Introduction to Biotechnology
1. What are Tissues?
Definition: A group of cells with the same origin, structure, and function is called a tissue.
Role: Tissues work together to perform specific functions in the body of multicellular organisms.
Example:
Muscles help in movement by contracting and relaxing.
In plants, conducting tissues transport water and food.
Hierarchy of Organization
Similar to how letters → words → sentences → lessons → textbook, the body of organisms is organized as:
Cells → Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems → Organism.
2. Types of Tissues
Tissues are classified into simple and complex based on the number of cell types.
Simple Tissues
Made up of only one type of cell.
Examples:
Epithelial tissue (in animals): Covers and protects surfaces.
Meristematic tissue (in plants): Helps in growth.
Complex Tissues
Made up of more than one type of cell.
Examples:
Blood (in animals): Transports oxygen and nutrients.
Xylem and Phloem (in plants): Transport water and food.
3. Animal Tissue
There are four main types of animal tissues, each with specific functions:
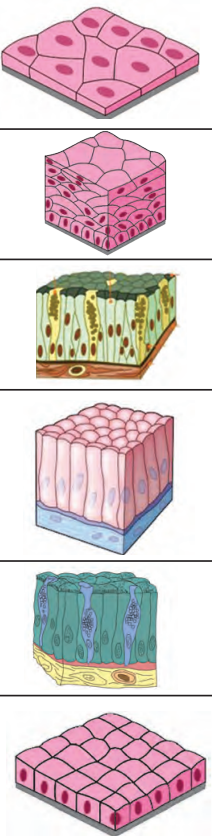
a. Epithelial Tissue
Function: Forms protective coverings (e.g., skin, lining of mouth, blood vessels).
Features:
Cells are closely packed, forming continuous layers.
Separated from other tissues by a fibrous membrane.
Types:
Simple squamous: Thin, flat cells (e.g., in alveoli of lungs).
Cuboidal: Cube-shaped cells (e.g., in kidney tubules).
Columnar: Tall, column-like cells (e.g., in intestines).
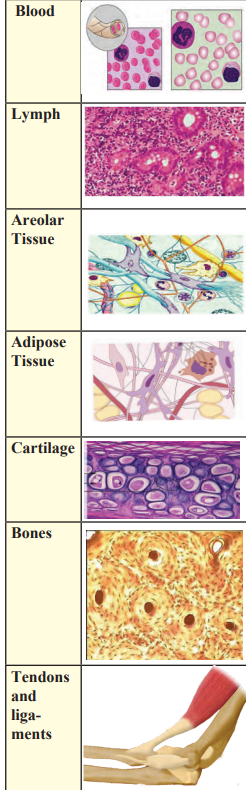
b. Connective Tissue
Function: Joins different parts of the body and provides support.
Features:
Cells are loosely arranged with a ground substance (solid, liquid, or jelly-like) between them.
Examples:
Blood: Transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste.
Bone: Provides structure and support.
Cartilage: Flexible support (e.g., in ears).
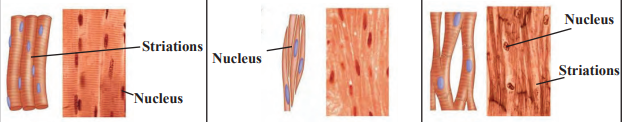
c. Muscular Tissue
Function: Enables movement through contraction and relaxation.
Features:
Made of long cells called muscle fibers with contractile proteins.
Types:
Striated (Skeletal): Voluntary, attached to bones (e.g., arm muscles).
Smooth: Involuntary, found in organs (e.g., intestines).
Cardiac: Involuntary, found only in the heart.
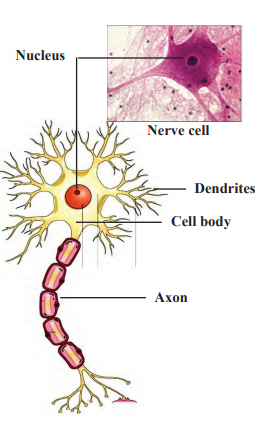
d. Nervous Tissue
Function: Responds to stimuli (e.g., touch, sound, smell) and conducts signals.
Features:
Made of nerve cells (neurons) with a cell body, dendrites, and a long axon.
Found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Example: Helps identify objects by touch or smell.
4. Plant Tissues
Plants have two main types of tissues: Meristematic and Permanent.
a. Meristematic Tissue
Function: Responsible for plant growth.
Features:
Cells are small, with thick cytoplasm, a large nucleus, and thin cell walls.
Cells are tightly packed, with no vacuoles.
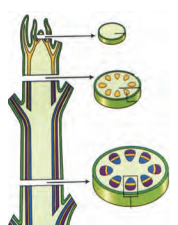
Found in specific areas (e.g., tips of roots and shoots).
Types:
Apical: At the tips, increases length.
Lateral: Increases girth (thickness).
Intercalary: At the base of leaves or nodes, helps in elongation.
b. Permanent Tissue
Definition: Formed when meristematic cells differentiate and lose the ability to divide.
