Life Processes in Living Organisms – Solutions
1. Match the pairs and explain.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Growth of pollen tube towards ovules (2) Growth of shoot system (3) Growth of root system (4) Growth towards the water | (a) Gravitropic movement (b) Chemotropic movement (c) Phototropic movement (d) Growth-irrelevant movement (e) Hydrotropic movement |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c),
(3 – a),
(4 – e).
2. Complete the paragraph.
The milk was on the stove. Rasika was engrossed in watching television. She smelled something burning. She ran towards the kitchen. The milk was boiling over. She held the vessel with her bare hands but, screaming, she let it go at once. This activity was controlled by ……………….. cells. Special ends of ……………….. in these cells collected the information, from where it was transferred to the ……………….. and then towards the terminal end of the ……………….. The chemicals produced at the terminal end passed through the minute space i.e. ………………. . In this way, ……………….. were conducted in the body and the process of ……………….. was completed by conducting the impulses from ……………….. to ……………… (Nerve, muscle cell, impulse, dendrite, synapse, axon, reflex action, cell body)
Answer: nerve, dendrite, cell body, axon, synapse, impulses, reflex action, nerve, muscle cell.
3. Write notes on –
Root pressure, Transpiration, Nerve cell, Human brain, Reflex action
Root Pressure: Root pressure is the force generated by root cells that pushes water and minerals into the xylem, aiding their transport in plants. When roots absorb water and minerals from soil, cells become turgid, creating pressure that drives the water upward, forming a continuous water column. This process is crucial for small plants and works best at night when transpiration is low, as seen when a stained solution travels up a plant’s stem.
Transpiration: Transpiration is the evaporation of water vapor from plant leaves through stomata, controlled by guard cells. It helps absorb water and minerals, cools the plant, and creates a transpiration pull to draw water from roots, ensuring distribution to all parts. For example, an oak tree releases about 151,000 liters of water yearly, highlighting its role in water movement.
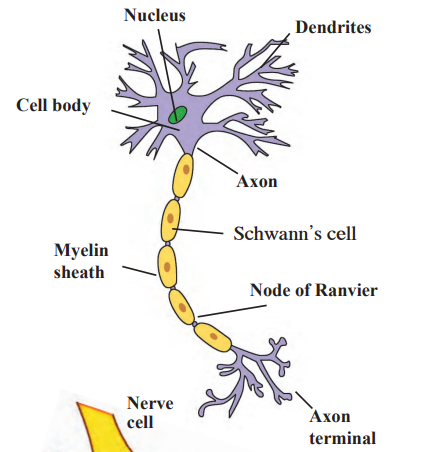
Nerve Cell: Nerve cells, or neurons, are specialized cells that transmit electrochemical impulses to coordinate body functions. Comprising dendrites, a cell body, and an axon, neurons relay signals across synapses using neurotransmitters, supported by neuroglia. They connect sensory organs to muscles and glands, enabling quick responses, like pulling away from a hot surface.
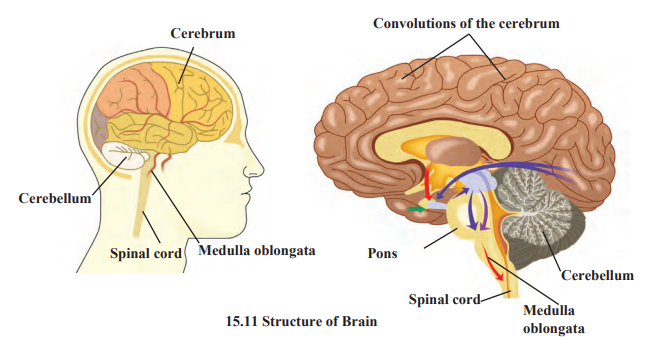
Human Brain: The human brain, the nervous system’s control center, weighs 1300-1400 grams and is protected by the skull and meninges. It includes the cerebrum (for thinking), cerebellum (for balance), and medulla oblongata (for vital functions like breathing), with cerebrospinal fluid cushioning it. The brain’s left side manages logic, while the right handles creativity, ensuring coordinated body responses.
Reflex Action: Reflex action is an involuntary, rapid response to a stimulus, like withdrawing a hand from heat, bypassing conscious brain control. Sensory neurons detect the stimulus, relay it to the spinal cord, and motor neurons trigger muscle action via a reflex arc, protecting the body by enabling quick, coordinated reactions without delay.
4. Name the hormones of the following endocrine glands and the function of each.
Pituitary, Thyroid, Adrenal, Thymus, Testis, Ovary.
Pituitary Gland:
- Hormones: Growth Hormone (GH), Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH).
- Functions: GH promotes growth, TSH stimulates thyroid activity, and ACTH regulates adrenal gland functions.
Thyroid Gland:
- Hormone: Thyroxine.
- Function: Controls metabolism, growth, and energy utilization in the body.
Adrenal Glands:
- Hormones: Adrenaline, Cortisol.
- Functions: Adrenaline boosts heart rate and energy during stress, while Cortisol manages stress and blood sugar levels.
