Carbon : An important element
Introduction to Carbon
What is an Element?
- An element is a pure substance made of only one type of atom (e.g., carbon, oxygen).
- Types: Metals (e.g., iron), non-metals (e.g., carbon), metalloids (e.g., silicon).
Carbon Basics:
- Carbon is a non-metal element.
- Symbol: C, Atomic Number: 6, Atomic Mass: 12, Electron Configuration: 2,4, Valency: 4.
- Found in nature in free (diamond, graphite) and combined forms (CO₂, carbonates).
Activity (Burning Organic Substances):
- Heat milk in an evaporating dish → black residue (carbon) remains.
- Heat sugar, wool, dry leaves, hair, seeds, pulses, plastic in test tubes → black residue (carbon) forms.
- Conclusion: Organic compounds (from plants/animals) contain carbon, which remains as a black substance after burning.
What is a Compound?
- A compound is a substance formed when two or more elements chemically combine (e.g., H₂O).
- Organic Compounds: Contain carbon, derived from living things (e.g., sugar, proteins).
- Inorganic Compounds: From minerals, may or may not contain carbon (e.g., NaCl, CaCO₃).
Importance of Carbon:
- Found in daily items: food (carbohydrates, proteins), clothes (cotton, wool), fuels (coal, petrol), DNA/RNA (heredity).
- Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds (started by Wohler, who made urea from ammonium cyanate).
Occurrence of Carbon
In Nature:
Free State: As diamond, graphite, fullerene.
Combined State:
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) in air (0.03%).
- Carbonates: CaCO₃ (limestone, marble), ZnCO₃ (calamine).
- Fossil Fuels: Coal, petroleum, natural gas.
- Nutrients: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats.
- Fibers: Cotton, wool, silk.
In Earth’s Crust: 0.27% (as carbonates, coal, petroleum).
Properties of Carbon
Allotropy:
- Some elements exist in different forms with the same chemical properties but different physical properties (e.g., carbon, sulphur).
- Carbon has crystalline (diamond, graphite, fullerene) and non-crystalline (coal, charcoal, coke) forms.
1. Crystalline Allotropes:
- Have a regular arrangement of atoms, definite shape, high melting/boiling points.
Diamond:
- Found in: Golconda (Telangana), Panna (Madhya Pradesh), South Africa, Brazil.
- Structure: Each carbon atom bonded to 4 others (3D structure), very hard.
- Properties:
- Hardest natural substance, density 3.5 g/cm³, melting point 3500°C.
- Burns at 800°C in oxygen to form CO₂ only.
- Does not dissolve in solvents, unaffected by acids/bases.
- Bad conductor of electricity (no free electrons).
- Uses:
- Glass cutting, rock drilling, eye surgery (diamond knives).
- Ornaments, polishing diamonds, radiation-proof windows in satellites.
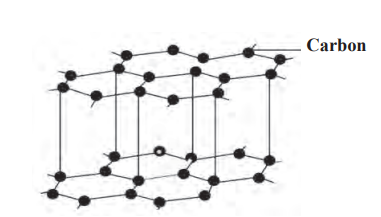
Graphite:
- Found in: Russia, New Zealand, America, India.
- Structure: Each carbon atom bonded to 3 others, forming hexagonal layers (graphene); layers slide over each other.
- Properties:
- Black, soft, brittle, slippery, density 1.9–2.3 g/cm³.
- Good conductor of electricity (free electrons in layers).
- Does not dissolve in most solvents.
- Uses:
- Lubricants, pencils, carbon electrodes, paints, arc lamps (bright light).
- Activity:
- Rub pencil lead (graphite) → soft and slippery.
- Test conductivity: Connect graphite in a circuit with a bulb → bulb glows (graphite conducts electricity).
- Add graphite to water/kerosene → insoluble in both.
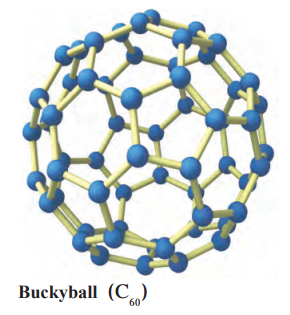
Fullerene:
- Found in: Soot, interstellar space (rare).
- Examples: C₆₀ (Buckminsterfullerene), C₇₀, C₈₂ (Nobel Prize 1996 to Kroto, Curl, Smalley).
- Structure: Buckyballs (C₆₀, spherical), buckytubes (tubes).
Properties:
- 30–900 carbon atoms per molecule.
- Soluble in organic solvents (e.g., carbon disulphide, chlorobenzene).
Uses:
- Insulators, catalysts in water purification, superconductors at certain temperatures.
2. Non-Crystalline (Amorphous) Forms:
- Irregular arrangement of atoms.
Coal:
- Fossil fuel, contains C, H, O, N, P, S.
