Notes For All Chapters Science Class 6
Objects Around Us
When we look around, we find ourselves surrounded by a number of objects. Some of these different objects are made from a number of different materials, while others are made using the same material. For Example, both desk and chair are made from wood while pen and dustbins are made using plastic. The material from which an object is made depends on its properties.
Properties of Materials
1. Appearance
Materials can be classified on the basis of how they look or appear to be. Some materials have lustre, which is a very gentle sheen or soft glow to them while others are plain and dull looking. Materials that have such lustre can usually be classified as Metals. Examples include gold, copper, aluminium, iron etc. Usually, a metal loses its lustre after some time due to the action of moisture and air on it. Therefore only freshly-cut metals appear to have lustre on them.
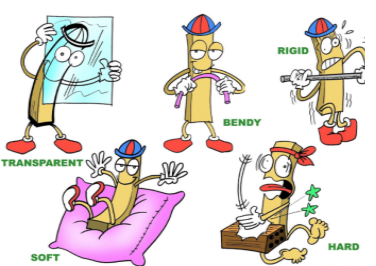
2. Hardness
Materials can also be classified on the basis of hardness.
Materials that can be easily compressed or scratched are called Soft.
Materials that cannot be scratched and are difficult to compress are termed as Hard.
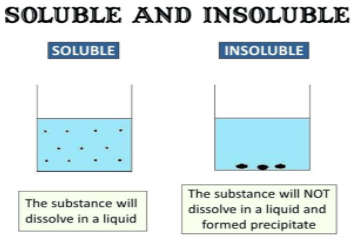
3. Soluble or Insoluble
Materials that can be dissolved in water upon stirring are said to be soluble materials. For Example, Sugar and Salt can be dissolved in water.
Materials that cannot be dissolved in water no matter how much we stir them are said to be insoluble materials. For Example, Stones and Clothes cannot be dissolved in water.
Not just solid materials, even liquids have the property of being soluble or insoluble. For Example, Lemon juice can easily dissolve in water while oil does not dissolve and deposits as a thin layer on the uppermost layer of water.
4. Objects may float or sink in water
There are some insoluble objects or materials which sink to the bottom of the surface when dissolved in water while some other float on the surface of the water. For Example, leaves and corks float in water while rocks and coins sink in water.
5. Transparency
Objects or materials which can be seen through are said to be transparent objects. For Example, Glass, clear water and some plastics can be seen through and are hence transparent materials.
Objects and materials through which things can be seen but only partially are called Translucent objects. Butter paper and frosted glass are some examples of translucent objects.
Objects which cannot be seen through are known as opaque objects. For Example, Metals, wood and cardboard are some examples of opaque materials as you cannot see through them.
Thus, we can group objects on the basis of their appearance, whether they are hard or soft, whether or not they can be compressed, if they dissolve in water or not and if they don’t do they float or sink and lastly if they can be seen through clearly, partially or at all. In this way, materials can be grouped on the basis of their similarities and differences.
Why do we need to group objects?
We need to group objects for a number of reasons:
Convenience to store: We often group objects in order to store similar objects together in order to make locating them easier in the future. Even in our homes, we store spices together in the kitchen while storing washing products in our bathrooms.
Convenience to study: We also group objects so that it becomes easy for us to study their features as well as the patterns of these features.





Leave a Reply