Simplification (सरलीकरण) In Hindi
Simplification (सरलीकरण) का अर्थ है किसी व्यक्ति या वस्तु को सरल और सुलभ बनाना या उसे सरल रूप में प्रस्तुत करना। इसका मुख्य उद्देश्य किसी जटिल या जटिल विषय को साधारण, सरल और समझने में सहायक बनाना होता है। यह विभिन्न प्रकार की गणना, समीकरण, विश्लेषण आदि के द्वारा किया जा सकता है।
सरलीकरण के नियम
B → Remove Brackets – in the order ( ) , { }, [ ]
O → Of
D → Division
M → Multiplication
A → Addition
S → Subtraction
Simplification In English
Simplification refers to the process of making something simpler or easier to understand. It involves reducing complexity or intricacy, often by removing unnecessary details or complications. Simplification aims to present information, tasks, or concepts in a clear, straightforward manner, making them more accessible and manageable.
The operations used to simplify follows a fixed order known as BODMAS
where,
B = Bracket
O = of
D = Division
M = Multiplication
A = Addition
S = Subtraction
Question:- {15 × 32 ÷ 2 × 5} ÷ 75
Solution :- {15 × 32 ÷ 2 × 5} ÷ 75
={15 × (32 ÷ 2) × 5} ÷ 75
={15 × 16 × 5} ÷ 75
=16
Rules of Simplification and Approximation
For Example:-
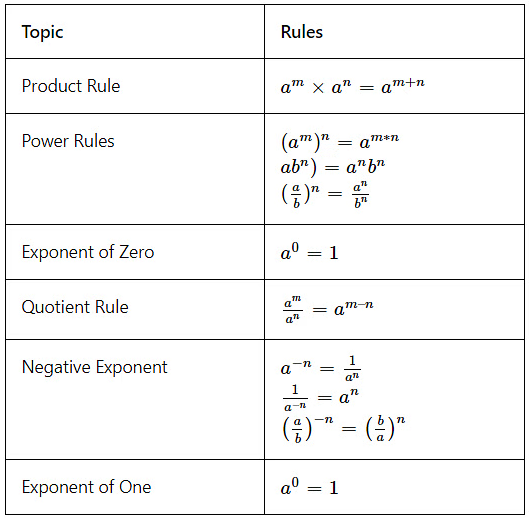
Product Rule
\(a^m \) × \(a^n \) = \(a^{m+n} \)
\(5^2 \) × \(5^1 \)
=\(5^3 \)
=125
Power Rule
\((a^m)^n \) = \(a^{m×n} \)
\((3^2)^3 \)=\(3^{2×3} \)
=\(3^{6} \)
=729
Exponent Of Zero
\(a^0 \) =1
\(1000^0 \) =1
Quotient Rule
\( \frac {a^m} {a^n } \) = \(a^{m-n} \)
\( \frac {5^3} {5^1 } \)= \(5^{3-1} \)
= \(5^{2} \)
= 25
Negative Exponent Rule
\(a^{-n} \) =\( \frac {1} {a^n } \)
\(6^{-2} \)=\( \frac {1} {6^2 } \)
=\( \frac {1} {36 } \)
Exponent Of One Rule
\(a^1 \) =a
\(56^1 \) =56
Tips and Tricks to Solve Simplification and Approximation Questions
(a+b)² = a² + b² + 2ab
(a−b)² = a² + b² − 2ab
a²−b² = (a + b)(a − b)
a³+b³ = (a + b)(a² − ab + b² )
(a+b)³ = a³ + b³ + 3ab(a+b)
(a−b)³ = a³ − b³ − 3ab(a − b)
Classification
Types Description
Natural Numbers: all counting numbers ( 1,2,3,4,5….∞)
Whole Numbers: natural number + zero( 0,1,2,3,4,5…∞)
Integers: All whole numbers including Negative number + Positive number(∞……-4,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,4,5….∞)
Even & Odd Numbers : All whole number divisible by 2 is Even (0,2,4,6,8,10,12…..∞) and which does not divide by 2 are Odd (1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19….∞)
Prime Numbers: It can be positive or negative except 1, if the number is not divisible by any number except the number itself.(2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,41,43,47,53,59,61….∞)
Composite Numbers: Natural numbers which are not prime
Co-Prime: Two natural number a and b are said to be co-prime if their HCF is 1.
