Information Communication Technology
Introduction
What is ICT?
ICT stands for Information Communication Technology, which includes devices and services used to collect, share, process, and communicate information.
Importance:
- The amount of information from science and technology is growing fast, and ICT helps manage this “information explosion.”
- Without ICT, our knowledge can become outdated, so it keeps us updated with the latest data.
Devices Used in ICT:
- Examples: Computers, telephones, smartphones, printers, scanners.
- These devices help produce, store, classify, manage, and share information.
Evolution of Computers
Generations of Computers:
- Computers have evolved through five generations since 1946.
- First Generation (1946-1959): Used valves (e.g., ENIAC), were large, consumed lots of electricity, generated heat, and often shut down.
Modern Computers:
- Today’s computers are fifth-generation, small, fast, and efficient due to advanced technology.
- Use the internet to learn about all generations and their differences (e.g., size, speed, components).
Fields Using Computers:
- Education, healthcare, banking, entertainment, weather forecasting, and research.
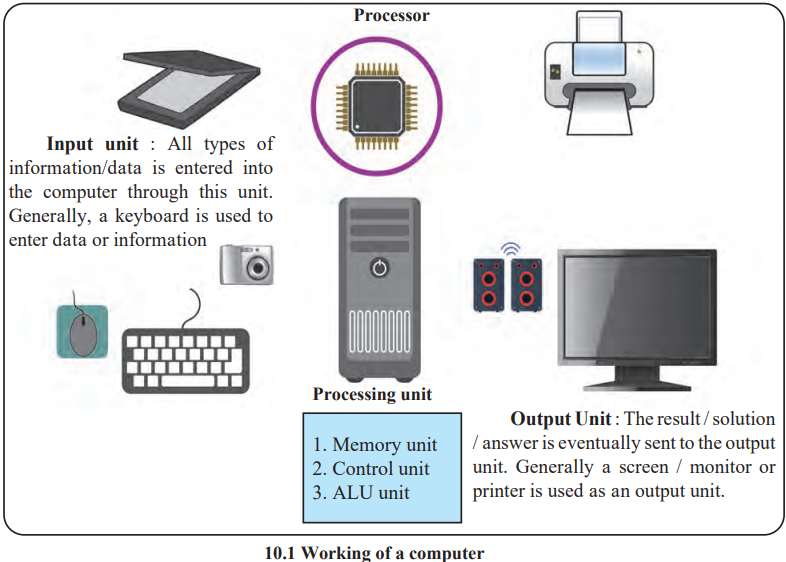
How a Computer Works
Main Components
1. Input Unit:
- Enters data or information (e.g., keyboard, mouse).
2. Processing Unit:
- Includes:
- Memory Unit: Stores data and results (RAM for temporary storage, ROM for permanent data).
- Control Unit: Manages operations.
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit): Performs calculations.
3. Output Unit:
- Displays or prints results (e.g., monitor, printer).
Memory Types:
Internal Memory:
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Temporary storage, needs electricity to function, data is lost when power is off.
- ROM (Read Only Memory): Permanent storage, data cannot be changed, used for basic instructions.
External Memory: Storage devices like hard disks or USB drives.
Operating System:
- A program (e.g., DOS) that acts as a bridge between the computer and the user.
- Essential for computer operation.
Data and Information:
- Data: Raw, unprocessed facts (e.g., numbers).
- Information: Processed data with meaning (e.g., a graph).
Hardware and Software:
- Hardware: Physical parts (e.g., monitor, CPU).
- Software: Programs and commands (e.g., Microsoft Word, operating systems).
Using Software
Microsoft Word:
- Used to create documents.
- Steps: Open, select “New” → “Blank Document,” type text, format with Home tab, insert equations via Insert → “Equation.”
Microsoft Excel:
- Used to draw graphs from numerical data.
- Steps: Open, select “New” → “Blank,” enter data, select data, choose graph from Insert tab, analyze results.
- Precautions: Use tables, avoid spaces/special characters, start formulas with “=,” use “smart tag” for drag-fill.
Microsoft PowerPoint:
- Used to create presentations.
- Steps: Open, select “New” → “Blank Slide,” add text/pictures (Design/Insert tabs), animate (Animation tab), create slideshow.
Other Software:
- Acrobat Reader: Views and prints PDF files.
- Internet Explorer: A search engine to find information online.
Importance of ICT in Science and Technology
Uses:
- Demonstration: Shows experiments (e.g., nervous system) using simulations/animations.
- Prediction: Forecasts weather or trends by processing data.
- Collecting Information: Uses internet, emails, blogs, video conferencing, Wikipedia.
Practical Application:
- Students should use ICT (e.g., software, internet) while studying science, with help from teachers or parents.
Opportunities in the Field of Computers
Software Field:
- Includes developing applications, software packages, operating systems, and scientific tools.
- Companies create software, offering jobs in programming and design.
Hardware Field:
- Involves designing, assembling, testing, maintaining, and repairing computers.
- Companies in India make and service computers, providing many jobs.
Training:
- Training new people for computer jobs requires skilled teachers.
- A growing field with demand for dedicated educators.
Marketing:
- Involves selling computers and accessories, needing skilled salespeople.
- Requires knowledge of computers and marketing skills.
Institutes at Work
C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing):
- Located in Pune, established to research computer technology.
- Developed India’s first supercomputer, “Param” (one billion calculations/second), used in space, medicine, meteorology, and more.
- Led by Vijay Bhatkar, it also created the ISCII code for Indian language scripts.

Leave a Reply