Our Environment
Solutions For All Chapters Science 10 CBSE
NCERT TEXTBOOK Solutions for Class 10 Science
Question 1
Which of the following groups contain only biodegradable item ?
(a) Grass, flowers and leather
(b) Grass, wood and plastic
(c) Fruit peels, cake and lime juice
(d) Cake, wood and grass
Answer:
(a) Grass, flowers and leather.
Question 2
Which of the following constitutes a food-chain ?
(a) Grass, wheat and mango
(b) Grass, goat and human
(c) Goat, cow and elephant
(d) Grass, fish and goat
Answer:
(b) Grass, goat and human.
Question 3
Which of the following are environment friendly practices ?
(a) Carrying cloth-bags to put purchases in while shopping
(b) Switching off unnecessary lights and fans
(c) Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop on her scooter
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question 4
What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level ?
Answer:
The food chain would end and ecological balance would be affected.
If the herbivores are killed, then the carnivores would not be able to get food and would die.
If carnivores are killed, then the population of herbivores would increase to unsustainable level.
If producers are killed, then the nutrient cycle in that area would not be completed.
Question 5
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels ? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem ?
Answer:
Yes, the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level will be different for different trophic levels. For example, on removing producers; herbivores would not be able to survive or they would migrate and ecosystem would collapse. If herbivores are removed, producers would grow unchecked and carnivores would not get food. If carnivores are removed, herbivores would increase to unsustainable levels and could destroy the producers. If decomposers are removed, the dead animals would pile up due to which the environment would become polluted. In addition to this, if dead animals will not decompose, the recycling of nutrients in the soil will be stopped and its fertility will be reduced. As a result the green cover of the earth will be lost. Thus to maintain the balance of the ecosystem the presence of organisms is necessary at each trophic level.
Question 6
What is biological magnification ? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem ?
Answer:
Biological magnification : The increase in concentration of harmful chemical substances like pesticides in the body of living organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification.
Yes, levels of bio-magnification would increase as the trophic level increases and would be the highest for topmost trophic level. It would affect their biological process such as growth, reproduction, etc.
Question 7
What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate ?
Answer:
The problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes are :
If the quantity of non-biodegradable matter increases in the nature then bio-magnification of poisonous chemicals in our body increases.
If the non-biodegradal waste keeps on increasing there will not be left any substance for new organisms.
The increasing quantity of non-biodegradable waste will cause imbalance of ecosystem.
Question 8
If all the waste we generate is biodegradable, will this have no impact on the environment ?
Answer:
If all the waste we generate is biodegradable, it will also have impact on the environment. If it is disposed off properly, the problem of air, water and soil pollution can be lessened to an extent. There would be less health problems and humans would be disease-free.
But if it is not disposed off properly, it will affect the environment adversely.
Question 9
Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern ? What steps are being taken to limit this damage ?
Answer:
The damage to the ozone layer is a cause for concern because if the ozone layer in the atmosphere disappears completely, then all the extremely harmful ultraviolet radiations coming from the sun would reach the earth. These ultraviolet radiations would cause skin cancer and other ailments in men and animals and also damage the plants.
In an attempt to protect the ozone layer, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) unanimously forged an agreement among its member countries to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 212
Question 1
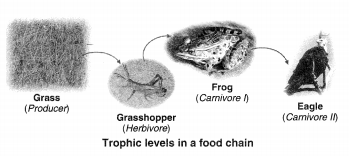
What are trophic levels ? Give an example of food chain and state the different trophic levels in it.
Answer:
Trophic Levels : The various steps in a food chain at which the transfer of food (or energy) takes place are called trophic levels.
Example : A food chain operating in a grassland is given below :
Grass → Insects → Frog → Birds
In this food chain
1. Grass represents first trophic level.
2. Grasshopper represents second trophic level.
3. Frog represents third trophic level.
4. Eagle represents fourth tropic level.
Question 2
What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem ?
Answer:
(i) Decomposers help in decomposing the dead bodies of plants and animals and hence act as cleansing agents of the environment.
(ii) Decomposers also help in putting back the various elements of which dead plants and animals are made, back into the soil, air and water for reuse by the producers like crop plants.
(iii) They help in recycling of the nutrients.
(iv) They decompose dead remains thereby providing space for new life to settle in the biosphere.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 214
Question 1
Why are some substances biodegradable and some non-biodegradable ?
Answer:
The microorganism like bacteria and other decomposer organisms (called saprophytes) present in our environment are specific in their action. They break down the materials or products made from natural materials (say, paper) but do not break down man-made materials such as plastics. So, it is due to the property of decomposer organisms of being specific in their action that some waste materials are biodegradable, whereas others are non-biodegradable.
Question 2
Give any two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
(i) Biodegradable substances are decomposed by the action of microorganisms and decomposed materials are recycled through geo-chemical cycle.
(ii) These substances keep the environment clean.
Question 3
Give any two ways in which non-biodegradable substances would effect the environment.
Answer:
(i) They cause air, water and soil pollution.
(ii) They may cause bio-magnification in the food chain and end up in humans.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 216
Question 1
What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem ?
Answer:
Ozone (O3) is an isotope of oxygen, i.e., it is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen.
At the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiations from the sun. These radiations are highly damaging to organisms. Ultraviolet rays can cause skin cancer.
Question 2
How can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal ? Give any two methods.
Answer:
(i) Recycling : The solid wastes like paper, plastics and metals, etc. are recycled.
(ii) Preparation of Compost: Biodegradable domestic wastes such as left over food, fruit and vegetable peels and leaves of potted plants, etc. can be converted into compost by burying in a pit dug into ground.

Leave a Reply