Human Eye and Colourful World
Solutions For All Chapters Science 10 CBSE
NCERT TEXTBOOK Solutions for Class 10 Science
Q1. The human eye can focus on objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
(a) presbyopia
(b) accommodation
(c) near-sightedness
(d) far-sightedness
Answer: (b) accommodation.
Q2. The human eye forms the image of an object at its
(a) cornea
(b) iris
(c) pupil
(d) retina
Answer: (d) retina.
Q3. The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about
(a) 25 m
(b) 2.5 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 2.5 m
Answer: (c) 25 cm.
Q4. The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
(a) pupil
(b) retina
(c) ciliary muscles
(d) iris
Answer: (c) ciliary muscles.
Q5. A person needs a lens of power -5.5 dioptres for correcting his distant vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens of power +1.5 dioptre. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting (i) distant vision, and (ii) near vision?
Answer:
(i) Focal length = 100 / -5.5 = -18.18 cm (≈ -0.18 m).
(ii) Focal length = 100 / 1.5 = 66.67 cm (≈ 0.67 m).
Q6. The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
Answer:
Far point = 80 cm = 0.8 m.
Power = -1 / 0.8 = -1.25 D.
Nature of lens = concave lens of power –1.25 D.
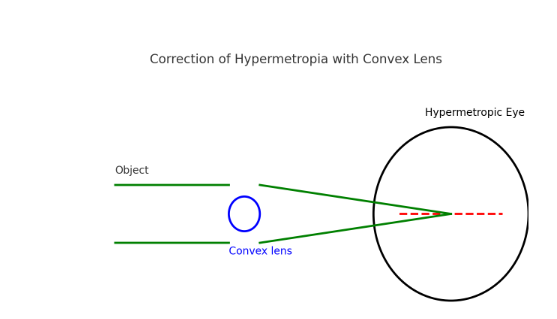
Q7. Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
Answer:
Power = (100 / 25) – (100 / 100)
= 400 – 100
= +300 cm⁻¹ = +3 D.
So, a convex lens of +3 D is required.
(Diagram shows convex lens forming the image of a nearby object at the near point of the eye.)
Q8. Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm?
Answer: A normal eye cannot see objects closer than 25 cm because the eye lens cannot decrease its focal length below a certain minimum limit, causing the image to blur or strain the eye.
Q9. What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
Answer: The image distance in the eye does not change. The image is always formed on the retina by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens.
Q10. Why do stars twinkle?
Answer: Stars twinkle because of atmospheric refraction. Their light undergoes continuous refraction due to varying air densities, making their apparent position fluctuate and brightness vary.
Q11. Explain why the planets do not twinkle.
Answer: Planets do not twinkle because they are closer to Earth and appear as extended sources of light. The variations in light from multiple point-sized sources on a planet average out to zero, nullifying the twinkling effect.
Q12. Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Answer: The sky appears dark to an astronaut because there is no atmosphere in space to scatter sunlight.
NCERT Intext Questions for Class 10 Science Page Number: 164
Q1. What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
Answer: The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length is called accommodation.
Q2. A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
Answer: A concave lens should be used to restore proper vision.
Q3. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Answer: The far point of the human eye with normal vision is infinity, and the near point is about 25 cm.
Q4. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it be corrected?
Answer: The student is likely suffering from myopia. It can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable power.

Leave a Reply