Notes For All Chapters – Geography Class 9th
Introduction
What are Endogenetic Movements?
- These are movements inside the earth that cause natural events like earthquakes and volcanoes.
- They happen because of energy and instability in the earth’s interior, especially in the mantle (layer below the crust).
Why Study Them?
- These events can be disasters, causing loss of life and property (e.g., Nepal earthquake in 2015).
- Understanding them helps us prepare and learn about earth’s changes.
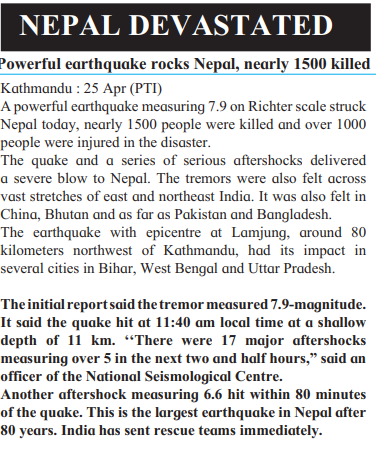
Example from News (Fig. 2.1):
- Nepal Earthquake (25 April 2015): 7.9 on Richter scale, killed nearly 1500 people, epicenter at Lamjung, focus 11 km deep.
- Affected India, China, Bhutan, Pakistan, Bangladesh; had 17 aftershocks.
What Causes These Movements?
Inside the Earth:
- Radioactive materials in the mantle release huge energy as waves.
- These waves move and create instability, leading to movements in the crust (earth’s outer layer).
Activities to Understand (Try This):
- Notebook Activity (Fig. 2.2 & 2.3): Stack notebooks, place objects (chalk, duster), pull one out or push them. Objects fall or shake, showing how earth moves and affects things.
- This mimics how energy waves shake the ground during earthquakes.
Types of Internal Movements
Classification (Table in Chapter):
1. Velocity (Speed):
- Slow Movements: Happen over a long time (e.g., forming mountains, continents).
- Sudden Movements: Happen quickly (e.g., earthquakes, volcanoes).
2. Direction:
- Horizontal: Sideways movements.
- Upward/Downward: Up or down movements.
3. Landforms:
- Continent-building: Makes continents and plateaus.
- Mountain-building: Makes mountains by folding or faulting.
Slow Movements
What Happens?
- Slow movements shape the earth’s surface over millions of years, forming mountains and continents.
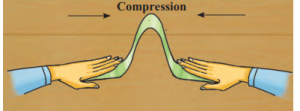
Two Forces:
- Pressure (Compression): Waves move toward each other.
- Tension: Waves move away from each other.
Effects (Fig. 2.4):
- On Hard Rocks: Breaks or faults form.
- On Soft Rocks: Folds or bends form.
(a) Mountain-Building (Orogenic) Movements
Fold Mountains:
- How They Form: Pressure from energy waves pushes soft rock layers into folds (like crumpled paper).
- Activity (Fig. 2.5): Push a paper strip from both ends-it folds, showing how mountains rise.
- Examples: Himalayas, Alps, Rockies, Andes, Aravalis (Fig. 2.7 shows Himalayas).
- Features: Large folds uplift the surface, creating peaks and ridges.
Block Mountains:
- How They Form: Tension pulls rocks apart, forming faults; a block between faults lifts up.
- Activity (Fig. 2.9): Move notebooks apart-middle one stays up, like a block mountain.
- Examples: Black Forest (Europe), Meghalaya Plateau (India).
- Features: Flat tops, steep slopes, no peaks at first.
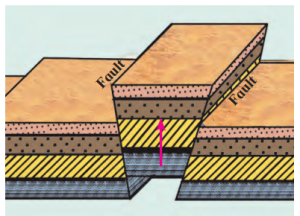
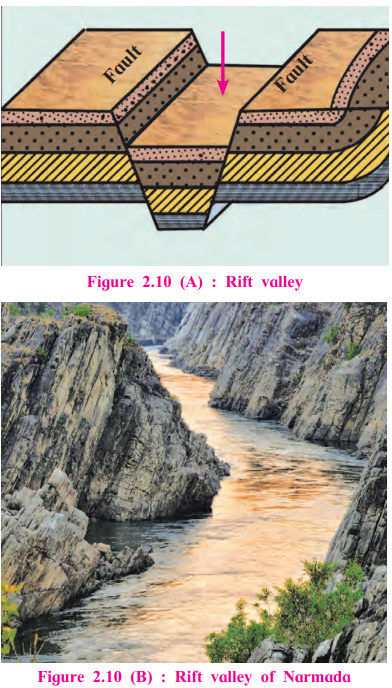
Rift Valleys:
- How They Form: Tension creates two faults; land between them sinks.