Thymus Gland:
- Hormone: Thymosin.
- Function: Stimulates the development of T-cells for immune system function.
Testis:
- Hormone: Testosterone.
- Function: Promotes male reproductive development and secondary sexual characteristics like facial hair.
Ovary:
- Hormones: Estrogen, Progesterone.
- Functions: Estrogen develops female characteristics, and progesterone supports pregnancy and regulates menstrual cycles.
5. Draw and label the diagrams.
Human endocrine glands
Human brain
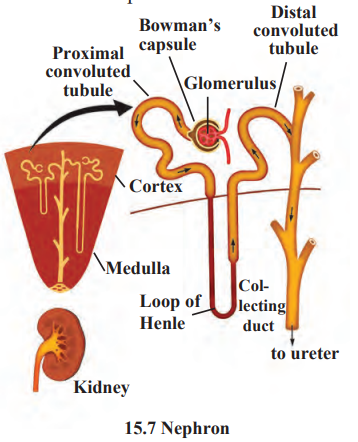
Nephron
Nerve cell
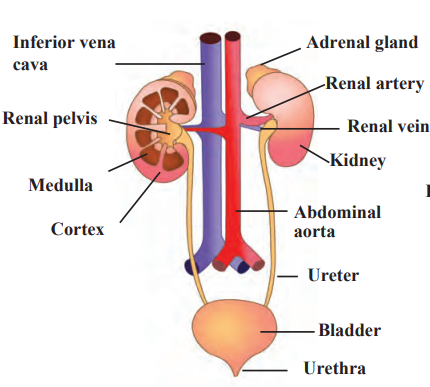
Human excretory system
6. Answer the following.
a. Explain chemical co-ordination in humans and give the names and functions of some hormones.
Answer:
Chemical coordination in humans involves hormones secreted by endocrine glands, which travel through blood to regulate body functions like growth and stress response. These ductless glands ensure hormones are released in the right amount, acting slowly but with lasting effects.
For example, whenever there is an increase in blood glucose level, certain cells in the pancreas get stimulated and as a response, they release a greater quantity of insulin, thus bringing down the sugar level to normal.
| Hormone | Function |
| (1) Growth hormone | Stimulates growth of bones. |
| (2) Luteinizing hormone | Controls menstrual cycle and ovulation. |
| (3) Thyroxine | Controls growth of body and metabolic activities. |
| (4) Insulin | Stimulates liver to convert excess blood glucose to glycogen. |
| (5) Testosterone | Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characters like beard, mustache, hoarse voice, etc. in men. |
b. Explain the Difference Between the Excretory System of Humans and Plants
| Excretory system of humans | Excretory system of plants |
| (i) In humans, the excretory system carries out the function of the removal of waste from the body. | (i) In plants, there is no special system or organ for excretion. |
| (ii) Waste substances are generally eliminated out of the body | (ii) Most of the waste substances are stored in the leaves, flowers, fruits and bark of the stem. |
| (iii) The excretory products are urea, uric acid, ammonia, etc. | (iii) The excretory products are gum, resin, latex of rubber, etc. |
c. Explain co-ordination in plants with the help of suitable examples.
Answer:
Plants coordinate by responding to stimuli using hormones and electrochemical impulses, without a nervous system, through tropic (growth-related) or non-tropic movements. Tropic movements include phototropism, where sunflowers grow toward sunlight, and gravitropism, where roots grow downward. Non-tropic movements occur in touch-me-not plants, whose leaves fold when touched due to water content changes. These responses ensure plants adapt to their environment effectively
Question 7: Explain in Your Own Words with Suitable Examples.
a. What is meant by co-ordination?
Coordination is the process where body parts work together to respond to internal or external changes, maintaining balance (homeostasis) for smooth functioning. In humans, it involves nerves and muscles acting together, like when you pull your hand away from a hot surface after nerves detect heat. In plants, coordination is seen when a sunflower turns toward sunlight to maximize photosynthesis. Proper coordination ensures all activities are completed efficiently.
b. How does excretion occur in human beings?
Excretion in humans removes harmful wastes like urea through the excretory system, which includes kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Kidneys filter blood in nephrons to form urine, which is stored in the bladder and expelled via the urethra. Skin and lungs also excrete sweat and carbon dioxide. For example, after drinking water, kidneys filter excess water to produce urine, keeping the body healthy.
c. How is excretion in plants useful to human beings?
Plant excretion removes wastes like resin, gum, and latex, which are stored in leaves, bark, or xylem and are valuable to humans. For example, latex from rubber trees is used to make tires, and resin from pine trees is used in varnishes. Gum from acacia trees is used in medicines and food. These waste products support industries and provide useful materials for human use.
d. Describe the transportation system in plants.
Plants transport water, minerals, and food using xylem and phloem tissues. Xylem moves water and minerals upward from roots to leaves, driven by root pressure and transpiration pull, as seen when stained water travels up a plant’s stem. Phloem carries food, like sucrose, to all parts using ATP energy. For example, sugar from roots reaches buds during flowering, supporting plant growth and function.


Leave a Reply