Question Answers For All Chapters – General Science Class 8
Solutions
Exercise
1. Answer the following:
(a) What is the difference in the atomic models of Thomson and Rutherford?
- Thomson’s Model: The atom has positive charge spread everywhere with negative electrons embedded like a “plum pudding.”
- Rutherford’s Model: The atom has a small, dense, positively charged nucleus at the center, with electrons revolving around it in empty space.
(b) What is meant by valency of an element? What is the relationship between the number of valence electrons and valency?
- Valency is the number of chemical bonds an atom can form.
- If an atom has 1 to 4 valence electrons, its valency is the same as the number of electrons.
- If an atom has 5 to 8 valence electrons, its valency is (8 – number of valence electrons).
(c) What is meant by atomic mass number? Explain how the atomic number and mass number of carbon are 6 and 12 respectively.
- Atomic mass number (A) = Number of protons + neutrons in an atom.
- Carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus, so A = 6 + 6 = 12.
- The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons, which is 6 for carbon.
(d) What is meant by subatomic particles? Give brief information about three subatomic particles with reference to electrical charge, mass, and location.
- Subatomic particles are the smaller parts of an atom: Proton, Neutron, and Electron.
| Particle | Charge | Mass | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proton (p) | +1 | 1 u | Nucleus |
| Neutron (n) | 0 | 1 u | Nucleus |
| Electron (e-) | -1 | Negligible | Around nucleus |
2. Give scientific reasons:
(a) All the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
- The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, which are much heavier than electrons.
- Electrons are very light and revolve around the nucleus.
(b) An atom is electrically neutral.
- The number of protons (positive charge) is equal to the number of electrons (negative charge) in a neutral atom.
- Since opposite charges cancel each other, the atom remains neutral.
(c) Atomic mass number is a whole number.
- Atomic mass number = Protons + Neutrons, and both are whole numbers.
- Electrons have negligible mass, so they do not affect the total atomic mass.
(d) Atoms are stable though negatively charged electrons are revolving within them.
- Bohr’s Model states that electrons move in fixed energy levels (orbits) around the nucleus.
- They do not lose energy while moving in their stable orbits, making the atom stable.
3. Define the following terms:
(a) Atom:
- The smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical identity.
(b) Isotope:
- Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers (due to a different number of neutrons).
(c) Atomic number:
- The number of protons in an atom.
(d) Atomic mass number:
- The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
(e) Moderator in a nuclear reactor:
- A material like graphite or heavy water used to slow down neutrons in a nuclear reactor.
4. Draw a neat labeled diagram:
(a) Rutherford’s scattering experiment
- Diagram: Show a gold foil, alpha particles, and a detector screen.
- Label: Alpha particle emitter, Gold foil, Fluorescent screen, Deflected particles.
(b) Thomson’s atomic model
- Diagram: Show a sphere of positive charge with embedded electrons.
- Label: Positive charge, Electrons, Atom.
(c) Electronic configuration of Magnesium (Atomic number 12)
- Diagram: Show K, L, and M shells with electrons (2, 8, 2).
(d) Electronic configuration of Argon (Atomic number 18)
- Diagram: Show K, L, and M shells with electrons (2, 8, 8).
5. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Electron, proton, neutron are the types of subatomic particles in an atom.
(b) An electron carries a negative (-) charge.
(c) The electron shell K is nearest to the nucleus.
(d) The electronic configuration of magnesium is 2, 8, 2. From this, it is understood that the valence shell of magnesium is M shell.
(e) The valency of hydrogen is ‘one’ as per the molecular formula H₂O. Therefore, the valency of Fe (iron) turns out to be three (3) as per the formula Fe₂O₃.
6. Match the pairs:
| Group A | Group B |
|---|---|
| (a) Proton | (iii) Positively charged |
| (b) Electron | (i) Negatively charged |
| (c) Neutron | (ii) Neutral |
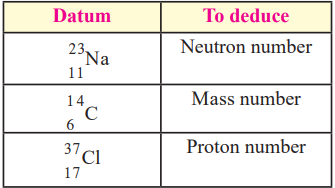
7. Deduce from the given data:
| To Find | Answer |
|---|---|
| Neutron number | 23−11=1223 – 11 = 1223−11=12 |
| Mass number | 14 |
| Proton number | 17 |

Leave a Reply