Heredity and Variation – Solutions
1. Complete the following sentences by choosing the appropriate words from the brackets.
(Inheritance, sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction, chromosomes, DNA, RNA, gene)
a. Hereditary characters are transferred from parents to offsprings by …………………………….., hence they are said to be structural and functional units of heredity.
b. Organisms produced by …………………………….. show minor variations.
c. The component which is in the nuclei of cells and carries the hereditary characteristics is called ……………………………..
d. Chromosomes are mainly made up of ……………………………..
e. Organisms produced through …………………………….. show major variations.
Answer:
a. genes
b. asexual reproduction
c. chromosome
d. DNA
e. sexual reproduction
2. Explain the following.
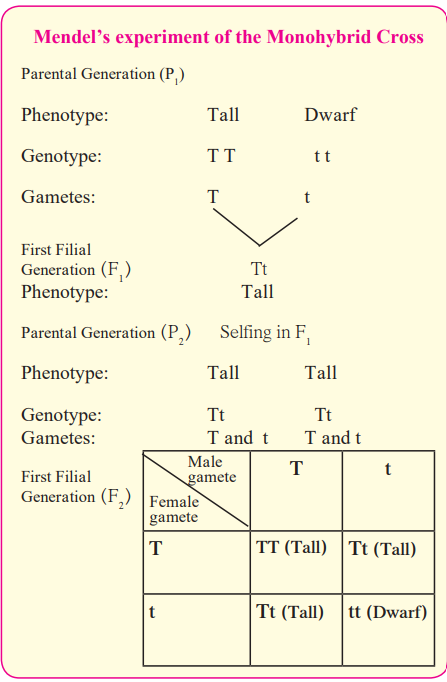
a. Explain Mendel’s monohybrid progeny with the help of any one cross.
Answer:
- Mendel brought about a cross between two pea plants with only pair of contrasting characters. This type of cross is called a monohybrid cross.
- Tall pea plants and dwarf pea plants were used in this cross. Hence this is parent generation (P1).
- All the plants produced in F1 genration are tall, having genotype Tt. This indicates that the gene responsible for tallness in pea plants is dominant over the gene responsible for dwarfness.
- When F1 plants are self pollinated they produce second filial generation (F2).
- In F2 generation both tall and dwarf plants appeared in the ratio 3:1.
- Thus, the genotypic ratio of F2 generation is 3 (Tall) : 1 (Dwarf) and the genotypic ratio is 1 TT : 2 Tt: 1 tt.
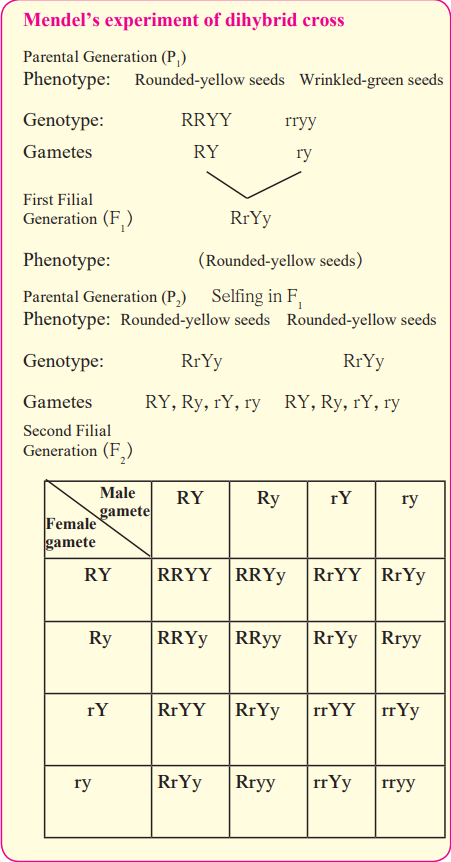
b. Explain Mendel’s dihybrid ratio with the help of any one cross.
Answer:
- In dihybrid cross, Mendel considered two pairs of contrasting characters.
- He made a cross between a pea plant producing rounded
- All the plants produced in F1 generation had rounded yellow seeds. This is because in pea plants, round shape of seed is dominant over wrinkled shape and yellow colour of seed is dominant over green colour.
- When F1 plants are self pollinated, they produce four types of gamates – RY, Ry, rY, ry.
- F2 plants formed by the fusion of four types of male gametes and four types of female gametes, had phenotypes such as round yellow, wrinkled yellow, round green and wrinkled green.
- Also, F2 generation showed nine different types of genotypes such as RRYY, RRYy, RRyy, RrYY, RrYy, Rryy, rrYY, rrYy, rryy.
- Phenotypic ratio of dihybrid cross is
c. Distinguish between monohybrid and dihybrid cross.
