Questions Answers For All Chapters – Geography Class 9th
Exercise
Solutions
Q 1. Answer in brief.
(a) What is mechanical weathering?
- Mechanical weathering is the process where rocks break into smaller pieces without any change in their chemical composition.
- It happens due to physical forces like temperature changes, frost, or pressure release.
- For example, rocks crack when they expand and contract due to heat or when water freezes in their crevices.
(b) What are the main types of chemical weathering?
- The main types of chemical weathering are carbonation, solution, and oxidation.
- Carbonation occurs when rainwater mixes with carbon dioxide to form carbonic acid, dissolving rocks like limestone.
- Solution happens when minerals in rocks dissolve in water, making them brittle.
- Oxidation is when iron in rocks reacts with water and oxygen, forming rust.
(c) How does biological weathering occur?
- Biological weathering occurs when living organisms break down rocks.
- Plant roots grow into cracks, expand, and split rocks apart.
- Burrowing animals like ants, rats, or rabbits dig into the ground, loosening rocks.
- Algae, moss, and lichens grow on rocks and help break them down over time.
(d) Distinguish between weathering and mass wasting.
- Weathering is the breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces by external processes like temperature, water, or organisms.
- Mass wasting is the movement of weathered rock materials down slopes due to gravity.
- Weathering happens in place, while mass wasting involves the shifting of materials.
- For example, exfoliation is weathering, but a landslide is mass wasting.
Q 2. Write whether the statements are true or false. Correct the incorrect ones.
(a) Climate affects earthquakes.
- False.
- Corrected: Climate does not affect earthquakes; earthquakes are caused by internal earth movements, not climate.
(b) Mechanical weathering is less effective in humid climates.
- True.
- In humid climates, chemical weathering is more effective due to more water, while mechanical weathering is less dominant.
(c) Mechanical weathering happens on a large scale in dry climates.
- True.
- In dry climates, temperature changes and lack of moisture make mechanical weathering more common.
(d) The breaking down of rocks into smaller particles is called weathering.
- True.
- Weathering is the process of breaking rocks into smaller pieces by external forces.
(e) Lateritic rocks are formed through exfoliation.
- False.
- Corrected: Lateritic rocks are formed through chemical weathering, not exfoliation, which is a mechanical process.
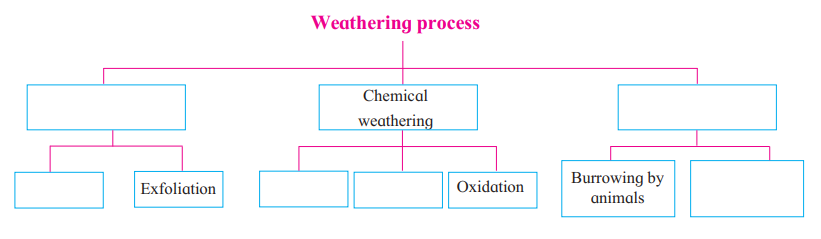
Q 3. Complete the flowchart below.
Weathering Process
Physical Weathering
Exfoliation
Frost action
Chemical Weathering
Solution
Oxidation
Carbonation
Biological Weathering
Burrowing by animals
Root action
Q 4. Identify the type of weathering from the given description.
(a) Some animals live inside the grounds by making burrows.
- Biological weathering.
- Burrowing animals break rocks by digging into them.
(b) The rock rusts.
- Chemical weathering (Oxidation).
- Rusting happens when iron in rocks reacts with water and oxygen.
(c) Water which has accumulated in the crevices of the rocks freezes. Consequently, the rock breaks.
- Mechanical weathering (Frost).
- Freezing water expands in cracks, breaking the rock.
(d) The pipes supplying water in colder regions break.
- Mechanical weathering (Frost).
- Water freezes and expands in pipes, causing them to break, similar to rocks.
(e) Sand formation occurs in deserts.
- Mechanical weathering (Granular weathering).
- Rocks break into sand particles due to wind and temperature changes in deserts.
Q 5. Using internet, look for incidences of a few landslides that have occurred in India and write about them briefly.
Malin Landslide (2014):
- Occurred on July 30, 2014, in Malin village, Pune district, Maharashtra.
- Heavy rainfall triggered a mudslide, burying over 40 houses and killing 151 people.
- The steep slope and weathered soil contributed to this rapid mass movement.
Kedarnath Landslide (2013):
- Happened in June 2013 in Uttarakhand during heavy floods.
- Landslides and flash floods destroyed homes, roads, and temples, killing over 5,000 people.
- Excessive rain and unstable slopes caused the disaster.
Kerala Landslides (2018):
- Took place in August 2018 in Idukki and Wayanad districts during monsoon floods.
- Heavy rain led to landslides, killing over 400 people and displacing thousands.
- Weathered slopes and deforestation worsened the event.

Leave a Reply