Current Electricity – Solutions
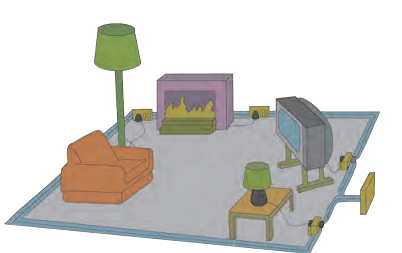
1. The accompanying figure shows some electrical appliances connected in a circuit in a house. Answer the following questions.
A. By which method are the appliances connected?
Answer:
Appliances are connected in parallel.
B. What must be the potential difference across individual appliances?
Answer:
The potential difference across all appliances is same in parallel connection.
C. Will the current passing through each appliance be the same? Justify your answer.
Answer:
No, as every appliance has a different load (resistance), the current flowing through each appliance will be different.
D. Why are the domestic appliances connected in this way?
Answer:
The domestic appliances are connected in parallel as the potential difference remains same.
E. If the T.V. stops working, will the other appliances also stop working? Explain your answer.
Answer:
No, the other devices will not stop working as the current flowing through them is along different paths.
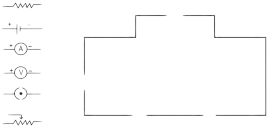
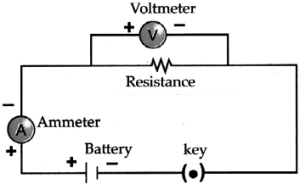
2. The following figure shows the symbols for components used in the accompanying electrical circuit.
Which law can you prove with the help of the above circuit?
Answer:
(b) This circuit can be used to prove Ohm’s law.
(c) V = 1R is the expression of Ohm’s law
3. Umesh has two bulbs having resistances of 15 W and 30 W. He wants to connect them in a circuit, but if he connects them one at a time the filament gets burnt. Answer the following.
A. Which method should he use to connect the bulbs?
B. What are the characteristics of this way of connecting the bulbs depending on the answer of A above?
C. What will be the effective resistance in the above circuit?
Answer :
A. Umesh should use the parallel method to connect the bulbs.
B. Characteristics of connecting bulbs in parallel:
- The same potential difference is applied across each bulb.
- The total current is the sum of currents through individual bulbs.
- If one bulb fails, the others will still work.
- The effective resistance is less than the smallest individual resistance.
C. Effective resistance in the circuit: = 15Ω + 30Ω = 45Ω.
4. The following table shows current in Amperes and potential difference in Volts.
a. Find the average resistance.
Answer :
From the following table,
V1 = 4V, V2 = 5V, V3 = 6V
I1 = 9 A, I2 = 11.25 A, I3 = 13.5 A
RVI
RVI
RVI
| V (Volt) | I (Ampere) | R(Ω) = VI
|
| 4 | 9 | 0.44 |
| 5 | 11.25 | 0.44 |
| 6 | 13.5 | 0.44 |
a. Average resistance (R) = RRR
=
=
∴ Average resistance (R) = 0.44 Ω
b. What will be the nature of the graph between the current and potential difference? (Do not draw a graph.)
b. A straight line will pass through the origin (0, 0) on the graph between current and potential difference.
c. Which law will the graph prove? Explain the law.
c. Here VIVIVI
i.e. Ohm’s law is clear from I ∝ V.
5. Match the pairs
‘A’ Group – ‘ B’ Group
1. Free electrons – a. V/ R
2. Current – b. Increases the resistance in the circuit
3. Resistivity – c. Weakly attached
4. Resistances in series – d. VA/LI
| ‘A’ Group | Answer |
| 1. Free electrons | c. Weakly attached |
| 2. Current | a. V/R |
| 3. Resistivity | d. VA/LI |
| 4. Resistances in series | b. Increases the resistance in the circuit |
6. The resistance of a conductor of length x is r. If its area of crosssection is a, what is its resistivity? What is its unit?
Resistivity of a conductor, ρ
Here, L = x, R = r and A = a
ρ
The unit of resistivity is ohm-metre (Ω m).
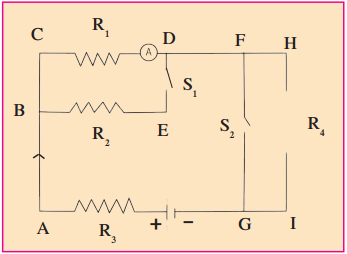
7. Resistances R1, R2, R3 and R4 are connected as shown in the figure. S1 and S2 are two keys. Discuss the current flowing in the circuit in the following cases.
a. Both S1 and S2 are closed.
b. Both S1 and S2 are open.
c. S1 is closed but S2 is open.
Answer:
(a) When both S1 and S2 are dosed, the effective resistance of the circuit decreases and hence, current will increase.
(b) When both S1 and S2 are open, the effective resistance of the rircuit increases and hence, current will decrease.
(c) When S2 is closed and S2 is open, the effective resistance of the tircuit decreases and hence current will increase. [Current will be more than case (b) but less than in case (a)]
8. Three resistances x1, x2 and x3 are connected in a circuit in different ways. x is the effective resistance. The properties observed for these different ways of connecting x1, x2 and x3 are given below. Write the way in which they are connected in each case. (I-current, V-potential difference, x-effective resistance)
a. Current I flows through x1, x2 and x3
b. x is larger than x1, x2 and x3
c. x is smaller than x1, x2 and x3
d. The potential difference across x1, x2and x3 is the same
e. x = x1 + x2 + x3
f. x =
Answer :
- Connected in series
- Connected in series
- Connected in parallel
- Connected in parallel
- Connected in series
- Connected in parallel
9. Solve the following problems.
A. The resistance of a 1m long nichrome wire is 6Ω. If we reduce the length of the wire to 70 cm. what will its resistance be? (Answer : 4.2Ω)
Answer:
Given, L1 = 1 m, R1 = 6 Ω, L2 = 70 cm = 0.7 m, R2 = ?
R = LA
RLAandRLA
RRLL
= 0.7
B. When two resistors are connected in series, their effective resistance is 80Ω. When they are connected in parallel, their effective resistance is 20Ω. What are the values of the two resistances? (Answer : 40Ω, 40Ω)
Answer:
Given:
Effective resistors in Series, RS = 80 Ω
Effective resistors in Series, RP = 20 Ω
Find: resistors (R1 and R2)
Formula:
- RS = R1 + R2
- RPRR
Calculations:
From Formula (1),
80 = R1 + R2
From Formula (2),
RR
RRRR
∵ R1 + R2 = 80
∴ RR
∴ R1 × R2 = 1600
∴ R1 = R
Substituting this value in formula (i),
RR
∴ RR
∴ RR
∴ RRR
∴ RRR
(R2 − 40) (R2 − 40) = 0
∴ R2 = 40 Ω
∴ R1 + 40 = 80
∴ R1 = 40 Ω
The values of two resistors are 40 Ω and 40 Ω.
C. If a charge of 420 C flows through a conducting wire in 5 minutes what is the value of the current? (Answer : 1.4 A)
Answer:
Given: Electric charge (Q) = 420 C
Time (t) = 5 min = 5 x 60
= 300 sec.
To find: Electric current (1) = ?
Formula:
I = Q/t
Solution:
I = Q/t
The current in the circuit is 1.4 A.

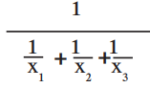
Leave a Reply