- Activity: Similar to block mountain but focus on sinking part.
- Examples: Narmada Rift Valley (India), Great Rift Valley (Africa), Rhine River Valley (Europe).
- Features: Deep with steep slopes (Fig. 2.10).
(b) Continent-Building (Epeirogenic) Movements
How They Happen: Slow up or down movements lift or sink large crust areas.
Results:
- Uplifting forms continents or plateaus (e.g., Meghalaya Plateau).
- Sinking makes sea-beds if land goes below sea level.
Why Important: Creates vast landforms over time.
Sudden Movements
- What Are They?
- Quick events like earthquakes and volcanoes caused by sudden energy release.
Earthquakes
What is an Earthquake?
- Shaking of the earth’s surface due to energy waves from the crust or mantle.
- Measured by Richter scale (e.g., Nepal quake was 7.9).
Causes (Fig. 2.11):
- Moving, colliding, or sliding plates.
- Fractures in rocks from tension.
- Volcanic eruptions.
Key Terms:
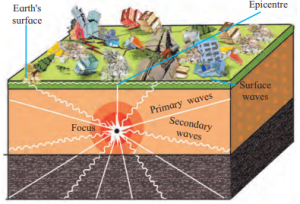
- Focus (Hypocenter): Point inside earth where energy starts.
- Epicenter: Point on surface above focus where tremors hit first (perpendicular to focus).
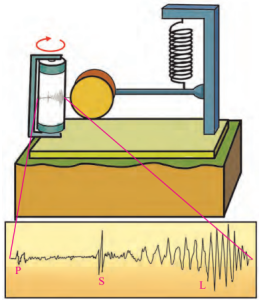
Seismic Waves (Fig. 2.12):
Primary (P) Waves:
- Fastest, reach first, move back and forth.
- Travel through solids, liquids, gases; shake buildings side to side.
Secondary (S) Waves:
- Slower, reach after P waves, move up and down.
- Only through solids; more destructive than P waves.
Surface (L) Waves:
- Slowest, travel along crust, most destructive.
- Cause major damage to buildings and land.
Seismogram:
- Instrument that records seismic waves as a graph (Fig. 2.11).
- Modern ones detect tiny tremors too.
Effects:
- Cracks, landslides, ground uplifts or sinks, tsunamis, avalanches.
- Buildings collapse, transport and communication fail, loss of life.
Volcanoes
What is a Volcano?
- Hot materials (magma, ash, gases) burst out from the mantle to the surface.
- Magma becomes lava when it reaches the surface.
Types by Eruption:
- Central-Type (Conical) Volcano:
- Magma comes out a single vent, forming a cone-shaped mountain.
- Examples: Mt. Fujiyama (Japan), Mt. Kilimanjaro (Tanzania) (Fig. 2.16).
- Fissure-Type Volcano:
- Magma flows out from many cracks, forming flat plateaus.
- Example: Deccan Plateau (India) (Fig. 2.17).
Types by Periodicity:
- Active: Erupt regularly now (e.g., Mt. Fujiyama, Mt. Stromboli).
- Dormant: Not erupted for long but could (e.g., Mt. Vesuvius, Barren Island).
- Extinct: No eruptions for ages, unlikely to erupt (e.g., Mt. Kilimanjaro).
Effects:
- Loss of life/property, tsunamis, air pollution from ash and gases.
- Fertile land from ash, new land or islands, minerals near surface, crater lakes.
Plates and Their Role
What are Plates?
- Earth’s crust is made of big pieces called plates (e.g., Indo-Australia, Eurasia).
- Oceans and continents sit on these plates.
Plate Boundaries:
- Subduction (Consuming): One plate slides under another, causing earthquakes/volcanoes.
- Constructive (Creating): New crust forms as plates move apart.
- Most volcanoes and earthquakes happen here (see map).
Map Questions:
- Plates: Indo-Australia, Africa, Eurasia, etc.
- Americas: Earthquake zones on west side (Andes).
- Asia: Himalayas zone.
- Africa: Volcanoes in east (rift valley).



Leave a Reply