Answer:
| Monohybrid cross | Dihybrid cross |
| (i) Cross involving a single pair of contrasting characters is called monohybrid cross. | (i) Cross involving two pairs of contrasting characters is called a dihybrid cross. |
| (ii) F1 plants of monohybrid cross produce two types of gametes. | (ii) F1 plants of dihybrid cross produce four types of gametes. |
| (iii) Monohybrid cross has a phenotypic ratio of 3 : 1 in F2 generation. | (iii) Dihybrid cross has a phenotypic ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 in F2 generation. |
d. Is it right to avoid living with a person suffering from a genetic disorder?
Answer:
- No, it is not right to avoid living with a person suffering from a genetic disorder.
- Genetic disorders are transmitted from parents to offsprings only and they are non-contagious, i.e., they do not spread from one person to another through contact.
3. Answers the following questions in your own words.
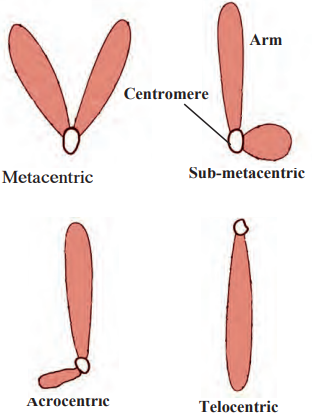
a. What is meant by ‘chromosome’. Explain its types.
Answer:
- The structure in the nucleus of cells that carries the hereditary characteristics is called the chromosome.
- It is made up mainly of nucleic acids and proteins.
- Depending upon the position of the centromere, there are four types of chromosomes.
(a) Metacentric: The centromere is exactly at the mid-point in this chromosome, and therefore, it looks like the English letter ‘V’. The arms of this chromosome are equal in length.
(b) Sub-metacentric: The centromere is somewhere near the mid-point in this chromosome which, therefore, looks like the English letter ‘U. One arm is slightly shorter than the other.
(c) Acrocentric: The centromere is near one end of this chromosome which therefore looks like the English letter One arm is much smaller than the other.
(d) Telocentric: The centromere is right at the end of this chromosome making the chromosome look like the English letter ‘i’. This chromosome consists of only one arm.
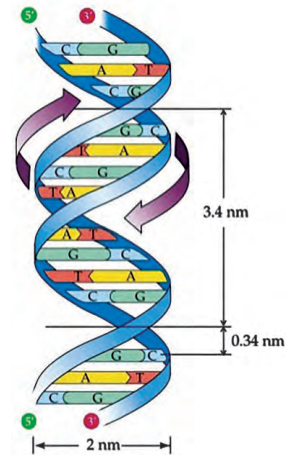
b. Describe the structure of the DNA molecule.
Answer:
- In 1953, Watson and Crick proposed a model of the DNA molecule.
- As per their model, two parallel threads (strands) of nucleotides are coiled around each other to form a double helix structure. This structure can be compared with a coiled and a flexible ladder.
- Each strand of DNA is made up of many small molecules known as nucleotides.
- Each nucleotide is made up of a molecule of nitrogen base and phosphoric acid joined to a molecule of sugar.
- There are four types of nitrogen bases-adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. Adenine and guanine are called as purines while cytosine and thymine are called as pyrimidines.
- Nucleotides are arranged like a chain in the DNA.
- The two threads (strands) of the DNA are comparable to the two rails of the ladder and each rail is made up of alternately joined molecules of sugar and phosphoric acid.
- Each rung of the ladder is a pair of nitrogenous bases joined by hydrogen bonds. Adenine always pairs with thymine and cytosine always pairs with guanine.
c. Express your opinion about the use of DNA fingerprinting.
Answer:
- DNA fingerprinting is the technique in which the sequence of the genes in the DNA of a person, i.e., the genome of the person is identified.
- This technique is useful to identify the lineage and to identify criminals because it is unique to every person.
- It is also useful to identify paternity and maternity disputes etc.
- This technique was developed by Professor of genetics Sir Alec Jeffreys.
- A common method of collecting a reference sample, is in the use of a buccal swab. If this is not available, blood or saliva or hair sample may be used.
- Just like your actual fingerprint, your DNA fingerprint is something that you are born with. It is unique to you.
- DNA fingerprint is very useful in forensic science.
d. Explain the structure, function and types of RNA.
Answer:
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is an important nucleic acid of the cell.
- RNA is made up of ribose sugar, phosphate molecules and four types of nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil.
- The nucleotide i.e., smallest unit of the chain of the RNA molecule is formed by the combination of a ribose sugar, phosphate molecule and one of the nitrogen bases.
- Large numbers of nucleotides are bonded together to form the macromolecule of RNA.
- RNA performs the function of protein synthesis.