Types:
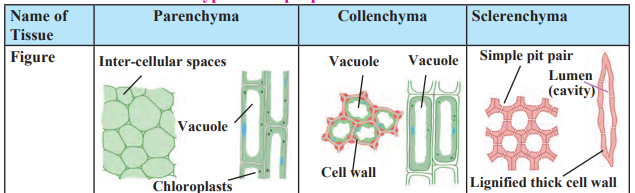
Simple Permanent Tissue:
Made of one type of cell.
Examples:
Epidermis: Outer protective layer of plants, covered by a waxy cuticle to retain water.
Parenchyma: Stores food and water.
Collenchyma: Provides flexibility.
Sclerenchyma: Provides strength.
Complex Permanent Tissue:
Made of more than one type of cell.
Examples:
Xylem: Transports water and minerals.
Phloem: Transports food.
5. Biotechnology
Definition: The use of techniques like genetic engineering and tissue culture to improve plants and animals for human benefit.
Applications:
Producing high-yielding crops.
Developing stress-resistant plants.
Vaccine production, organ transplants, cancer research, and more.
6. Tissue Culture
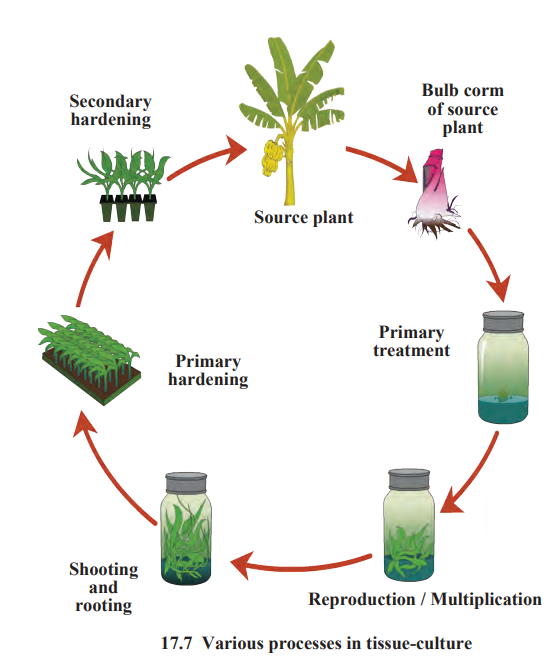
Definition: Growing cells or tissues in an aseptic, nutrient-rich medium (e.g., agar) outside the organism (**1.
Process:
Select a healthy plant part (e.g., bulb or corm).
Treat it, grow it in a nutrient medium, and allow it to form shoots and roots.
Harden the plantlets (primary and secondary hardening) to adapt to natural conditions.
Advantages:
Produces many plantlets quickly.
Grows disease-free and virus-free plants.
Saves rare or endangered plants.
Grows plants that don’t germinate easily (e.g., orchids).
Produces fully grown plants in less time.
7. Genetically Modified (GM) Crops
Definition: Crops with artificially altered DNA to introduce useful traits.
Examples:
BT Cotton: Pest-resistant.
Golden Rice: Rich in Vitamin A.
Amflora Potato: Improved starch content.
Benefits:
Resistant to pests, diseases, and harsh environments.
Reduces pesticide use.
Improves nutrition and reduces crop loss.
8. Applications of Biotechnology
Floriculture, Nurseries, and Forestry:
Produces high-quality flowers and fruits.
Grows plants without pollination or seeds.
Uses bioreactors for large-scale production.
Protects endangered plants.
Agriculture:
Increases crop yield and quality.
Supports the Green Revolution for food security.
9. Agritourism
Definition: A business combining agriculture and tourism, where people visit farms or gardens for relaxation and education.
Features:
Grow fruit trees (e.g., mango, guava), ornamental plants, medicinal plants, and organic vegetables.
Include butterfly gardens and shade-giving plants.
Benefits:
Profitable through sales of seedlings, fruits, and vegetables.
Attracts visitors seeking nature and relaxation.
10. Agro-complementary Occupations
These are businesses related to agriculture that support farmers.
a. Animal Husbandry
Definition: Raising animals like cows and buffaloes for milk and farm work.
Care:
Provide a balanced diet, clean sheds, and vaccinations.
Examples: Indian breeds (Sahiwal, Gir) and exotic breeds (Jersey, Holstein).
White Revolution: Increased milk production in India, pioneered by Dr. Verghese Kurien.
b. Poultry Farming
Definition: Raising chickens for eggs and meat.
Varieties: Rhode Island Red, Leghorn, Plymouth Rock.
Goals:
Produce high-quality chickens.
Use agricultural by-products as feed.
Develop heat-resistant varieties.
c. Sericulture
Definition: Rearing silkworms (e.g., Bombyx mori) for silk production.
Process:
Eggs → Larvae → Pupa → Adult.
Larvae feed on mulberry leaves and spin cocoons.
Cocoons are boiled to loosen silk fibers for weaving.
Why boil cocoons?: To kill the pupa and loosen silk fibers before the adult moth emerges.

Leave a Reply