Solutions For All Chapters Geography Class 6
Download PDF Geography class 6 Solutions ch 4
1. Answer the following questions briefly:
(a) What are the three components of a map?
(b) What are the four cardinal directions?
(c) What do you mean by the term ‘the scale of the map’?
(d) How are maps more helpful than a globe?
(e) Distinguish between a map and a plan.
(f) Which map provides detailed information?
(g) How do symbols help in reading map?
Answers:
(a) Three components of a map.
(i) Distance
(ii) Direction
(iii) Symbols
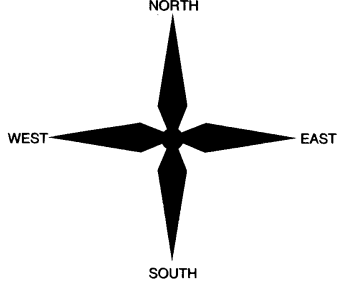
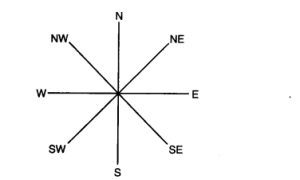
(b) Four cardinal directions:
(i) North
(ii) South
(iii) East
(iv) West
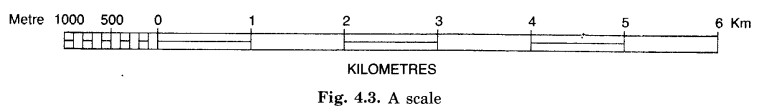
(c) The Scale of the Map:
Ratio between the distance on the paper and the distance on the ground is defined as the scale of the map.
Example: 1 cm = 5 kms.
(i) It means the distance on the paper between two points is 1 cm.
(ii) The distance on the ground (actual distance) is 5 kms.
(iii) 1 cm distance on the paper represents 5 km distance on the ground.
(d) Maps are more helpful than globe because of the following reasons:
(i) Globe cannot be used in all conditions.
(ii) Globe can be used only when we want to study the whole Earth.
(iii) It cannot be used when we want to study a village, road, building etc.
(iv) Maps are used in the study of minutest items/features.
(a) It contains innumerable facts.
(b) Maps can be found in the form of an Atlas.
(c) Maps provide more information than Globe.
(e) Differences between a map and a plan.
(f) A thematic map provides detailed information.
(g) Symbols are an important part of a map. They give a lot of information in a limited space. With the use of symbols maps can be drawn easily and are simple to read. Even if we don’t know the language of an area and therefore cannot ask someone for directions. We can collect information from maps with the help of symbols.
2. Tick the correct answer:
(a) Maps showing distribution of forests are
(i) Physical map (ii) Thematic map (iii) Political map.
(b) The blue colour is used for showing
(i) Water bodies (ii) Mountains (iii) Plains.
(c) A compass is used
(i) To show symbols (ii) To find the main direction (iii) To measure distance.
(d) A scale is necessary
(i) For a map (ii) For a sketch (iii) For symbols.
Answers:
(a)—(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i).
Things to do
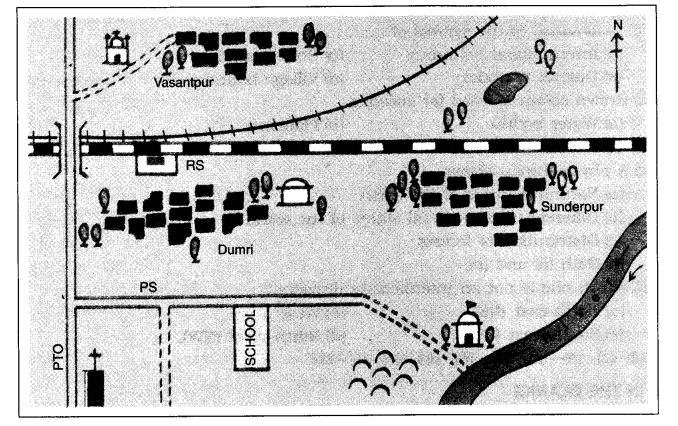
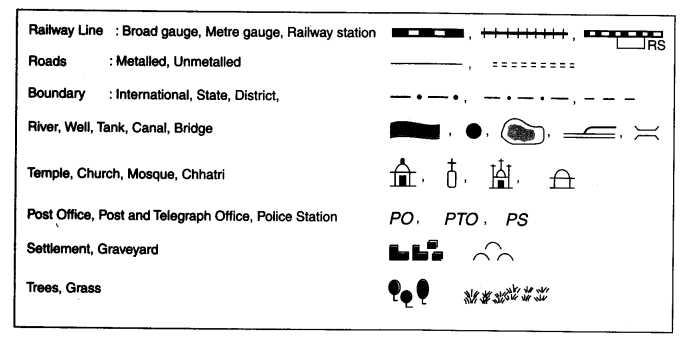
2. Look at the Figure 4.4 and find out:
(i)In which direction is the river flowing?