- According to function, there are three types of RNA:
(a) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): It is the component of cellular organelle ribosome. Ribosomes perform the function of protein synthesis.(b) Messenger RNA (mRNA): It carries the information for protein synthesis from genes (i.e. DNA segment in the cell nucleus) to ribosomes (in the cytoplasm) which produce the proteins.(c) Transfer RNA (tRNA): It carries the amino acid up to the ribosomes as per the message of the mRNA.
e. Why is it necessary for people to have their blood examined before marriage?
Answer:
- If people have their blood examined before marriage, the partners will know about the possible genetic diseases that their children might inherit. So they may decide not to have children or not to get married.
- Blood tests before marriage are also done to check for any contagious disease in the partners. This will help to protect the partners from contagious diseases like STDs.
4. Write a brief note on each.
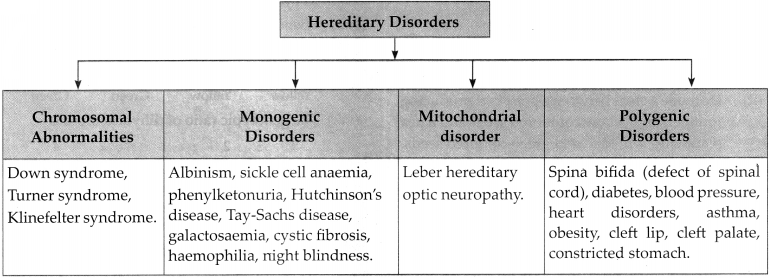
a. Down syndrome
Answer:
- Down syndrome is the disorder arising due to chromosomal abnormality.
- This is the first discovered and described the chromosomal disorder in human beings.
- This disorder is characterized by the presence of 47 chromosomes. It is described as the trisomy of the 21st pair.
- Infants with this disorder have one extra chromosome with the 21st pair in every cell of the body. Therefore, they have 47 chromosomes instead of 46.
- Children suffering from Down syndrome are usually mentally retarded and have a short lifespan. Mental retardation is the most prominent characteristic.
- Other symptoms include short height, short wide neck, flat nose, short fingers, scanty hair, single horizontal crease on palm and a life expectancy of about 16-20 years.
b. Monogenic disorders
Answer:
- Disorders occurring due to mutation in any single gene into a defective one are called monogenic disorders.
- Approximately 4000 disorders of this type are now known.
- Due to abnormal genes, their products are either produced in insufficient quantity or not produced at all.
- It causes abnormal metabolism and may lead to death at a tender age.
- Examples of monogenic disorders are Hutchinson’s disease, Tay-Sachs disease, galactosaemia, phenylketonuria, sickle cell anaemia, cyctic fibrosis, albinism, haemophilia, night blindness etc.
c. Sickle cell anaemia: symptoms and treatment.
Answer:
- Sickle-cell anaemia is a hereditary disease caused due to mutation in a single gene. It is a monogenic disorder.
- Normal haemoglobin has glutamic acid as the 6th amino acid in its molecular structure. However, if it is replaced by valine, the shape/structure of the haemoglobin molecule, changes.
- Due to this, the erythrocytes (RBCs) which are normally biconcave become sickle-shaped. This condition is called sickle-cell anaemia. The oxygen-carrying capacity of haemoglobin in such individuals is very low.
- In this condition, clumping and thereby, destruction of erythrocytes occurs most often. As a result, blood vessels are obstructed and the circulatory system, brain, lungs, kidneys, etc. are damaged.
- Symptoms of sickle-cell anaemia are swelling of legs and hands, pain in joints, severe general body aches, frequent cold and cough, constant low-grade fever, exhaustion, pale face, low haemoglobin count.
- A person suffering from sickle-cell anaemia should take a tablet of folic acid daily.
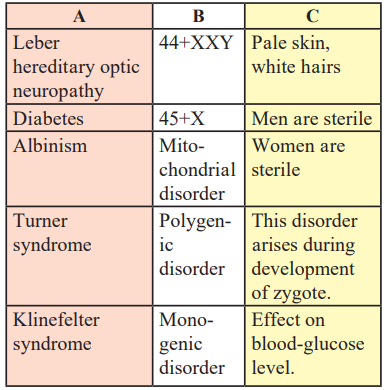
5. How are the items in groups A, B and C inter-releated?
6. Filling the blanks based on the given relationship.
a. 44 + X : Turner syndrome : : 44 + XXY: – ………………
b. 3:1 Monohybrid : : 9:3:3:1 : ……………
c. Women : Turner syndrome : : Men : ……………………
Answer:
a. Klinefelter syndrome
b. Dihybrid
c. Klinefelter syndrome
7. Complete the tree diagram below based on types of hereditary disorders.
Answer:


Leave a Reply