Question Answers For All Chapters – General Science Class 8
Solutions
Exercise
1. Find out my partner:
| Group A | Group B |
|---|---|
| Heart beats | 72 times per minute |
| RBC count | 50 – 60 lakh/mm³ of blood |
| WBC count | 5000 – 6000/mm³ of blood |
| Blood donation amount | 350 ml per donation |
| Normal body temperature | 37°C |
| pH of oxygenated blood | 7.4 (slightly alkaline) |
2. Complete the following table:
| Organ System | Organs | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory system | Nose, Pharynx, Windpipe, Lungs, Diaphragm | Helps in breathing, oxygen supply, and removal of carbon dioxide. |
| Circulatory system | Heart, Blood, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries | Transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste throughout the body. |
3. Draw neat and labeled diagrams.
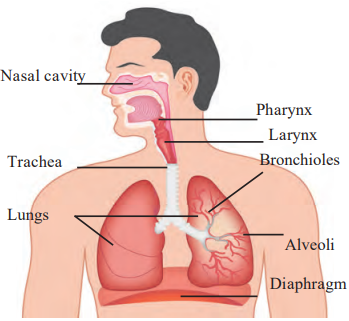
a. Respiratory System
- (Describe: Draw nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchioles, lungs, alveoli, and diaphragm. Label each part clearly.)
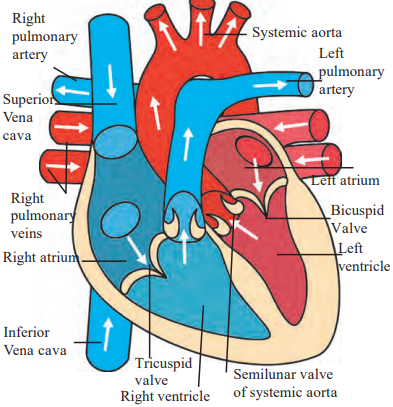
b. Internal Structure of Heart
- (Describe: Draw right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle, tricuspid valve, bicuspid valve, semilunar valves, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and systemic aorta. Label all parts.)
4. Explain with reasons:
(a) Human blood is red-colored.
- Blood appears red because it contains hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein that binds with oxygen.
(b) Upward and downward movement of the diaphragm occurs consecutively.
- The diaphragm moves down when we inhale, allowing air into the lungs.
- It moves up when we exhale, pushing air out of the lungs.
(c) Blood donation is considered to be superior to all donations.
- Blood saves lives in accidents, surgeries, and diseases like anemia.
- A healthy person can donate blood regularly without any harm.
(d) A person with ‘O’ blood group is considered a universal donor.
- Blood type O-negative has no antigens, so it can be given to patients of any blood group.
(e) Food must have a limited amount of salts.
- Excess salt can lead to high blood pressure (hypertension), which affects heart health.
5. Answer the following questions in your own words:
(a) Explain the functional correlation of the circulatory system with the respiratory, digestive, and excretory systems.
- The circulatory system transports oxygen from the respiratory system to all body cells.
- It carries nutrients from the digestive system and removes waste materials through the excretory system (kidneys).
(b) Explain the structure and function of human blood.
- Blood is a fluid connective tissue containing plasma, RBCs, WBCs, and platelets.
- It transports oxygen, fights infections, and helps in clotting wounds.
(c) Explain the importance and need for blood donation.
- Blood donation helps save lives in cases of accidents, surgeries, and diseases.
- It prevents blood shortages in hospitals and is safe for healthy donors.
6. Explain the differences:
a. Arteries and veins.
| Feature | Arteries | Veins |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. | Carry carbon dioxide-rich blood back to the heart. |
| Walls | Thick and elastic. | Thin and less elastic. |
| Valves | No valves. | Have valves to prevent backflow of blood. |
b. External and internal respiration.
| Feature | External Respiration | Internal Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange of gases between the lungs and blood. | Exchange of gases between blood and body cells. |
| Oxygen Movement | Oxygen moves from lungs into blood. | Oxygen moves from blood into cells. |
7. Which health parameters of a blood donor should be checked?
Age: Must be 18-65 years old.
Weight: Should be above 50 kg.
Hemoglobin level: Should be at least 12.5 g/dL.
Blood pressure: Should be normal.
No recent illness, infections, or chronic diseases.
8. Fill in the blanks using appropriate words given in the bracket.
(hemoglobin, alkaline, diaphragm, red bone marrow, acidic, voluntary, involuntary,)
(a) RBCs of the blood contain hemoglobin, an iron compound.
(b) Diaphragm is present between thoracic and abdominal cavity.
(c) Cardiac muscles are involuntary.
(d) pH of oxygenated blood is alkaline (7.4).
(e) Production of RBCs occurs in red bone marrow.
9. Find the odd one out:
(a) A, O, K, AB, B
– K (not a blood group).
(b) Blood plasma, platelets, blood transfusion, blood corpuscles
– Blood transfusion (others are components of blood).
(c) Trachea, alveoli, diaphragm, capillaries
– Capillaries (not part of the respiratory system).
(d) Neutrophils, globulins, albumins, prothrombin
– Neutrophils (others are blood proteins).
10. Read the following paragraph and identify the disease:
Situation: A child is weak, crying continuously, and has shortness of breath with blue nails.
Disease: Anemia or Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) (lack of oxygen in the blood).
11. Your neighboring uncle has been diagnosed with hypertension. What should he do to keep his blood pressure normal?
- Eat a low-salt, low-fat diet.
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking, alcohol, and stress.
- Take prescribed medications and monitor blood pressure.

Leave a Reply