impact | Causes stress, anxiety, sleep disorders, and eye strain. | Leads to severe physical damage (e.g., cancer, liver failure) and mental health issues. |
| Accessibility | Easily accessible, often socially accepted, and legal. | Often illegal or restricted, requiring illicit means to obtain. |
| Social Perception | Seen as a modern lifestyle issue, less stigmatized. | Highly stigmatized, associated with criminality or moral failure. |
| Example | Obsessively checking social media or taking selfies. | Habitual use of marijuana or heroin. |
Q.4 Explain the following concepts with examples.
(1) Domestic violence
Answer: Concept: Domestic violence refers to psychological, emotional, verbal, or physical abuse within a family, involving a perpetrator and a victim. It is often normalized in patriarchal societies and may go unreported as a “personal matter.” Victims can include women, men, children, the elderly, or transgender persons. Domestic violence stems from power imbalances, such as those created by patriarchy, insecurity, or dysfunctional relationships.
- Example: A husband verbally abusing his wife due to suspicions of infidelity, or a parent physically disciplining a child excessively, causing trauma. Such acts reflect patriarchal control or emotional insecurity.
(2) Skill development
Answer: Concept: Skill development involves cultivating practical, employment-worthy abilities to enhance employability and promote self-employment. It addresses the gap between educational training and industry needs, focusing on vocational and technical skills to adapt to a changing economy. Programs like Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) emphasize capacity building for employment.
- Example: A student trained in computer programming through a vocational course secures a job in the IT sector, or a farmer learning modern irrigation techniques to improve crop yield, demonstrating how skills align with market demands.
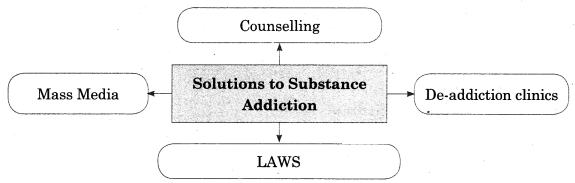
Q.5 (A) Complete the concept map.
Answer:
(B) State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons.
(1) Technology is always useful for social progress.
Answer: False.
- Reasons: While technology drives advancements (e.g., improved communication, healthcare), it can also create social problems. For instance, excessive mobile or internet use leads to addiction, reducing interpersonal relationships and causing stress. Technology’s benefits depend on its responsible use; otherwise, it may hinder social progress by fostering isolation or misinformation.
(2) There is a strong causal relationship between addiction and socialisation.
Answer: True.
- Reasons: Socialisation influences addiction through peer pressure, social status, or lack of positive role models. For example, teenagers may start smoking due to peer influence to “fit in,” or individuals may develop mobile addiction seeking validation on social media. Social expectations and interactions shape behaviors that can lead to addictive habits.
Q.6 Give your personal response.
(1) Why do you think women are usually the victims in most reported cases of domestic violence?
Answer: Women are often victims in reported domestic violence cases due to the deeply rooted patriarchal structure of Indian society, which places men in positions of power within families. This imbalance normalizes male authority, leading to the acceptance of violence against women as a means of control. Cultural norms, such as gender socialization, reinforce women’s subservience, making them vulnerable to abuse. Additionally, economic dependence and fear of social stigma discourage women from reporting abuse, though increased awareness is gradually changing this. Transgender persons and children also face violence, but women’s systemic disempowerment makes them the most reported victims.
(2) There is a strong causal relationship between addiction and socialisation.
Answer:
Positive Consequences: Placing aged parents in a Home for the Aged can provide professional care tailored to their physical and mental health needs, which families may struggle to offer. These homes offer social engagement with peers, reducing loneliness, and ensure safety from abuse or neglect. For families with demanding schedules, this arrangement can relieve caregiving stress, allowing better focus on work or personal life.
Negative Consequences: Such homes may lead to emotional isolation if the elderly feel abandoned by their families, fostering guilt or depression. Many homes lack adequate facilities or personalized care, and commercial greed can result in substandard conditions. The elderly may lose their sense of belonging, missing family interactions and their role in the household, which can negatively impact their emotional well-being.
Q.7 Answer the following question in detail. (About 150-200 words)
Discuss why farmers’ suicide is a social problem today. Suggest suitable socioeconomic measures to support the farmers.
Answer: Farmers’ suicides are a pressing social problem in India, particularly in regions like Vidarbha and Marathwada, due to their widespread impact on society. The primary causes include indebtedness, as farmers borrow heavily for expensive seeds (e.g., BT cotton) and face crop failure due to irregular monsoons or inadequate irrigation. Environmental deterioration, such as droughts and floods, destroys crops, while globalization and free-trade policies lead to price drops from imported produce. Ignorance of modern farming techniques and disparities in land holdings exacerbate economic insecurity, particularly for small farmers. Social pressures like the dowry system also divert funds, deepening debt. These suicides devastate families, leaving widows and children in economic and emotional distress, discourage youth from farming, and hinder agricultural contributions to the economy, creating a cycle of despair in rural communities.
Socioeconomic Measures:
- Crop and Life Insurance: Provide insurance to protect against crop failure and ensure family support post-suicide.
- Direct Sales: Eliminate middlemen to ensure fair profits for farmers.
- Water Management: Promote water harvesting to address irrigation issues.
- Subsidized Inputs: Supply affordable seeds, fertilizers, and training in multi-cropping.
- Counseling Services: Offer mental health support to alleviate despair and prevent suicides.
- Debt Relief: Simplify bank loan processes and implement effective debt-waiver schemes to reduce reliance on private moneylenders.


Leave a Reply