Introduction to Biotechnology – Solutions
1. Each of the following statements is wrong. Rewrite them correctly by changing either one or two words.
a. Simple squamous epithelium is present in the respiratory tract.
b. Glandular epithelium is present in kidneys.
c. Chlorenchyma helps the plant to float in water.
d. Striated muscles are also called involuntary muscles.
e. Chloroplast is present in permanent tissue.
Answer:
a. False. Ciliated columnar epithelium is present in respiratory tract.
b. False. Cuboidal epithelium is present in kidneys.
c. False. Aerenchyma helps the plant to float in water.
d. False. Striated muscles are also called voluntary muscles.
e. False. Chlorenchyma is present in permanent tissue.
2. Identify the odd word and explain why it is odd.
a. Xylem, phloem, permanent tissue, meristematic tissue.
Answer:
Meristematic tissue. It has the ability to divide whereas the others have lost the ability to divide.
b. Epithelium, Muscle fibre, nerve fibre, the epidermis.
Answer:
Epidermis. It is a plant tissue whereas the others are animal tissues.
c. Cartilage, bone, tendon, cardiac muscle.
Answer:
Cardiac muscle. It is a muscular tissue whereas the others are connective tissues.
3. Write the names of the following tissues.
a. Tissue lining inner surface of mouth.
Answer:
Squamous epithelium.
b. Tissue joining muscles and bones.
Answer:
Tendon
c. Tissue responsible for increasing height of plants.
Answer:
Apical meristem.
d. Tissue responsible for increasing girth of stem.
Answer:
Lateral meristem.
4. Write the differences.
Simple tissue and complex tissues in plants.
Answer:
| Simple Tissue in plants | Complex Tissues in plants |
| (i) They are made up of only one type of cells. | (i) They are made up of more than one type of cells. |
| (ii) They are found in all parts of the plant. | (ii) They are found in the vascular regions of the plant. |
| (iii) They perform different functions like storage | (iii) They mainly perform the function of |
| of food, support, giving strength etc. | conduction of water and food. |
| (iv) Examples – Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma. | (iv) Example – Xylem and phloem. |
5. Write short notes.
a. Meristematic tissue.
Answer:
- Meristematic tissue is present in specific parts of a plant where growth takes place.
- Cells of meristematic tissue contain thick cytoplasm, a conspicuous nucleus and a thin cell wall and are compactly packed together.
- Vacuoles are usually absent in these cells and they are highly active.
- The main function of meristematic tissue is to bring about plant growth.
- According to the location, meristematic tissues are of three types: Apical meristem, intercalary meristem and lateral meristem.
b. Xylem
Answer:
- Xylem is a complex permanent tissue in plants.
- It consists of thick-walled dead cells.
- The type of cells in xylem are trachieds, vessels, xylem fibres (dead cells) and xylem parenchyma (living cells).
- Its structure is like interconnected tubes conduct water and minerals only in upward direction.
c. Striated muscles.
Answer:
- The cells of striated muscles are long, cylindrical, multinucleate and have no branches.
- These are alternate dark and light bands on these muscles.
- As they are attached to bones, they are also called skeletal muscles.
- They move as per our will, hence they are called voluntary muscles.
- Striated muscles bring about movements of arms and legs, running, speaking etc.
d. Agro-complementary business.
Answer:
(i) The business that are complementary to agriculture and generate supplementary income for the farmers are called agro complementary business.
(ii) These include:
- Animal Husbandry: It is practiced for milk production and for using the cattle as help in farming operations, e.g. cows and buffaloes are raised for milk whereas bulls and male buffaloes for pulling heavy loads.
- Poultry farming: It is the rearing of egg and meat yielding chickens. Chickens raised for eggs are called layers while those raised for meat are called broilers.
- Sericulture: It is the rearing of silkworms (moths) for silk production. The silk fibres obtained are processed, reeled and then woven into fabric.
e. Genetic engineering
Answer:
- Genetic engineering is the deliberate modification of the characteristics of an organism by manipulating its genetic material.
- An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is called a genetically modified organism (GMO).
- Genetic engineering is applied in many fields like research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology and medicine.
- In agriculture, genetic engineering is used in the production of cash crops, improvement in varieties of cash crops, increase in ability of plants to withstand environmental stresses.
- In medicine, genetic engineering is used for vaccine production, early diagnosis of congenital disease, organ transplant, cancer research, production of artificial skin, cartilage etc. in laboratories.
f. Sericulture
Answer:
- Sericulture is the rearing of silkworms (moths) for production of silk.
- Bombyx mori is the most commonly used variety of silkworm for this purpose.
- The life cycle of silkworm consist of four stages namely egg, larva, pupa and adult.
- Thousands of eggs deposited by female moths are incubated artificially to shorten the incubation period.
- Larvae hatching out of eggs are released on mulberry plants.