(ii)What kind of road passes by the side of village Dumri?
(iii)On what type of railway line is Sunderpur situated?
(iv) On which side of the railway bridge is police station situated?
(v)On which side of the railway line do the following lie:
(a) Chhatri (b) Church
(c) Pond (d) Mosque
(e) River (f) Post and Telegraph Office
(g) Graveyard.
Answers:
(i) The river is flowing southward.
(ii) Metalled road.
(iii) Broad gauge.
(iv) North side.
(v)(a) South, (b) South, (c) North, (d) North, (e) South, If] South, (g) South.
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct options to complete the statements given below:
(i) Which one is not a component of map?
(a)Direction (b) Symbol
(c) Scale (d) Distance.
(ii)………..is the symbol of………………
(a) International boundary (b) State boundary
(c) District boundary (d) Village boundary.
(iii) Brown colour is used for showing
(a) Water bodies (b) Plateaus
(c) Plains (d) Mountains.
(iv) A physical map shows
(a)Natural features of the earth
(b)Different countries and states of the world
(c)Distribution of forests
(d)Both (a) and (b).
(v) Which one is not an intermediate direction?
(a) North-east (NE) (b) West
(c) South-west (SW) (d) North-West (NW).
Answers:
(i)—(c), (ii)—(a), (iii)—(d), (iv)—(a), (v)—(b).
II. Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence:
(i) A……….. is used to show large areas like continents or countries on a paper.
(ii) A………. is an instrument used to find out main directions.
(iii) Maps have a…………. language that can be understood by all.
(iv) In a sketch match …………. is not needed.
(v) Maps are more informative than a …………
Answers:
(i) small scale (ii)compass (iii) universal (iv) scale (v) globe.
III.True/False
State whether these sentences are true (T) or false (F).
(i) A globe is used to study the earth as a whole.
(ii) Political maps show natural features of the earth.
(iii) A large scale map is used to show large areas like countries on a paper,
(iv) There are four intermediate directions.
(v) Large scale maps give less information than small scale maps.
Answers:
(i) True, (ii) False, (iii) False, (iv) True, (v) False.
IV. Matching Skill
Match the items in column A correctly with those given in column B.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Very Short Answer Type Questions
1. When do you use a globe?
Answer: We use a globe when we want to study the earth as a whole.
2. What is an atlas?
Answer: An atlas is a collection of maps.
3. What do physical maps show? (Imp.)
Answer:
Political maps show natural features of the earth such as mountains, plateans, plains, rivers, oceans, etc.
4. What do political maps show?
Answer:
Political maps show cities, towns and villages and different countries and state of the world with their boundaries.
5. What do you mean by a thematic map? [V. Imp.]
Answer:
A map which gives focus on specific information is known as thematic map. For example, road maps, maps showing distribution of industries, etc.
6. Differentiate between a small scale map and a large scale map. [V. Imp.]
Answer:
(i) A small scale map is used to show large areas like continents or countries on a paper while a large scale map is used to show a small area such as village or town on a paper.
