Work and Energy
Introduction to Work
What is Work in Physics?
- Work happens when a force moves an object in the direction of the force.
- Formula: Work = Force × Displacement (W = F × s).
- Example: Pushing a box on the floor does work if the box moves.
When is Work Not Done?
- No work is done if:
- The object doesn’t move (displacement = 0).
- The force and displacement are perpendicular (like carrying a bag while walking).
Mental vs. Physical Work:
- In physics, we focus on physical work (e.g., lifting a book), not mental work (e.g., studying).
Work When Force and Displacement Are at an Angle
Special Case:
- Sometimes, the force is not in the same direction as the displacement (e.g., pulling a toy cart with a string).
- Use the component of the force in the direction of displacement.
- Formula: W = F × s × cosθ (where θ is the angle between force and displacement).
- Example: If a child pulls a cart at 60° to the ground, only the horizontal part of the force does work.
Effect of Angle (θ):
- θ = 0° (same direction): Work is positive (W = F × s).
- θ = 90° (perpendicular): Work is zero (cos 90° = 0).
- θ = 180° (opposite direction): Work is negative (W = -F × s).
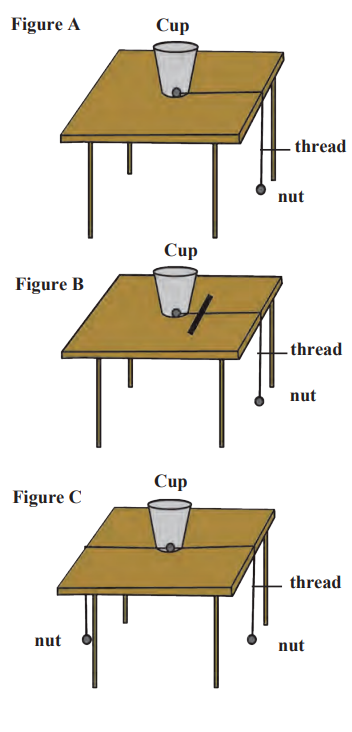
Activity Example:
A cup with nuts tied to threads (Figure 2.4):
Figure A: Nut pulls the cup (force and displacement in the same direction → positive work).
Figure B: Ruler stops the cup (force opposite to motion → negative work).
Figure C: Two nuts balance each other (no displacement → zero work).
Unit of Work:
- SI Unit: Joule (J) → 1 J = 1 Newton × 1 meter.
- CGS Unit: Erg → 1 erg = 1 dyne × 1 cm.
- Conversion: 1 J = 10⁷ erg (since 1 N = 10⁵ dyne, 1 m = 10² cm).
Examples of Work:
- Positive Work: Pushing a stalled vehicle (force and motion in the same direction).
- Negative Work: Stopping a car with brakes (force opposite to motion).
- Zero Work: Swinging a stone in a circle (force toward the center, motion along the circle → perpendicular).
Energy
What is Energy?
- The ability to do work is called energy.
- Units: Same as work (Joule in SI, erg in CGS).
- Forms of Energy: Mechanical, heat, light, sound, chemical, nuclear, solar, etc.
Types of Mechanical Energy
1. Kinetic Energy (K.E.):
- Energy due to motion.
- Examples: A moving cricket ball, a car, a rolling marble.
- Formula: K.E. = (1/2) × m × v² (m = mass, v = velocity).
Derivation:
- Work done = Force × Displacement = F × s.
- Force = m × a (Newton’s second law).
- Displacement s = (1/2) × a × t² (since initial velocity u = 0).
- Using v = a × t, we get s = (1/2) × (v² / a).
- So, Work = m × a × (v² / 2a) = (1/2) × m × v² = K.E.
Example: A 250 g (0.25 kg) stone moving at 2 m/s has K.E. = (1/2) × 0.25 × 2² = 0.5 J.
- Note: If mass doubles, K.E. doubles. If velocity doubles, K.E. becomes 4 times (v² effect).