- Types:
- Peat: <60% carbon, high water, low heat.
- Lignite: 60–70% carbon (2nd stage).
- Bituminous: 70–90% carbon (3rd stage).
- Anthracite: ~95% carbon, hardest, purest.
- Uses:
- Fuel (factories, homes), thermal power plants, produces coke, coal gas, coal tar.
Charcoal:
- Made from animal bones/horns or wood (burned with less air).
- Uses: Water purification, organic material purification.
Coke:
- Pure coal after removing coal gas.
- Uses: Domestic fuel, reducing agent, produces gases like water gas (CO + H₂).
Hydrocarbons
What Are Hydrocarbons?
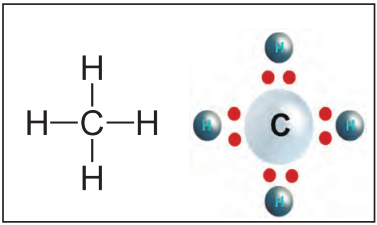
- Basic organic compounds made of only carbon and hydrogen.
- Carbon (2,4) shares 4 electrons to complete its octet (like neon, 2,8) → forms covalent bonds.
- Example: Methane (CH₄) → 1 C shares electrons with 4 H atoms.
Properties of Covalent Compounds:
- Low melting/boiling points.
- Insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents.
- Poor conductors of heat/electricity.
Types of Hydrocarbons:
- Saturated: Only single bonds between carbon atoms (e.g., ethane C₂H₆, propane C₃H₈).
- Unsaturated: At least one double or triple bond (e.g., ethene C₂H₄, ethyne C₂H₂, propene C₃H₆).
Solubility of Carbon:
- Activity: Add coal powder to water, kerosene, cooking oil → does not dissolve in any.
- Conclusion: Carbon is insoluble in water and organic solvents.
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Molecular Formula: CO₂, Molecular Mass: 44, Melting Point: -56.6°C.
Occurrence:
- In air: 0.03%, exhaled air: 4%.
- As carbonates: Chalk, limestone (CaCO₃).
- Released during combustion of wood, coal.
Preparation (Activity):
- React CaCO₃ (limestone) with dilute HCl in a flask → CO₂ gas forms.
- Equation: CaCO₃ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + H₂O + CO₂.
- Collect CO₂ by upward displacement of air (denser than air).
Properties of CO₂:
Physical:
- Colorless, odorless gas.
- Slightly soluble in water (forms carbonic acid: CO₂ + H₂O → H₂CO₃).
- Denser than air.
Chemical:
- Turns moist blue litmus red (acidic due to H₂CO₃).
- Turns limewater milky: CO₂ + Ca(OH)₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂O.
- Universal indicator in CO₂ solution → orange/red (pH < 7, acidic).
- Extinguishes a burning candle (does not support combustion).
- Reacts with NaOH:
- 2NaOH + CO₂ → Na₂CO₃ + H₂O (sodium carbonate).
- Na₂CO₃ + H₂O + CO₂ → 2NaHCO₃ (sodium bicarbonate).
Uses of CO₂:
- Aerated drinks, cold storage (solid CO₂, dry ice), fire extinguishers.
- Solvent in eco-friendly dry cleaning, decaffeinating coffee.
- Plants use CO₂ for photosynthesis.
- Fire Extinguisher:
- Contains NaHCO₃ and H₂SO₄ → 2NaHCO₃ + H₂SO₄ → Na₂SO₄ + 2H₂O + 2CO₂.
- CO₂ is non-corrosive, non-conductive, used for electrical fires.
Methane (CH₄)
Molecular Formula: CH₄, Molecular Mass: 16.
Occurrence:
- Natural gas (87% methane), biogas, coal mines, marshy areas (called marsh gas).
- Formed by decomposition of organic matter without air (anaerobic).
- Made by heating H₂ and CO with nickel catalyst at 300°C.
Properties of CH₄:
Physical:
- Colorless gas, melting point: -182.5°C, boiling point: -161.5°C.
- Less dense than water, sparingly soluble in water, highly soluble in organic solvents.
Chemical:
- Burns in oxygen: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + heat (213 kcal/mol, bluish flame).
- Chlorination: CH₄ + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + HCl (at 250–400°C with UV light).
Uses of CH₄:
- Fuel in industries (fabric mills, paper mills, food processing).
- Domestic fuel (less CO₂ emission).
- Produces ethanol, methyl chloride, acetylene.
Biogas Plant:
- Produces methane (55–60%) from animal dung, wet garbage (anaerobic decomposition).
Process:
- Organic matter → organic acids.
- Organic acids → CH₄ + CO₂ (by methanogenic bacteria).
Uses: Cooking gas, electricity generation; byproduct is good manure.
Eco-friendly: Reduces waste, renewable fuel.




Leave a Reply