Prism (प्रिज्म) In Hindi
प्रिज्म एक त्रि-आयामी मिट्टी की वस्तु है जिसमें दो समान और समानांतर आकृतियाँ एक-दूसरे के सामने होती हैं। समान आकृतियों को आधार कहा जाता है। आधारों में बहुभुज का कोई भी आकार हो सकता है जैसे त्रिकोण, वर्ग, आयत या पंचकोण। नीचे दिया गया चित्र एक त्रिकोणीय प्रिज्म दिखाता है।
“प्रिज्म” एक ज्यामितिक आकार है जिसमें एक समान आकार की आठ कोने होते हैं। यह एक थोस और त्रिविमीय आकार है, जिसमें एक आवृत्ति या एक अंतर का प्रकार हो सकता है। प्रिज्म के दो बुनियादी प्रकार होते हैं – आयतन प्रिज्म और विकर्ण प्रिज्म।
Prism In English
A prism is a three-dimensional solid shape characterized by parallel congruent polygonal faces (known as the bases) and rectangular lateral faces connecting the corresponding sides of the bases. Here’s a detailed explanation along with examples and diagrams:
Definition:
A prism is a geometric solid with two parallel and congruent polygonal faces (known as the bases) and rectangular lateral faces connecting the corresponding sides of the bases. The lateral edges of a prism are perpendicular to the bases.
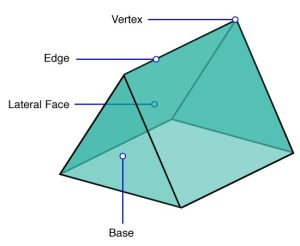
Parts
A prism has bases, lateral faces, edges, and vertices.
1. Base – The parallel faces which makes the 2 ends of any prism. They are congruent. The base determines the cross-section of any prism and it remains uniform throughout the shape.
2. Lateral faces – The non-parallel faces which connects the 2 bases.
3. Vertices – The corners.
4. Edges – Where any 2 faces meet.
Examples:
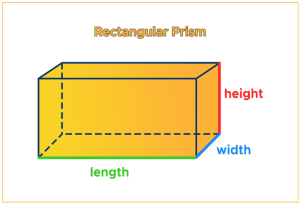
Rectangular Prism: It has two rectangular bases and rectangular lateral faces. The lateral faces are perpendicular to the bases.
Triangular Prism: It has two congruent triangular bases and three rectangular lateral faces. Each lateral face connects a corresponding side of one base to the corresponding side of the other base.
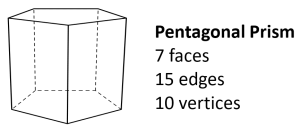
Pentagonal Prism: It has two congruent pentagonal bases and five rectangular lateral faces connecting the corresponding sides of the bases.
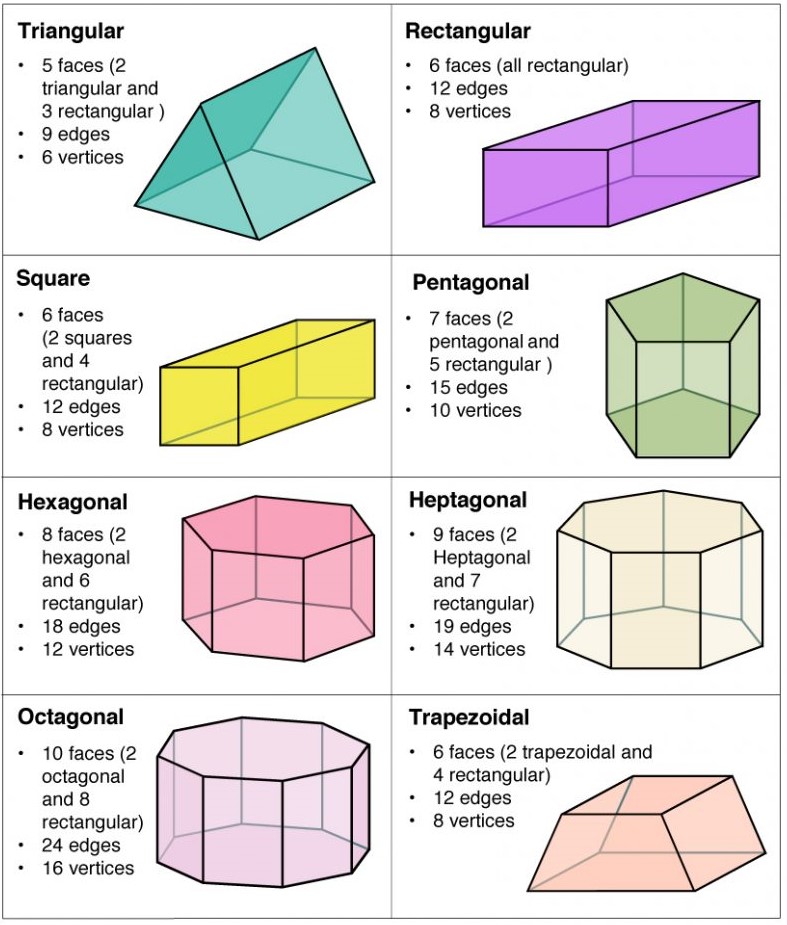
Shapes
