How Do Organisms Reproduce?
Solutions For All Chapters Science 10 CBSE
NCERT TEXTBOOK Solutions for Class 10 Science
Question 1
Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) amoeba
(b) yeast
(c) plasmodium
(d) leishmania
Answer:
(b) Yeast
Question 2
Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings ?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer:
(c) Vas deferens
Question 3
The anther contains
(a) sepals
(b) ovules
(c) carpel
(d) pollen grains
Answer:
(d) Pollen grains
Question 4
What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction ?
Answer:
(i) In asexual reproduction, the offspring are almost identical to their parent because they have the same genes as their parent. So, much genetic variation is not possible in asexual reproduction. This is a disadvantage because it inhibits the further evolution of the organism.
(ii) In sexual reproduction the offspring, although similar to their parents, are not identical to them or to one another. This is because the offspring receive some genes from the mother and some from the father. Because of the mixing of genes of mother and father in various different combinations, all of the offspring have genetic variations. In this way, sexual reproduction leads to a greater variety in population. This means that a species (animal or plant) can adapt quickly to changes in its surroundings. This is because there are always likely to be some individuals which are more suited to the changes than others, and these individuals will survive and reproduce themselves.
Question 5
What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings ?
Answer:
The functions of testes in humans are following :
(i) After the stage of adolescent, testes produce male gametes in the human males which are called sperms.
(ii) A hormone called testosterone is produced in testes. Testosterone controls the development of reproductive organs and secondary sexual characters.
Question 6
Why does menstruation occur ?
Answer:
If the ovum (or egg) does not get fertilised (due to non-availability of sperm in the female body) then the thick and soft inner lining of uterus is no longer needed and hence it breaks. So, the thick and soft inner lining of uterus alongwith the blood vessels and the dead ovum (or egg) comes out of the vagina in the form of blood called menstruation. Menstruation occurs after the interval of every 28 days and the time period between ovulation and menstruation is about 14 days.
Question 7
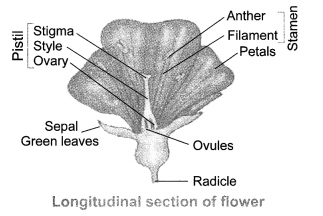
Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Answer:
Question 8
What are the different methods of contraception ?
Answer:
The different methods of contraception are as follow :
(i) Barrier method : In this method, condom, diaphragm and cervical caps are used. These prevent the entry of sperms in the female genital tract during sexual intercourse.
(ii) Chemical method : In this method a woman uses two kinds of pills (oral and vaginal pills). The oral pills are hormonal preparations which suppress the release of ovum in fallopian tube. These are called oral contraceptives. The vaginal pills/ creams are spermicidal. The chemicals in these spermicidals kill the sperms during their journey in the vaginal tract.
(iii) Intrauterine contraceptive devices : Intrauterine contraceptive devices such as copper-T are placed safely in the uterus by a skilled doctor. It prevents the sperms to reach the uterus.
(iv) Surgical method : In this method, a small part of vas deferens of male and fallopian tube of female is cut or tied by surgery. It is called vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females.
Question 9
How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms ?
Answer:
| Reproduction mode in unicellular organisms | Reproduction mode in multicellular organisms |
| (i) A sexual reproduction takes place in unicellular organisms. | (i) Sexual reproduction takes place in multicellular organisms. |
| (ii) Only one organism is required in this method. | (ii) A male and a female both are required in this method. |
| (iii) No special cells are present for reproduction. | (iii) Special cells are present for reproduction. |
| (iv) No special organs are present for reproduction. | (iv) Special organs are present for reproduction located at the fixed position in the body. |
Question 10
How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species ?
Answer:
The introduction of variations during reproduction provides stability to the populations of various species by preventing them from getting wiped out during adverse conditions. Reproduction also helps to generate copies of individuals which are suited to a particular environment.
Question 11
What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods ?
