Substances in Common Use
Introduction to Substances in Daily Life
What Are They? Substances like table salt, soap, toothpaste, and baking soda are used daily for cooking, cleaning, and health.
Classification:
Acids: E.g., vinegar (in curds).
Bases: E.g., soap, toothpaste.
Metals: E.g., iron.
Non-metals: E.g., sulphur.
Salts: E.g., table salt, baking soda, washing powder.
Scientific View:
- Substances are classified based on their chemical properties (e.g., pH, ionic nature).
Important Salts in Daily Life
What Are Salts?
- Simple salts are ionic compounds with one cation and one anion, excluding H⁺ and OH⁻ ions (e.g., Na₂SO₄, CaCl₂).
Sea as a Salt Source:
- Contains about 80 million tons of salts yearly, rich in sodium chloride, magnesium, potassium, calcium, and bromine salts.
Sodium Chloride (NaCl) – Table Salt
Formation:
- Made by neutralizing sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- [NaOH + HCl -> NaCl + H₂O]
Properties and Uses:
- Colorless, crystalline, neutral salt (pH 7).
- Used to flavor food and produce other salts like Na₂CO₃ and NaHCO₃.
- Electrolysis of brine (25% NaCl solution) produces NaOH, Cl₂, and H₂.
- [2NaCl + 2H₂O -> 2NaOH + Cl₂ + H₂]
- Fused salt electrolysis yields sodium metal and chlorine gas.
- Rock salt (e.g., Himalayan salt) treats diseases.
Preparation:
- Evaporate saturated brine to crystallize salt.
Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) – Baking Soda
Properties and Uses:
- White, non-crystalline powder, basic (turns red litmus blue).
- Makes bread, cake, and dhokla porous; reduces stomach acidity.
- Used in fire extinguishers to release CO₂.
- [2NaHCO₃ + heat -> Na₂CO₃ + H₂O + CO₂]
- Cleans ovens.
Research:
- Baking powder contains NaHCO₃ and an acid; used in cooking.
Bleaching Powder (CaOCl₂) – Calcium Oxychloride
Formation:
- Made by reacting chlorine gas with slaked lime.
- [Ca(OH)₂ + Cl₂ -> CaOCl₂ + H₂O]
Properties and Uses:
- Yellowish-white solid with chlorine odor.
- Disinfects drinking water and swimming pools.
- Bleaches cloth; disinfects roads and garbage sites.
- Releases Cl₂ with dilute H₂SO₄ or HCl.
- [CaOCl₂ + H₂SO₄ -> CaSO₄ + Cl₂ + H₂O]
- Slow reaction with CO₂ releases Cl₂.
- [CaOCl₂ + CO₂ -> CaCO₃ + Cl₂]
Experiment:
- Apply to colored cloth to see bleaching.
Washing Soda (Na₂CO₃·H₂O)
Formation:
- Crystalline Na₂CO₃·10H₂O loses water to form Na₂CO₃·H₂O.
- [Na₂CO₃·10H₂O ->[heat] Na₂CO₃·H₂O + 9H₂O]
Properties and Uses:
- White, odorless, hygroscopic powder; basic in solution.
- Softens hard water by forming insoluble MgCO₃ and CaCO₃.
- [MgCl₂ + Na₂CO₃ -> MgCO₃ + 2NaCl]
- Used for washing clothes, glass/paper industry, petrol refining.
- Reacts with H₂SO₄.
- [Na₂CO₃ + H₂SO₄ -> Na₂SO₄ + H₂O + CO₂]
Experiment:
- Add to hard water with soap to form lather.
Crystalline Salts with Water of Crystallization
Examples:
- Alum (K₂SO₄·Al₂(SO₄)₃·24H₂O) – Water purification.
- Borax (Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O) – Cleaning, antiseptic.
- Epsom salt (MgSO₄·7H₂O) – Laxative, bath soak.
- Barium chloride (BaCl₂·2H₂O) – Chemical tests.
- Sodium sulphate (Na₂SO₄·10H₂O) – Laxative.
Water of Crystallization:
- Water molecules in salt crystals, giving structure (e.g., Na₂CO₃·10H₂O).
