Notes For All Chapters Science Class 10 CBSE
1. Introduction to Light
Light makes objects visible; in darkness, objects are invisible.
Light enables us to see by reflection (object reflects light to eyes) and transmission (through transparent media).
Common phenomena related to light:
- Image formation in mirrors
- Twinkling of stars
- Rainbow colours
- Bending of light
Light generally travels in straight lines → explained as rays.
Diffraction of light:
- When object is very small, light bends around it.
- Needs wave theory for explanation.
Modern theory: Quantum theory of light → reconciles wave and particle nature.
2. Reflection of Light
Laws of Reflection
- Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection.
- Incident ray, normal, and reflected ray lie in the same plane.
- Valid for all surfaces (plane & spherical).
Image by Plane Mirror
- Always virtual, erect, and laterally inverted.
- Size = same as object.
- Distance of image behind mirror = distance of object in front.
3. Spherical Mirrors
- Concave mirror: Reflecting surface curved inwards.
- Convex mirror: Reflecting surface curved outwards.
Terms Related to Spherical Mirrors
Pole (P): Centre of mirror surface.
Centre of Curvature (C): Centre of the sphere of which mirror is part.
Radius of Curvature (R): Distance PC.
Principal Axis: Line through P and C.
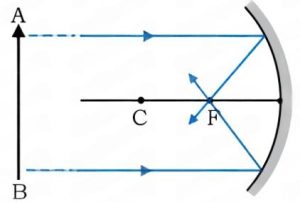
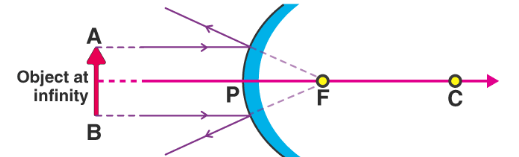
Principal Focus (F):
- Concave → Rays parallel to axis meet at F.
- Convex → Rays appear to diverge from F.
Focal Length (f): Distance PF; relation → R = 2f.
Aperture: Diameter of mirror’s reflecting surface.
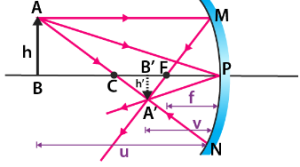
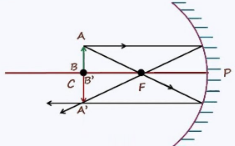
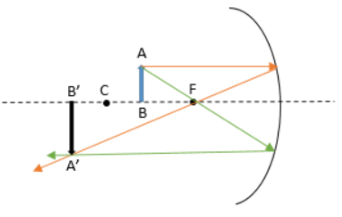
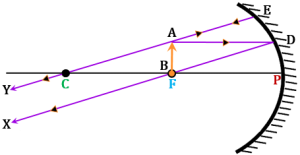
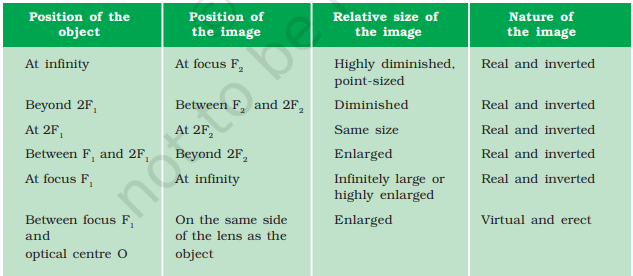
4. Image Formation by Concave Mirrors
Depends on object’s position
| Position of Object | Position of Image | Size | Nature |
|---|---|---|---|
| At infinity | At F | Highly diminished, point-sized | Real, inverted |
| Beyond C | Between F & C | Diminished | Real, inverted |
| At C | At C | Same size | Real, inverted |
| Between C & F | Beyond C | Enlarged | Real, inverted |
| At F | At infinity | Highly enlarged | Real, inverted |
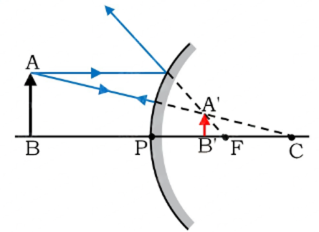
| Between P & F | Behind mirror | Enlarged | Virtual, erect |
At infinity
Beyond C
At C
Between C & F
At F
Between P & F
Uses of Concave Mirrors
- Torches, headlights, searchlights.
- Shaving mirrors.
- Dentist mirrors.
- Solar furnaces.
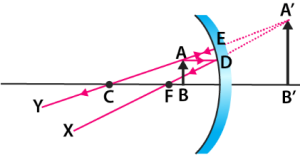
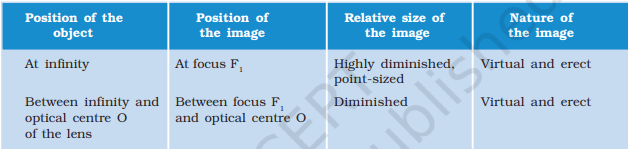
5. Image Formation by Convex Mirrors
| Position of Object | Position of Image | Size | Nature |
|---|---|---|---|
| At infinity | At F, behind mirror | Highly diminished, point-sized | Virtual, erect |
| Between infinity & P | Between P & F, behind mirror | Diminished | Virtual, erect |
At infinity
Between infinity & P
Uses of Convex Mirrors
Used as rear-view mirrors in vehicles:
- Always erect.
- Wider field of view.
6. Sign Convention (New Cartesian)
Object always to left of mirror.
Pole is origin; principal axis = X-axis.
Distances towards right (+x) → positive; left (–x) → negative.
Distances above axis (+y) → positive; below (–y) → negative.
7. Mirror Formula & Magnification
Mirror Formula:
Magnification (m):
- Negative m → real image.
- Positive m → virtual image.
8. Refraction of Light
- Change in direction of light when passing obliquely from one medium to another.
- Examples: Raised coin in water, bent pencil, raised letters under glass slab.
Laws of Refraction
Incident ray, refracted ray, and normal lie in the same plane.
Snell’s Law:
Refractive Index
Absolute refractive index:
Optical density: Larger refractive index → optically denser medium.
9. Lenses
- Transparent medium bounded by spherical surfaces.
- Convex lens: Thicker in middle, converges rays.
- Concave lens: Thicker at edges, diverges rays.
Important Terms
- Optical centre (O): Central point, no deviation.
- Principal axis: Line joining centres of curvature.
- Principal focus (F1, F2): Rays parallel to axis meet (convex) or appear to diverge (concave).
- Focal length (f): Distance between O and F.
10. Image Formation by Lenses
Convex Lens
- Forms real, inverted images except when object is between F and O (virtual, erect, enlarged).
Concave Lens
- Always forms virtual, erect, and diminished images.
11. Lens Formula & Magnification
Lens Formula:
Magnification:
12. Power of a Lens
Unit: Dioptre (D)
- 1D = focal length 1 m.
Convex lens → Positive power.
Concave lens → Negative power.
Combination of lenses: P = P1+P2+P3+…
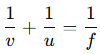
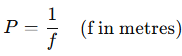

I want notes with new syllabus of RBSE NCERT book’s cut syllabus
There are no notes for refraction and lens