Question Answers For All Chapters – General Science Class 8
Solutions
Exercise
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The perpendicular to the mirror at the point of incidence is called normal.
(b) The reflection of light from a wooden surface is irregular reflection.
(c) The working of a kaleidoscope is based on the properties of multiple reflections.
2. Draw a figure describing the following:
When two mirrors make a 90° angle and a ray is incident at 30° on one mirror, what is the angle of reflection from the second mirror?
Answer: The angle of reflection from the second mirror will be 60°.
Explanation:
- The first reflection follows the law of reflection (angle of incidence = angle of reflection).
- The second mirror receives the reflected ray as an incident ray, and again the law of reflection applies.
- The calculation shows the final reflection angle is 60°.
3. How will you explain the statement “We cannot see objects in a dark room”?
- We see objects when light reflects from them into our eyes.
- In a dark room, there is no light, so no reflection happens, making objects invisible.
4. Explain the difference between regular and irregular reflection of light.
| Regular Reflection | Irregular Reflection |
|---|---|
| Happens on a smooth surface like a plane mirror. | Happens on a rough surface like wood or paper. |
| The reflected rays are parallel. | The reflected rays scatter in different directions. |
| Forms a clear image. | Forms a blurred or no image. |
| Example: Reflection from a mirror. | Example: Reflection from wall or water waves. |
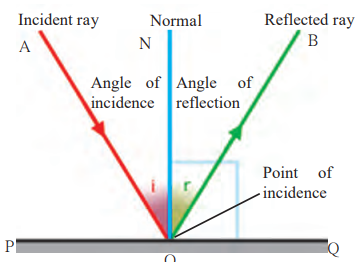
5. Draw a figure showing the following:
- Incident Ray
- Normal
- Angle of Incidence
- Angle of Reflection
- Point of Incidence
- Reflected Ray
6. Study the following incident:
Swara and Yash were looking at their reflections in still water. When Yash threw a stone in the water, their images became blurred.
(a) Is there a relation between the reflection of light and the blurring of images?
- Yes, when the water surface is smooth, regular reflection occurs, forming a clear image.
- When the water surface becomes wavy, irregular reflection happens, and the image becomes blurred.
(b) Which types of reflection of light can you notice from this?
- Still water → Regular reflection (clear image).
- Moving water → Irregular reflection (blurred image).
(c) Are the laws of reflection followed in these types of reflection?
- Yes, the laws of reflection are always followed, even in irregular reflection.
- However, in irregular reflection, the angles of incidence and reflection vary at different points.
7. Solve the following examples:
(a) If the angle between the plane mirror and the incident ray is 40°, what are the angles of incidence and reflection?
- Angle of incidence = 50°
- Angle of reflection = 50°
- Explanation: The angle of incidence is calculated as 90° – 40° = 50°, and since angle of incidence = angle of reflection, the answer is 50°.
(b) If the angle between the mirror and the reflected ray is 23°, what is the angle of incidence of the incident ray?
- Angle of incidence = 67°
- Explanation: The angle of incidence is found as 90° – 23° = 67°.

Leave a Reply