Soap
Formation:
- Boiling oil/fat with NaOH or KOH forms soap (sodium/potassium salts of fatty acids).
- Hard water forms insoluble Ca/Mg salts, reducing lather.
Types:
- Bathing soap vs. washing soap (differ in ingredients, fragrance).
Radioactive Substances
What is Radioactivity?
- Spontaneous emission of high-energy radiation (alpha, beta, gamma) from unstable nuclei of elements like uranium, thorium, radium.
Discovery:
- Henri Becquerel (1896) found uranium emitted rays; Marie Curie identified thorium’s radioactivity.
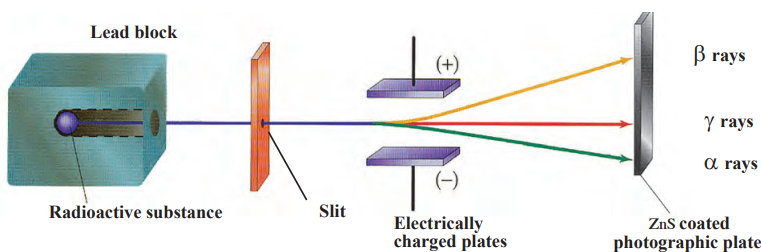
Types of Radiation :
- Alpha (α): Slightly deviates toward negative plate, low penetration.
- Beta (β): Substantially deviates toward positive plate, medium penetration.
- Gamma (γ): No deviation, high penetration.
Characteristics:
- Alpha: Heavy, stopped by paper.
- Beta: Lighter, stopped by aluminum.
- Gamma: Highly penetrating, stopped by lead.
Uses of Radioactive Isotopes:
1. Industry:
- Radiography (Co-60, Ir-192) for metal flaws.
- Thickness/density measurement.
- Luminescent paint (Ra, Pm-147) for clocks.
2. Agriculture:
- Modifies seeds (Co-60).
- Preserves food (Co-60, Sr-90).
3. Medicine:
- Polycythemia (P-32), bone cancer (Sr-89), hyperthyroidism (I-123), tumors (Co-60).
Hazards:
- Causes cancer, genetic defects, nervous system damage.
- Chernobyl (1986) incident led to thyroid issues and genetic disorders.
Chemical Substances in Daily Life
Food Colours and Essences
Uses:
- Added to drinks, ice cream, sweets for appeal.
Harmful Effects:
- Artificial colors (e.g., tartrazine) may cause ADHD; lead/mercury in pickles/jams harm health.
Natural vs. Artificial:
- Natural (beetroot, flowers); artificial (tetrazene) risky if overused.
Dyes
Types:
- Natural (saffron, henna); artificial (petroleum-based).
Uses:
- Colors cloth, hair, shoes; fluorescent dyes for signs.
Adverse Effects:
- Hair fall, skin burn; carmine in lipstick causes stomach issues.
Artificial Colours (Rang Panchami)
Harmful Effects:
- Mercury in red color causes blindness, cancer, asthma.
Eco-Friendly Option:
- Use natural colors from beetroot, spinach.
Deodorants
Types:
- Ordinary (low aluminum), antiperspirant (15% aluminum), clinical (20-25% aluminum).
Harmful Effects:
- Aluminum compounds cause skin cancer, respiratory issues.
Teflon
Properties:
- Chemically inert, non-sticky, heat-resistant (melting point 327°C), poor conductor.
Uses:
- Non-stick cookware, wire insulation, vehicle coatings.
Powder Coating
Process:
- Electrostatic powder applied, heated to form a durable layer.
Uses:
- Prevents rust on iron, used on plastic/MDF.
Anodizing
Process:
- Electrolysis thickens aluminum’s oxide layer.
- [ 2Al + 3O₂ -> Al₂O₃]
Uses:
- Protective, colorful coatings on utensils.
Ceramics
Types:
- Porous ceramic (pots, tiles), porcelain (kaolin-based), bone china, advanced ceramics.
Process:
- Clay kneaded, shaped, fired (1000-1800°C), glazed.
Uses:
- Heat-resistant items, electrical insulators, space shuttle tiles.





Leave a Reply