Answer:
The reasons for adopting contraceptive devices are as follow:
1. To control the birth rate and prevent the increase in population.
2. To reduce the adverse effects on mother’s body due to frequent pregnancy.
3. To provide safety from sexually transmitted diseases.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 114
Question 1
What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer:
DNA copying has following importance in reproduction:
1. It maintains the characteristics of species.
2. It maintains the continuity of life.
3. From this, the characteristics and features of organisms are transformed to their progeny.
4. It produces variations in organisms which is the basis of evolution of new species.
Question 2
Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Answer:
The various populations of organisms interact with many types of ecological niches. This is important for them to survive in given conditions. In case of any damage caused to the ecological conditions of the population, the population gets adversely affected. The organisms which are able to survive, may reproduce to develop population which is adapted or suited to the varied conditions. Hence variation is beneficial to species, but not to the individuals.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 119
Question 1
How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Answer:
1. In binary fission, the parent organism splits into two daughter cells.
Example – Amoeba, Leishmania.
2. In multiple fission, the parent organism divides into many daughter cells simultaneously.
Example – Plasmodium
Question 2
How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores ?
Answer:
An organism is benefited by reproducing through the spores because spores are surrounded by a thick layer which protects them in adverse conditions. When the favourable conditions occur, these spores start to grow again. In this way they are successfully live in unfavourable conditions.
Question 3
Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration ?
Answer:
In complex multicellular organisms, specialised cells make up tissues, tissue make up organs, organs make up organ systems and finally organ systems make up organisms. Since complex multicellular organisms have a very high degree of organisation in their body, they cannot be reproduced from their cut body parts by the process of regeneration.
For example, a dog is a complex multicellular organism which cannot be regenerated from its cut body part say, a cut tail. This is because the cells present in the cut tail of a dog cannot produce dog’s organs like heart brain, lungs, stomach, intestines and limbs, etc, needed for the making of a complete dog.
Question 4
Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants ?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is practiced for growing such plants which usually do not produce seeds or produce non-viable seeds.
Question 5
Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction ?
Answer:
DNA copying is essential part of the process of reproduction so that the characteristics of the parent organisms are transmitted to its offspring and at the same time some occasional variations are also produced in the offspring. The changes in the copy of DNA provide an organism the capability to survive in changing conditions.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 126
Question 1
How is the process of pollination different from fertilisation ?
Answer:
| Pollination | Fertilisation |
| 1. The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel is called pollination. | 1. Fertilisation occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grain joins with the female gamete (or egg) present in ovule. |
| 2. It takes place by various pollinating agents. | 2. It takes place by natural or artificial means. |
Question 2
What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland ?
Answer:
(i) Both seminal vesicle and prostate gland secretes fluids which forms a part of the semen. The fluid secreted from seminal vesicle forms 60% of semen while the fluid secreted from the prostate gland forms 30% of the semen. It makes the path smooth through which the sperms travel.
(ii) This fluid protects the sperms from the acids present in the urethra.
(iii) This fluid provides nutrition to sperms in the form of fructose, calcium and some enzymes.
Question 3
What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty ?
Answer:
The various changes occur in girls at puberty are :-
1. Hair grow under armpits and pubic region.
2. Mammary glands (or breasts) develop and enlarge.
3. The hips broaden.
4. Extra fat is deposited in various parts of the body like hips and thighs.
5. Fallopian tube, uterus and vagina enlarge.
6. Ovaries start to release eggs.
7. Menstruation (monthly periods) starts.
8. Feelings and sexual drives associated with adulthood begin to develop.
Question 4
How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body ?
Answer:
In mother’s body, the embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood. For this, there is a special structure, called placenta. Placenta contains villi. There are empty spaces in mother’s tissues that cover the villi. It provides a large surface area for the transfer of glucose, oxygen and other substances from the mother to the embryo.
Question 5
If a woman is using a copper-T. Will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases ?
Answer:
Copper-T is a contraceptive method which prevents implantation of the zygote inside the uterus. It cannot prevent a women from sexually transmitted diseases. These diseases are transmitted by contact which cannot be prevented by copper-T.

The inclusion of real-life examples and success stories made your article relatable and inspiring. If you want to read more success stories,