- Larvae are nourished by feeding on mulberry leaves.
- After feeding for 3-4 days, larvae move to branches of mulberry plant.
- The silk thread is formed from the secretion of their salivary glands.
- Larvae spin this thread around themselves to form a cocoon. The cocoon may be spherical in nature.
- Ten days before the pupa turns into an adult, all the cocoons are transferred into boiling water.
- Due to the boiling water, the pupa dies in the cocoon and silk fibres become loose.
- These fibres are unwound, processed and reeled. Various kinds of fabric is woven from silk threads.
6. Explain the meaning of biotechnology and its impact on agricultural management with suitable examples.
Answer:
The techniques of bringing about improvements in living organisms by artificial genetic changes and by hybridization for the welfare of human beings, are together called biotechnology. Impact of biotechnology on agricultural management:
- Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are being produced by introducing changes in DNA of natural crops.
- Normally such varieties are not found in nature.
- Thus, new varieties are produced artificially Different useful characters are introduced in such varieties.
- Some naturally occurring varieties cannot withstand environmental stress like frequently changing temperature.
- Wet and dry famines, changing climates etc. However, GM crops can grow in any of such adverse conditions.
- As GM crops are resistant to insect pests, pathogens, chemical weedicides, etc. the use of harmful chemicals like pesticides can be avoided.
- Due to use of seeds of GM crops, there is improvement in nutritive value and decrease in loss of crops.
7. Which two main techniques are used in biotechnology? Why?
Answer:
- The two main techniques used in biotechnology are – Genetic engineering and tissue culture.
- These techniques are used to bring about improvements in living organisms by artificial genetic changes and by hybridization for the welfare of human beings.
- Its uses are in the production of cash crops, improvement in varieties of cash crops, early diagnosis of congenital diseases, organ transplant, cancer research, production of artificial skin, cartilage etc. in laboratories.
8. Discuss ‘Agritourism’ in the class and write a project on an agrotourism centre nearby. Present it in the class in groups.
Answer:
- In agritourism, plantlets of flowering, medicinal, ornamental, vegetable plants and fruit trees are produced on a large scale by tissue culture technique.
- By growing some of the plants fully, an agritourism centre can be developed.
- If sufficient land is available, the emerging field of agritoursim would be a good business.
- An agritourism centre consists of following:
(a) Mango, chikoo (sapota), guava, coconut, custard apple and some other regional fruit trees.
(b) Shade giving local or exotic attractive plants.
(c) Ornamental and flowering plants.
(d) Butterfly garden.
(e) Medicinal plant garden.
(f) Organic vegetables and fruits. - People visit places with such attraction in large numbers.
- Selling plantlets/seedlings, fruits, vegetables at such places can be quite profitable.
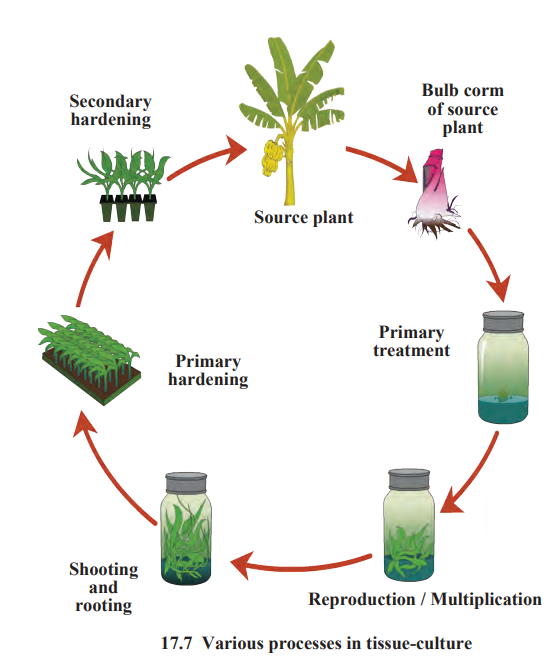
9. Define the term tissue and explain the concept of tissue culture.
Answer:
A group of cells having the same origin, same structure and same function is called tissue. Concept of tissue culture:
- Ex vivo growth of cells or tissues in an aseptic and nutrient-rich medium is called tissue culture.
- Nowadays, a complete organism can be developed from a single cell or from tissue with the help of the tissue culture technique.
- A liquid, solid or gel-like medium prepared from agar, which supplies nutrients and energy necessary for tissue culture is used in this technique.
- Tissue culture can be used to grow plants on a large scale, which bear flowers, fruits of excellent quality, in shorter durations and are disease free.
- The various processes involved in tissue culture are:
10. ‘Rearing of sheep is a livestock’. Justify this statement.
Answer:
- The term livestock refers to animals reared for profit or for use.
- Sheep provides us with wool, skin, meat and milk.
- Therefore, rearing of sheep is a livestock.

Leave a Reply