2. Potential Energy (P.E.):
- Energy due to position or state.
- Examples: A stretched bow, water at a height, a compressed spring.
- Formula: P.E. = m × g × h (m = mass, g = 9.8 m/s², h = height).
- Derivation: Work done to lift an object to height h = Force × Displacement = m × g × h = P.E.
- Example: 500 kg water at 10 m height has P.E. = 500 × 9.8 × 10 = 49000 J.
- Note: P.E. depends on the reference point (e.g., Ajay and Atul measure different heights for the same ball).
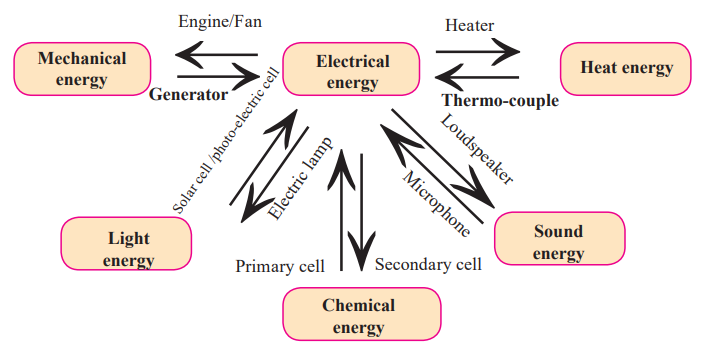
Transformation of Energy
What is It?
- Energy changes from one form to another.
Examples:
- Firecrackers: Chemical → Light + Sound + Heat.
- Electric fan: Electrical → Mechanical.
- Solar cell: Light → Electrical.
- Heater: Electrical → Heat.
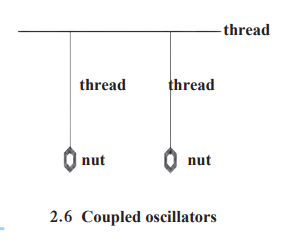
Activity:
- Two pendulums tied to a thread (Figure 2.6):
- Swing one pendulum; its K.E. transfers to the second pendulum, making it swing (K.E. → K.E.).
Law of Conservation of Energy
Principle:
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it only changes forms. Total energy stays constant.
- Example: A falling object converts P.E. to K.E., but total energy remains the same.
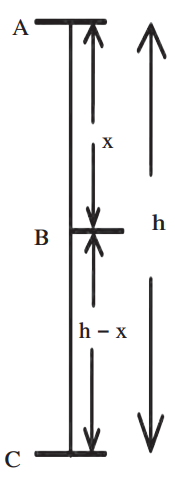
Free Fall Example (Figure 2.7):
Object of mass m falls from height h:
Point A (at height h):
- K.E. = 0 (velocity = 0).
- P.E. = m × g × h.
- Total Energy = mgh.
Point B (height h-x):
- Velocity at B: v² = 2gx (using v² = u² + 2as).
- K.E. = (1/2) × m × (2gx) = mgx.
- P.E. = m × g × (h-x).
- Total Energy = mgx + mgh – mgx = mgh.
Point C (ground):
- Velocity at C: v² = 2gh.
- K.E. = (1/2) × m × (2gh) = mgh.
- P.E. = 0 (height = 0).
- Total Energy = mgh.
Total energy (P.E. + K.E.) is always mgh, proving the law.
Power
What is Power?
- The rate of doing work.
- Formula: Power = Work / Time (P = W / t).
- Unit: Watt (W) → 1 W = 1 J/s.
- Other Units:
- Horsepower (1 HP = 746 W).
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh) for electricity: 1 kWh = 3.6 × 10⁶ J = 1 unit.
Examples:
Swaralee lifts a 20 kg bag to 5 m in 40 s:
- Work = m × g × h = 20 × 9.8 × 5 = 980 J.
- Power = 980 / 40 = 24.5 W.
A 25 W bulb used for 10 hours daily:
- Energy = Power × Time = 0.025 kW × 10 h = 0.25 kWh.

Leave a Reply