Divisibility rule
Divisible by 2 End with 0,2,4,6,8 are divisible by 2
Divisible by 3 Sum of its digits is divisible by 3
Divisible by 4 Last two digit divisible by 4
Divisible by 5 Ends with 0 or 5
Divisible by 6 Divides by Both 2 & 3
Divisible by 8 Last 3 digit divide by 8
Divisible by 10 End with 0
Divisible by 11 [Sum of its digit in
odd places-Sum of its digits
in even places]= 0 or multiple of 11
Division & Remainder Rules
Dividend = ( divisor × quotient ) + remainder
or
Divisor= [(dividend) – (remainder)] / quotient
could be write it as
x = kq + r
where, x = dividend,
k = divisor,
q = quotient,
r = remainder
Arithmetic Progression (A.P.)
An Arithmetic Progression (A.P.) is a sequence of numbers in which the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant. This constant difference is called the common difference and is denoted by d.
a,a+d,a+2d,a+3d,…
Where:
a is the first term of the sequence,
d is the common difference between consecutive terms.
Let the nth term = an and last term = l, then
a) nth term = a + ( n – 1 )×d
b) Sum of n terms = (\( \frac{n}{2} \))×[2×a + (n-1)×d]
c) Sum of n terms = (\( \frac{n}{2} \))×(a+l) where l is the last term.
Sum Rules
(1+2+3+………+n) = \( \frac{n(n+1)}{2} \)
(12+22+32+………+n2) = \( \frac{n (n+1) (2n+1)}{6} \)
(13+23+33+………+n3) = \( \frac{n2 (n+1)2}{4} \)
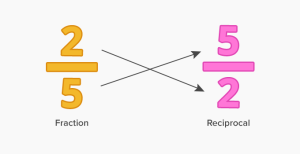
Reciprocals
The reciprocals are easy to memorize upto 10. Reciprocals after that along with more are below-
1/7 = 0.142857
2/7 = 0.285714
3/7 = 0.42857
5/7 = 0.714285
6/7 = 0.857142
1/8 = 0.125
2/8 = ¼ = 0.25
3/8 = 3 × 1/8 = 0.375
4/8 = ½ = 0.5
5/8 = 4/8 + 1/8 = 0.5 + 0.125 = 0.625
6/8 = ¾ = 0.75
7/8 = 6/8 + 1/8 = 0.75 + 1.25 = 0.875
1/9 = 0.1111…
H.C.F. & L.C.M.
HCF stands for Highest Common Factor. It’s a concept used in number theory to find the largest number that divides two or more integers completely.
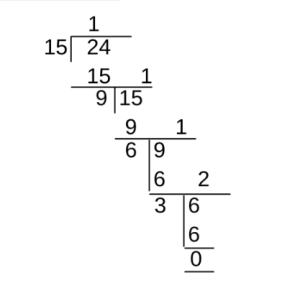
For Example :- let’s find the LCM of 15 and 24.
Therefore, HCF(15, 24) = 3
LCM :-
The LCM of two numbers and is equal to the product of the numbers divided by their greatest common divisor (GCD).
LCM(a,b)=\( \frac{a×b}{GCD(a,b)} \)
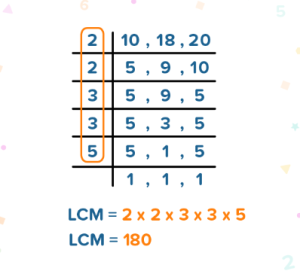
For an example, let’s find the LCM of 10, 18 and 20.
Solution:



Leave a Reply