Question Answers For All Chapters – General Science Class 7
Motion, Force and Work
Exercise
1. Fill in the blanks with the proper words from the brackets.
(Stationary, zero, changing, constant, displacement, velocity, speed, acceleration, stationary but not zero, increases)
(a) If a body traverses a distance in direct proportion to the time, the speed of the body is constant.
(b) If a body is moving with a constant velocity, its acceleration is zero.
(c) Speed is a scalar quantity.
(d) Velocity is the distance traversed by a body in a particular direction in unit time.
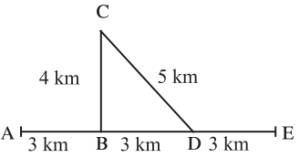
2. Observe the figure and answer the questions.
Sachin and Sameer started on a motorbike from place A, took the turn at B, did a task at C, travelled by the route CD to D and then went on to E. Altogether, they took one hour for this journey. Find out the actual distance traversed by them and the displacement from A to E. From this, deduce their speed. What was their velocity from A to E in the direction AE? Can this velocity be called average velocity?
(i) Find out the actual distance traversed by Sachin and Sameer and the displacement from A to E.
- Distance = 4 km + 5 km + 3 km + 3 km = 15 km
- Displacement (shortest path from A to E) = 5 km
(ii) Find their speed.
Speed = Total distance ÷ Time
15 km ÷ 1 hour = 15 km/h
(iii) What was their velocity from A to E in the direction AE?
Velocity = Displacement ÷ Time
5 km ÷ 1 hour = 5 km/h
(iv) Can this velocity be called average velocity?
Yes, because it is the total displacement divided by total time taken for the journey.
3. From groups B and C, choose the proper words for each of the words in group A.
| A (Quantity) | B (SI Unit) | C (CGS Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Work | Newton | erg |
| Force | Metre | cm |
| Displacement | Joule | dyne |
4. A bird sitting on a wire flies, circles around, and comes back to its perch. Explain the total distance and displacement.
- Total distance: The bird covers a large path while flying in circles.
- Displacement: Since the bird returns to the same place, its displacement is zero because displacement is the shortest straight-line distance between start and end points.
5. Explain the following concepts in your own words with everyday examples : force, work, displacement, velocity, acceleration, distance.
(a) Force → A push or pull on an object. Example: Kicking a football.
(b) Work → Work is done when force moves an object. Example: Lifting a bag.
(c) Displacement → The shortest distance between the starting and ending points. Example: A boy walks 5m east and 5m west, his displacement is 0m.
(d) Velocity → Speed with direction. Example: A car moving 40 km/h east.
(e) Acceleration → Change in velocity over time. Example: A bike speeding up from 20 km/h to 40 km/h.
(f) Distance → Total length traveled. Example: Walking around a park covers 500m distance.
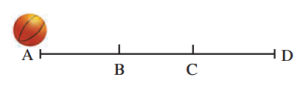
6. A ball is rolling from A to D on a flat and smooth surface. Its speed is 2 cm/s. On reaching B, it was pushed continuously up to C. On reaching D from C, its speed became 4 cm/s. It took 2 seconds for it to go from B to C. What is the acceleration of the ball as it goes from B to C?
Formula:
Acceleration = Final velocity−Initial velocity / Time
Given:
- Initial velocity = 2 cm/s
- Final velocity = 4 cm/s
- Time = 2 seconds
Answer: The acceleration of the ball is 1 cm/s².
7. Solve the following problems.
(a) A force of 1000 N was applied to stop a car that was moving with a constant velocity. The car stopped after moving through 10 m. How much work was done?
Formula:
Given:
- Force = 1000 N
- Displacement = 10 m
Answer: Work done = 10,000 Joules (J).
(b) A cart with mass 20 kg went 50 m in a straight line on a plain and smooth road when a force of 2 N was applied to it. How much work was done by the force?
Given:
- Force = 2 N
- Displacement = 50 m
Answer: Work done = 100 Joules (J).

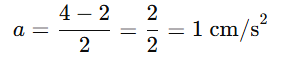
Leave a Reply