Questions Answers For All Chapters – Geography Class 9th
Exercise
Solutions
Q1. Identify the type of precipitation from the statement:
(a) A white cotton-like layer spreads on the earth’s surface. Because of this form of precipitation, the State of Jammu and Kashmir has to change its capital in winters. In Maharashtra, it does not precipitate like this.
Answer: Rainfall
This description refers to rainfall, which is the most common form of precipitation. It is the main source of water and is very important for farming, especially in India. It can be heavy (torrential) or light and steady (continuous).
(b) It seems as if water droplets are floating in the atmosphere. In London, one cannot see the Sun till the afternoon during winters because of this phenomenon.
Answer: Fog
This describes fog, which looks like floating water droplets in the air. In cities like London during winter, fog can be so thick that sunlight is not seen until later in the day.
(c) It never precipitates like this in equatorial areas. Precipitation in the solid form sometimes causes damage to the crops.
Answer: Hail
This is hail, which occurs in the form of ice balls falling from the sky. Hail does not happen in equatorial regions and can damage crops when it falls heavily.
(d) A white cotton-like layer spreads on the earth’s surface. Because of this form of precipitation, the State of Jammu and Kashmir has to change its capital in winters. In Maharashtra, it does not precipitate like this.
Answer: Snowfall
This describes snowfall, which covers the ground like a white cotton sheet. Due to heavy snowfall, Jammu and Kashmir changes its capital in winter, while places like Maharashtra do not experience snowfall.
Q2. Look at the following pictures and identify the correct rainfall type:
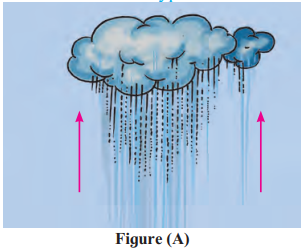
- This matches the description of convectional rainfall (Figure 5.4 in the document).
- Hot air rises, cools, condenses, and forms clouds that lead to rain, typical in equatorial areas.
- Answer: Convectional rainfall
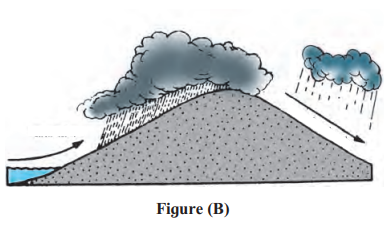
- This matches orographic rainfall (Figure 5.5(A) in the document).
- Moisture-laden winds rise over mountains, cool, condense, and cause rain on one side.
- Answer: Orographic rainfall
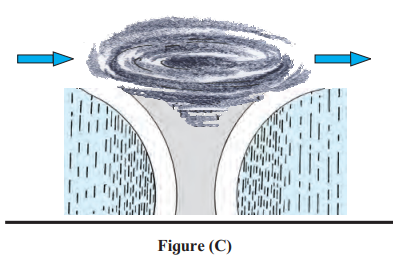
- This matches cyclonic rainfall (Figure 5.6 in the document).
- Air moves toward a low-pressure center, rises, cools, and causes rain, often with storms.
- Answer: Cyclonic rainfall
Q3. Look at the figures above and answer the following questions:
(1) In fig B, on which side of the mountain is it raining more?
- In Figure B (orographic rainfall), rain occurs more on the windward side.
- Winds carrying moisture hit the mountain, rise, cool, and drop rain on the side facing the wind.
- Answer: Windward side
(2) Shade the rain shadow region in fig B and name it.
- The rain shadow region is on the leeward side of the mountain in Figure B.
- After winds drop rain on the windward side, the leeward side gets less rain, forming the rain shadow.
- Answer: Leeward side (rain shadow region)
(3) What is the difference between A and C?
- Figure A shows convectional rainfall, caused by heated air rising and cooling in equatorial areas.
- Figure C shows cyclonic rainfall, caused by low-pressure systems where air converges and rises.
- Convectional is heat-driven and local, while cyclonic involves larger weather systems and storms.
- Answer: Convectional (A) is heat-induced; Cyclonic (C) is pressure-induced with storms.
(4) Stormy winds and floods are associated with which rainfall type?
- Cyclonic rainfall (Figure C) involves stormy winds and heavy rain that can cause floods.
- The document mentions cyclones bringing rain with strong winds over affected areas.
- Answer: Cyclonic rainfall
(5) What type of rainfall occurs in Singapore?
- Singapore is near the equator, where convectional rainfall occurs daily in the afternoons.
- The document explains this type for equatorial areas like the Congo and Amazon basins.
- Answer: Convectional rainfall
Q4. Identify the odd man out:
(1) Orographic rainfall, acid rain, cyclonic rainfall, convectional rainfall
- Orographic, cyclonic, and convectional are natural rainfall types caused by atmospheric processes.
- Acid rain is not a natural type but a result of pollution (chemical reaction with gases).
- Answer: Acid rain
(2) Snowfall, rainfall, hailstones, dew
- Snowfall, rainfall, and hailstones are precipitation forms falling from clouds to the ground.
- Dew is condensation near the surface, not falling precipitation.
- Answer: Dew
(3) Thermometer, rain gauge, anemometer, measuring jar
- Thermometer measures temperature, anemometer measures wind speed, and rain gauge measures rainfall.
- Measuring jar is a tool used with the rain gauge, not an independent instrument.
- Answer: Measuring jar
Q5. Answer in brief:
(1) In what ways does precipitation occur on the earth?
Precipitation is the process by which water falls from the atmosphere to the earth. It occurs in different forms such as rain, snow, hail, sleet, and drizzle. These forms depend on the temperature and moisture in the atmosphere.
(2) Comment on the rainfall occurring in the rain shadow area.
The rain shadow area receives very little rainfall. This happens because the mountains block the moist winds and force them to rise. By the time the winds cross the mountain, they have lost most of their moisture, so the other side remains dry.
(3) Which type of rainfall occurs in most of the world? Why?
Convectional rainfall is the most common type of rainfall in the world, especially in tropical areas. It happens when the land gets very hot during the day, causing warm air to rise and cool down, leading to rainfall. This kind of rain often occurs in the afternoon.
(4) If condensation occurs closer to the earth’s surface, what types of forms become visible?
When condensation happens close to the earth’s surface, forms like dew, fog, and frost become visible. These are tiny water droplets or ice crystals that appear early in the morning. They form when the air near the ground cools down and water vapor turns into liquid or solid.
(5) What precautions should be taken while measuring rainfall?
To measure rainfall correctly, a standard rain gauge should be used and placed in an open area. It must not be near buildings or trees which can block the rain. The reading should be taken daily at the same time to ensure accuracy.
Q6. Distinguish between:
(1) Dew and Frost
| Dew | Frost |
|---|---|
| Formed when water vapour condenses into water droplets. | Formed when water vapour freezes into ice crystals. |
| Occurs when temperature is above 0°C. | Occurs when temperature is below 0°C. |
| Appears as drops on surfaces like grass. | Appears as white icy coating. |
(2) Snow and Hail
| Snow | Hail |
|---|---|
| Formed when water vapour freezes directly into ice crystals in clouds. | Formed when raindrops freeze while moving up and down in thunder clouds. |
| Falls gently as soft flakes. | Falls as hard, round pellets. |
| Common in cold regions. | Occurs during storms. |


Leave a Reply