Depending on the base, a prism can be of different shapes. Some common shapes are: triangular, rectangular, square, pentagonal, hexagonal, heptagonal, octagonal, and trapezoidal. For example, a triangular prism has a triangular base and a square prism has a square base, here are some more shapes:
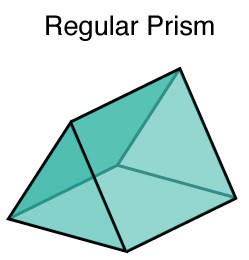
Regular and Irregular Prisms
Regular Prisms:
1. A regular prism has a regular polygon as its base.
2. A regular polygon has all sides equal in length and all angles equal in measure.
3. Common examples of regular polygons include triangles, squares, pentagons, hexagons, etc.
4. Since the base is a regular polygon, all the lateral faces of a regular prism will also be regular polygons with the same number of sides as the base.
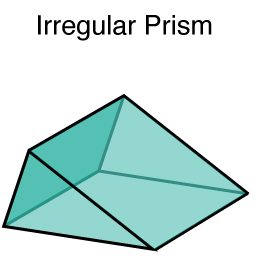
Irregular Prisms:
1. An irregular prism has an irregular polygon as its base.
2. An irregular polygon has sides with different lengths and angles that are not all equal.
3. Examples of irregular polygons include trapezoids, pentagons with unequal sides, etc.
4. The lateral faces of an irregular prism can be parallelograms but won’t necessarily be regular polygons.
Right and Oblique Prisms
Right Prism:
1. A right prism is a prism where the lateral edges are perpendicular (90 degrees) to the base faces.
2. This creates straight sides and right angles at the points where the lateral faces meet the base.
3. As a consequence of perpendicular sides, the lateral faces of a right prism are always rectangles.
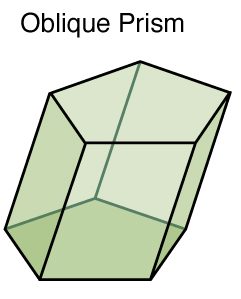
Oblique Prism:
1. An oblique prism is a prism where the lateral edges are not perpendicular to the base faces.
2. This creates a slanted appearance, and the lateral faces are not perpendicular to the base, resulting in angles other than 90 degrees where they meet.
3. Due to the tilt, the lateral faces of an oblique prism are parallelograms (which can be rectangles in special cases).
Formulas
Surface Area
- Lateral Surface Area (LSA) = Perimeter × Height
- Total Surface Area (TSA) = (2 × Base Area) + LSA
- TSA = (2 × Base Area) + (Perimeter × Height)
Volume
- Volume = Base Area × Height





Leave a Reply