Heredity
Solutions For All Chapters Science 10 CBSE
NCERT TEXTBOOK Solutions for Class 10 Science
Question 1.
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short.
This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as:
(a) TTWW
(b) TTww
(c) TtWW
(d) TtWw
Answer:
(c) TtWW
Question 2.
A study found that children with light coloured eyes are likely to have parents with light coloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive ? Why or why not ?
Answer:
This information is not complete. On the basis of this, it cannot be decided light colour trait is dominant or recessive. So it cannot be said until one does not know the nature of this trait in the parents.
Question 3.
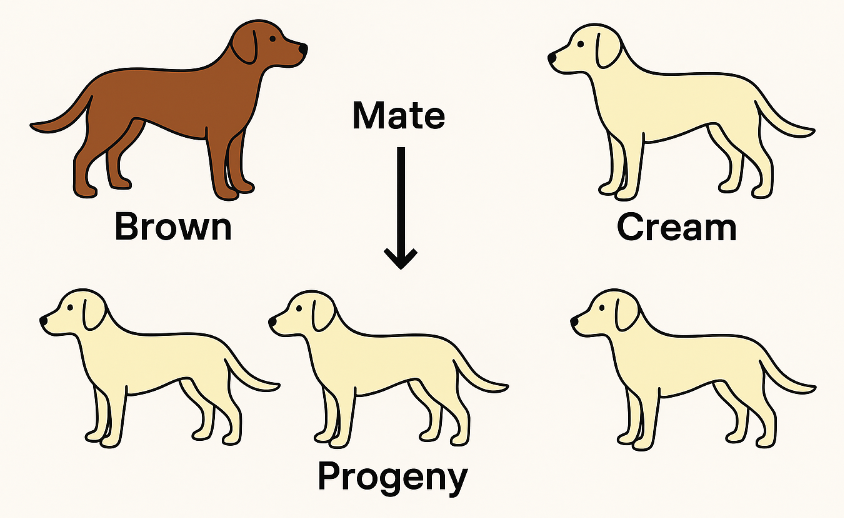
Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
Answer:
To find the dominant coat colour in dogs, select two dogs of different coat colours and mate them. Note the coat colour of the progeny. If all the progeny show the coat colour of one parent, that colour is the dominant coat colour .
Question 4.
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny ?
Answer:
Genetic material in most organisms is present in pairs of chromosomes. Gametes in the sexually reproducing organisms are formed by the process of meiosis during which half of the genetic material goes into each gamete. When the gametes from male and female parents fuse with each other during sexual reproduction, the normal complement is restored. Half of the genetic material comes from the female and half from the male.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 129
Question 1.
If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier ?
Answer:
Trait B, because it is present in more members of the population. It is likely to have arisen earlier and has now spread to 60% of the population. Trait A is new and has spread to only 10% of the population.
Question 2.
How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival ?
Answer:
The variations provide stability to the population of various species by preventing them from getting wiped out during adverse conditions.
The natural environment also changes, and variations in species which become suited to the environment help it to survive.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 133
Question 1.
How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive ?
Answer:
Mendel took pea plants with contrasting characteristics tall plant and dwarf (or short) plant. On cross pollination, he got all tall plants in first generation (F1). But by the self¬pollination of F1 tall plants, the plants of second generation consisted of tall and short pants in the ratio of 3 : 1. On the basis of these experiments, the characteristics appeared in first generation were called dominant (i.e. tall plants) and the characteristics that did not appear were called recessive (dwarf i.e. plants).
Question 2.
How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently ?
Answer:
Mendel took two pairs of alternate expression of two traits and carried out dihybrid crosses by crossing them. The traits appeared in first generation were termed as dominant. When he used these F1 progeny to generate F2 progeny by self-pollination plants of different types were produced. In some plants both the traits were dominant, while in some plants both were recessive and some plants exhibited mixed traits. This indicates that traits are inherited independently.
Question 3.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits – blood group A or O – is dominant ? Why or why not ?
Answer:
This information is not enough. This is because each individual is carrying two alleles. The recessive trait can occur only when who alleles are similar. It blood group A is dominant and O is recessive, then daughter can have blood group O only when both recessive alleles occur together in mother, and father has one allele of O and other of A.
Question 4.
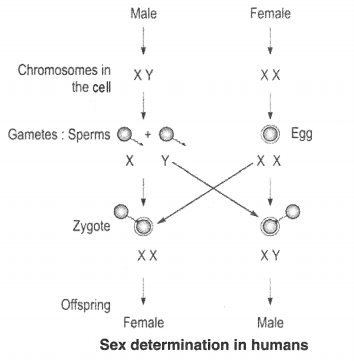
How is the sex of the child determined in human beings ?
Answer:
Half of the male gametes (sperms) carry X chromosome and other half carry Y chromosomes. All the female gametes carry only X chromosomes. When a sperm fertilizes an egg, the following situations become possible.
(i) When a sperm carrying X chromosome fertilises an egg that contains only X chromosome), the resulting zygote develops into a female (XX condition).
(ii) When a sperm carrying Y chromosome fertilises an egg (that contains only X chromosome), the resulting zygote develops into a male (XY condition).
Thus there are 50 – 50 chances of a male or female child and none of the parents may Sex determination in humans be considered responsible for it.
The sex-determination mechanism is shown alongside.

Leave a Reply