(ii)A large scale map is more informative than a small scale map.
7.What is called the north line?
Answer:
Maps usually contain an arrow marked with the letter ‘N at the upper right hand comer. This arrow shows the north direction and is called the north line.
8. What is a compass?
Answer:
A compass is an instrument used to find out main directions.
9. What are conventional symbols? [V. Imp.]
Answer:
Some symbols have a fixed meaning and are understood uniformally throughout the world. Such symbols are known as conventional symbols.
10. What colours are used for the following:
(i)mountains
(ii)plains
(iii)plateaus
(iv)water bodies
Answers:
(i) Mountains — Brown colour
(ii)Plains — Green
(iii)Plateaus — Yellow
(iv)Water bodies — Blue
11.What is a sketch map?
Answer:
A sketch map is a rough drawing of an area. It is drawn without scale.
12. What is a plan?
Answer:
A plan is a drawing of a small area on a large scale.
Geography NCERT Class 6 Chapter 4 Maps Short Answer Type Questions
1. Differentiate between a small scale map and a large scale map. [V. Imp.]
Answer:
(i) A small scale map is used to show large areas like continents or countries on a paper while a large scale map is used to show a small area such as village or town on a paper.
(ii)A large scale map is more informative than a small scale map.
2. What are cardinal points and intermediate directions? [Imp.]
Answer:
The four major directions—North, South, East and West are called cardinal points. Beside these major directions we have four intermediate directions—North-east (NE), South-east (SE), South-west (SW) and North-west (NW). The intermediate directions are very helpful in locating any place more accurately.
3.Write a note on ‘compass’.[Imp.]
Answer:
The direction of a place is traced out with the help of a compass. It is an instrument used to find out main directions. Its magnetic needle always points towards north-south direction.
CBSE Class 6 Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 4 Long Answer Type Questions
1. Define and discuss ‘distance’ as a component of a map. [V. Imp.]
Answer:
Maps are drawings. They reduce the whole world or a part of it to fit on a sheet of paper. In other words we can say that maps are drawn to reduced scales. But it needs great care while doing this reduction work in order to keep the distance between the real places. It can only be possible when a small distance on paper represents a large distance on the ground. For this purpose a scale is used.
Scale is the ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the distance shown on the map. We can understand this with the help of an example. Suppose, the distance between your coaching centre and your school is 8 km. If you show this 8 km distance by 2 cm on a map. It means, 1 cm on the map will show 4 km on the ground. Thus, the scale of your drawing will be 1 cm = 4 km Scale is very important in any map.
If scale is known, calculation of distance between any two places on a map will be easy. A small scale is used to show large areas on a paper like continents or countries. For example, 10 cm on the map shows 1000 km of the ground. A large scale is used to show a small area like a village or town on paper. For example, 10 cm on the map shows 1000 metres only on the ground.
2. Give an account of ‘direction’ as a major component of a map. [Imp.]
Answer: Direction is an important component of a map. Most maps contain an arrow marked with the letter ‘N’ at the upper right hand comer. This arrow show the north direction. It is called the north line. After knowing the north direction, other directions, east, west and south can be easily found out.
There are four major directions—North, South, East and West. They are called cardinal points. Besides these, there are four intermediate directions. They are north-east (NE), south-east (SE), south-west (SW) and north-west (NW). Location of any place with more accuracy can be possible with the help of these intermediate directions.
3.Discuss symbols as a major component of a map. [V. Imp.]
Answer:
Drawing different features such as buildings, roads, etc. in their actual shape and size on a map is perhaps not possible. It is therefore, they are shown by using certain letters, shades, colours, pictures and lines. These are symbols that give a lot of information is a limited space.
With the use of these symbols, maps can be drawn easily and are simple to read. These symbols help us greatly in a situation when we don’t know the language of an area and therefore cannot ask someone for directions. We can collect information from maps with the help of these symbols.
Maps have a universal language, known and understood by all. There is an international agreement regarding the use of these symbols, which are known as conventional symbols.



Leave a Reply